examples used in this article uses the Pubs database that comes as a sample database when you install SQL Server. If you need to rebuild the Pubs database, follow the steps to install a fresh copy :
- Run the osql command prompt utility and detach the Pubs database from SQL Server by using the sp_detach_db system stored procedure.
osql -U sa -P "" -Q "exec sp_detach_db 'Pubs'"
- Delete the database files for pubs database (pubs.mdf, pubs_log.ldf). These files are located in the \Data directory.
- Re-creating the Pubs database requires the Instpubs.sql script to be executed. Run the script from the command line (if the .sql files are in a different directory, adjust the path accordingly). You can also run this script file from the Query Analyzer.
osql -U sa -P "" -i "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\Install\InstPubs.sql"(The osql utility uses case-sensitive options. If neither the -U or -P options are used, SQL Server 2000 attempts to connect using Windows Authentication Mode. More information about the osql Utility can be found in the Sql Server Books Online)
Transactions
Transactions group a set of tasks into a single execution unit. Each transaction begins with a specific task and ends when all the tasks in the group successfully complete. If any of the tasks fails, the transaction fails. Therefore, a transaction has only two results: success or failure. Incomplete steps result in the failure of the transaction.
Users can group two or more Transact-SQL statements into a single transaction using the following statements:
- Begin Transaction
- Rollback Transaction
- Commit Transaction
If anything goes wrong with any of the grouped statements, all changes need to be aborted. The process of reversing changes is called rollback in SQL Server terminology. If everything is in order with all statements within a single transaction, all changes are recorded together in the database. In SQL Server terminology, we say that these changes are committed to the database.
Here is an example of a transaction :
USE pubs
DECLARE @intErrorCode INT
BEGIN TRAN
UPDATE Authors
SET Phone = '415 354-9866'
WHERE au_id = '724-80-9391'
SELECT @intErrorCode = @@ERROR
IF (@intErrorCode <> 0) GOTO PROBLEM
UPDATE Publishers
SET city = 'Calcutta', country = 'India'
WHERE pub_id = '9999'
SELECT @intErrorCode = @@ERROR
IF (@intErrorCode <> 0) GOTO PROBLEM
COMMIT TRAN
PROBLEM:
IF (@intErrorCode <> 0) BEGIN
PRINT 'Unexpected error occurred!'
ROLLBACK TRAN
END
Before the real processing starts, the BEGIN TRAN statement notifies SQL Server to treat all of the following actions as a single transaction. It is followed by two UPDATE statements. If no errors occur during the updates, all changes are committed to the database when SQL Server processes the COMMIT TRAN statement, and finally the stored procedure finishes. If an error occurs during the updates, it is detected by if statements and execution is continued from the PROBLEM label. After displaying a message to the user, SQL Server rolls back any changes that occurred during processing. Note: Be sure to match BEGIN TRAN with either COMMIT or ROLLBACK.
Nested Transactions
SQL Server allows you to nest transactions. Basically, this feature means that a new transaction can start even though the previous one is not complete. Transact-SQL allows you to nest transaction operations by issuing nested BEGIN TRAN commands. The @@TRANCOUNT automatic variable can be queried to determine the level of nesting - 0 indicates no nesting , 1 indicates nesting one level deep, and so fourth.
A COMMIT issued against any transaction except the outermost one doesn't commit any changes to disk - it merely decrements the@@TRANCOUNT automatic variable. A ROLLBACK, on the other hand, works regardless of the level at which it is issued, but rolls back all transactions, regardless of the nesting level. Though this is counterintuitive, there's a very good reason for it. If a nested COMMIT actually wrote changes permanently to disk, an outer ROLLBACK wouldn't be able to reverse those changes since they would already be recorded permanently.
When you explicitly begin a transaction, the @@TRANCOUNT automatic variable count increases from 0 to 1; when you COMMIT, the count decreases by one; when you ROLLBACK, the count is reduced to 0. As you see, the behavior of COMMIT and ROLLBACK is not symmetric. If you nest transactions, COMMIT always decreases the nesting level by 1, as you can see illustrated in Figure 1. The ROLLBACK command, on the other hand, rolls back the entire transaction, illustrated in Figure 2. This asymmetry between COMMIT and ROLLBACK is the key to handling errors in nested transactions.
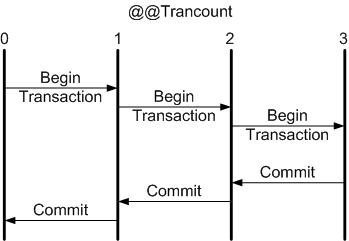 |
| Figure 1: A COMMIT always balances a BEGIN TRANSACTION by reducing the transaction count by one. |
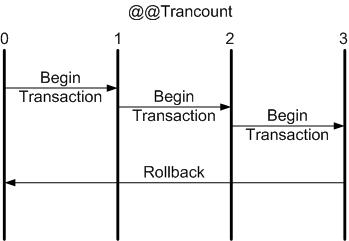 |
| Figure 2: A single ROLLBACK always rolls back the entire transaction. |
As you can see from Figure 1 and Figure 2, you can nest transactions and use the @@TRANCOUNT automatic variable to detect the level. You also learned that COMMIT and ROLLBACK do not behave symmetrically; COMMIT just decreases the value of @@TRANCOUNT, while ROLLBACK resets it to 0. The implication is that a transaction is never fully committed until the last COMMIT is issued. No matter how deeply you nest a set of transactions, only the last COMMIT has any effect.
Here is an example of a nested transaction :
USE pubs
SELECT 'Before BEGIN TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT -- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0
BEGIN TRAN
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT -- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 1
DELETE sales
BEGIN TRAN nested
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN nested', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 2
DELETE titleauthor
COMMIT TRAN nested
-- Does nothing except decrement the value of @@TRANCOUNT
SELECT 'After COMMIT TRAN nested', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 1
ROLLBACK TRAN
SELECT 'After ROLLBACK TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT -- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0
-- because ROLLBACK TRAN always rolls back all transactions and sets
-- @@TRANCOUNT to 0.
SELECT TOP 5 au_id FROM titleauthor
In this example we see that despite the nested COMMIT TRAN, the outer ROLLBACK still reverses the effects of the DELETE titleauthor command.
Here is another similar example of nested transaction :
USE pubs
SELECT 'Before BEGIN TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT -- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0
BEGIN TRAN
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT -- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 1
DELETE sales
BEGIN TRAN nested
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN nested', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 2
DELETE titleauthor
ROLLBACK TRAN
SELECT 'After COMMIT TRAN nested', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0 because
-- ROLLBACK TRAN always rolls back all transactions and sets @@TRANCOUNT
-- to 0.
IF (@@TRANCOUNT > 0) BEGIN
COMMIT TRAN -- Never makes it here cause of the ROLLBACK
SELECT 'After COMMIT TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT
END
SELECT TOP 5 au_id FROM titleauthor
In this example, execution never reaches the out COMMIT TRAN because the ROLLBACK TRAN reverses all transactions currently in progress and sets @@TRANCOUNT to 0. Unless ROLLBACK TRAN is called with a save point, ROLLBACK TRAN always rolls back all transactions and sets @@TRANCOUNT to 0, regardless of the context in which it's called.
SAVE TRAN and Save Points
Savepoints offer a mechanism to roll back portions of transactions. A user can set a savepoint, or marker, within a transaction. The savepoint defines a location to which a transaction can return if part of the transaction is conditionally canceled. SQL Server allows you to use savepoints via the SAVE TRAN statement, which doesn't affect the @@TRANCOUNT value. A rollback to a savepoint (not a transaction) doesn't affect the value returned by @@TRANCOUNT, either. However, the rollback must explicitly name the savepoint: using ROLLBACK TRAN without a specific name will always roll back the entire transaction.
The following script demonstrates how savepoints can be used :
USE pubs
SELECT 'Before BEGIN TRAN main', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0
BEGIN TRAN main
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN main', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 1
DELETE sales
SAVE TRAN sales -- Mark a save point
SELECT 'After SAVE TRAN sales', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is still 1
BEGIN TRAN nested
SELECT 'After BEGIN TRAN nested', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 2
DELETE titleauthor
SAVE TRAN titleauthor -- Mark a save point
SELECT 'After SAVE TRAN titleauthor', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is still 2
ROLLBACK TRAN sales
SELECT 'After ROLLBACK TRAN sales', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is still 2
SELECT TOP 5 au_id FROM titleauthor
IF (@@TRANCOUNT > 0) BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRAN
SELECT 'AFTER ROLLBACK TRAN', @@TRANCOUNT
-- The value of @@TRANCOUNT is 0 because
-- ROLLBACK TRAN always rolls back all transactions and sets @@TRANCOUNT
-- to 0.
END
SELECT TOP 5 au_id FROM titleauthor
Error Handling
The examples presented here are specific to stored procedures as they are the desired method of interacting with a database. When an error is encountered within a stored procedure, the best you can do is halt the sequential processing of the code and either branch to another code segment in the procedure or return processing to the calling application. The @@ERROR automatic variable is used to implement error handling code. It contains the error ID produced by the last SQL statement executed during a client�s connection. When a statement executes successfully, @@ERROR contains 0. To determine if a statement executes successfully, an IF statement is used to check the value of @@ERROR immediately after the target statement executes. It is imperative that @@ERROR be checked immediately after the target statement, because its value is reset to 0 when the next statement executes successfully. If a trappable error occurs, @@ERROR will have a value greater than 0. SQL Server resets the @@ERROR value after every successful command, so you must immediately capture the @@ERROR value. Most of the time, you'll want to test for changes in @@ERROR right after any INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement.
CREATE PROCEDURE addTitle(@title_id VARCHAR(6), @au_id VARCHAR(11),
@title VARCHAR(20), @title_type CHAR(12))
AS
BEGIN TRAN
INSERT titles(title_id, title, type)
VALUES (@title_id, @title, @title_type)
IF (@@ERROR <> 0) BEGIN
PRINT 'Unexpected error occurred!'
ROLLBACK TRAN
RETURN 1
END
INSERT titleauthor(au_id, title_id)
VALUES (@au_id, @title_id)
IF (@@ERROR <> 0) BEGIN
PRINT 'Unexpected error occurred!'
ROLLBACK TRAN
RETURN 1
END
COMMIT TRAN
RETURN 0
This kind of solution contains substantial repetition especially if your business logic requires more than two Transact-SQL statements to be implemented. A more elegant solution is to group codes into a generic error handling procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE addTitle(@title_id VARCHAR(6), @au_id VARCHAR(11),
@title VARCHAR(20), @title_type CHAR(12))
AS
BEGIN TRAN
INSERT titles(title_id, title, type)
VALUES (@title_id, @title, @title_type)
IF (@@ERROR <> 0) GOTO ERR_HANDLER
INSERT titleauthor(au_id, title_id)
VALUES (@au_id, @title_id)
IF (@@ERROR <> 0) GOTO ERR_HANDLER
COMMIT TRAN
RETURN 0
ERR_HANDLER:
PRINT 'Unexpected error occurred!'
ROLLBACK TRAN
RETURN 1

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号