synchronized关键字小结(一)
1. synchronized同步方法
1) synchronized修饰方法,表示方法是同步的,当某线程进入并拿到当前整个对象的锁时
a. 其他synchronized方法排队等锁
b. 非synchronized方法可异步执行
示例代码(折叠)

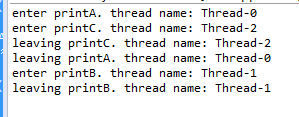
1 package com.khlin.thread; 2 3 public class SynchronizedTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Service service = new Service(); 7 /** 8 * A B 两个方法是同步的,因此访问A时候,要等A方法执行完,A线程释放锁,B线程才能拿到锁从而访问B方法。 9 * 而C方法并不是同步的,可以异步执行 10 */ 11 ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(service); 12 threadA.start(); 13 14 ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(service); 15 threadB.start(); 16 17 ThreadC threadC = new ThreadC(service); 18 threadC.start(); 19 } 20 } 21 22 class ThreadA extends Thread { 23 24 private Service service; 25 26 public ThreadA(Service service) { 27 this.service = service; 28 } 29 30 public void run() { 31 super.run(); 32 service.printA(); 33 } 34 } 35 36 class ThreadB extends Thread { 37 38 private Service service; 39 40 public ThreadB(Service service) { 41 this.service = service; 42 } 43 44 public void run() { 45 super.run(); 46 service.printB(); 47 } 48 } 49 50 class ThreadC extends Thread { 51 52 private Service service; 53 54 public ThreadC(Service service) { 55 this.service = service; 56 } 57 58 public void run() { 59 super.run(); 60 service.printC(); 61 } 62 } 63 64 class Service { 65 public synchronized void printA() { 66 67 System.out.println("enter printA. thread name: " 68 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 69 70 try { 71 Thread.sleep(3000L); 72 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 73 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 74 e.printStackTrace(); 75 } 76 77 System.out.println("leaving printA. thread name: " 78 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 79 } 80 81 public synchronized void printB() { 82 83 System.out.println("enter printB. thread name: " 84 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 85 86 System.out.println("leaving printB. thread name: " 87 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 88 } 89 90 public void printC() { 91 92 System.out.println("enter printC. thread name: " 93 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 94 95 System.out.println("leaving printC. thread name: " 96 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 97 } 98 }
运行结果:
2) 拥有锁重入的功能,当一个线程获得一个对象锁之后 ,再次请求此对象锁的时候是可以再次获得的。
示例代码,修改上面示例代码,在A方法后面调用B方法,可以再次获得锁,运行结果:

3) 重写方法后,synchronized关键字并不继承。但没有被重写的方法,仍然是同步的。

1 package com.khlin.thread; 2 3 public class SynchronizedTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 /** 7 * 子类方法的实现若调用了父类的同步方法,一样有效 8 */ 9 SubService service = new SubService(); 10 /** 11 * A B 两个方法是同步的,因此访问A时候,要等A方法执行完,A线程释放锁,B线程才能拿到锁从而访问B方法。 12 * 而C方法并不是同步的,可以异步执行 13 */ 14 ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(service); 15 threadA.setName("threadA"); 16 threadA.start(); 17 18 ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(service); 19 threadB.setName("threadB"); 20 threadB.start(); 21 22 ThreadC threadC = new ThreadC(service); 23 threadC.setName("threadC"); 24 threadC.start(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 class ThreadA extends Thread { 29 30 private Service service; 31 32 public ThreadA(Service service) { 33 this.service = service; 34 } 35 36 public void run() { 37 super.run(); 38 service.printA(); 39 // service.printB(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 class ThreadB extends Thread { 44 45 private Service service; 46 47 public ThreadB(Service service) { 48 this.service = service; 49 } 50 51 public void run() { 52 super.run(); 53 service.printB(); 54 } 55 } 56 57 class ThreadC extends Thread { 58 59 private Service service; 60 61 public ThreadC(Service service) { 62 this.service = service; 63 } 64 65 public void run() { 66 super.run(); 67 service.printC(); 68 } 69 } 70 71 class Service { 72 public synchronized void printA() { 73 74 System.out.println("enter printA. thread name: " 75 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 76 77 try { 78 Thread.sleep(3000L); 79 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 80 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 84 System.out.println("leaving printA. thread name: " 85 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 86 87 // printB(); 88 } 89 90 public synchronized void printB() { 91 92 System.out.println("enter printB. thread name: " 93 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 94 95 System.out.println("leaving printB. thread name: " 96 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 97 } 98 99 public void printC() { 100 101 System.out.println("enter printC. thread name: " 102 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 103 104 System.out.println("leaving printC. thread name: " 105 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 106 } 107 } 108 109 class SubService extends Service { 110 111 public void printSubA() { 112 System.out.println("enter printSubA. thread name: " 113 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 114 printA(); 115 System.out.println("leaving printSubA. thread name: " 116 + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 117 } 118 }
运行结果和1)是一样的。
2. synchronized同步代码块
同步代码块,通过synchronized(一个对象)的写法,把一个代码块变成同步的。
其中,括号里待同步的对象,也可以使用this关键字,指向当前对象,这时与synchronized方法效果是一样的。
1) 被同步的对象是this的情况
与synchronized方法效果一样,示例代码:

1 package com.khlin.thread; 2 3 public class SynchronizedTestSecond { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 7 8 ThreadAA threadAA = new ThreadAA(service); 9 threadAA.setName("ThreadAA"); 10 threadAA.start(); 11 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(500L); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 19 ThreadBB threadBB = new ThreadBB(service); 20 threadBB.setName("ThreadBB"); 21 threadBB.start(); 22 } 23 24 } 25 26 class ServiceSecond { 27 28 public void methodA() { 29 String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 30 synchronized (this) { 31 System.out.println("invoke methodA. " + threadName); 32 try { 33 Thread.sleep(1000L); 34 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 35 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 System.out.println("finish invoking methodA. " + threadName); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public synchronized void methodB() { 43 String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 44 System.out.println("invoke methodB. " + threadName); 45 System.out.println("finish invoking methodA. " + threadName); 46 } 47 } 48 49 class ThreadAA extends Thread { 50 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 51 52 public ThreadAA(ServiceSecond service) { 53 this.service = service; 54 } 55 public void run() { 56 service.methodA(); 57 } 58 } 59 60 class ThreadBB extends Thread { 61 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 62 63 public ThreadBB(ServiceSecond service) { 64 this.service = service; 65 } 66 public void run() { 67 service.methodB(); 68 } 69 }
运行结果:

2) 被同步的对象非this的情况
假设synchronized(x),此时,访问x对象里的同步方法,是同步访问的。
而访问主对象的同步方法,不受同步影响,属于异步。
让我们把上面的代码改为,synchronized(operation),锁住另一个对象。
1 package com.khlin.thread; 2 3 public class SynchronizedTestSecond { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 7 8 /** 9 * 锁住了operation对象,该对象的同步方法必须等待锁 10 * 而methodB并不属于该对象,ServiceSecond对象的锁,其实线程AA并没有获取,所以线程BB可以异步访问methodB方法。 11 */ 12 13 ThreadAA threadAA = new ThreadAA(service); 14 threadAA.setName("ThreadAA"); 15 threadAA.start(); 16 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(500L); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 24 ThreadBB threadBB = new ThreadBB(service); 25 threadBB.setName("ThreadBB"); 26 threadBB.start(); 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 class ServiceSecond { 32 33 private ServiceOperation operation = new ServiceOperation(); 34 35 public void methodA() { 36 String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 37 38 synchronized (operation) { 39 System.out.println("invoke methodA. " + threadName); 40 try { 41 Thread.sleep(1000L); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 System.out.println("finish invoking methodA. " + threadName); 47 } 48 } 49 50 public synchronized void methodB() { 51 String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 52 System.out.println("invoke methodB. " + threadName); 53 System.out.println("finish invoking methodB. " + threadName); 54 } 55 } 56 57 class ServiceOperation { 58 59 public synchronized void methodOperation() { 60 System.out.println("this is operation method."); 61 } 62 } 63 64 class ThreadAA extends Thread { 65 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 66 67 public ThreadAA(ServiceSecond service) { 68 this.service = service; 69 } 70 public void run() { 71 service.methodA(); 72 } 73 } 74 75 class ThreadBB extends Thread { 76 ServiceSecond service = new ServiceSecond(); 77 78 public ThreadBB(ServiceSecond service) { 79 this.service = service; 80 } 81 public void run() { 82 service.methodB(); 83 } 84 }
运行结果:

因为线程BB在访问methodB的时候,service对象的锁并没有被占用着,所以可以直接占用并调用方法。
3. 静态方法的synchronized方法和synchronized(class)方法
这是对类加锁,注意,在java中,类是一种特殊的对象。
原理与上述的非静态方法同步是一样的,不再赘述。
示例代码:

1 package com.khlin.thread; 2 3 public class SynchronizedStatic { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 ThreadAAA threadAAA = new ThreadAAA(); 7 threadAAA.setName("ThreadAAA"); 8 threadAAA.start(); 9 10 try { 11 Thread.sleep(500L); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 17 ThreadBBB threadBBB = new ThreadBBB(); 18 threadBBB.setName("ThreadBBB"); 19 threadBBB.start(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 class StaticService { 24 public synchronized static void methodA() 25 { 26 String threadname = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 27 28 System.out.println("invoking methodA. " + threadname); 29 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(1000L); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 System.out.println("finish methodA. " + threadname); 38 } 39 40 public synchronized static void methodB() 41 { 42 String threadname = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 43 44 System.out.println("invoking methodB. " + threadname); 45 46 System.out.println("finish methodB. " + threadname); 47 } 48 } 49 50 class ThreadAAA extends Thread { 51 52 53 public void run() { 54 StaticService.methodA(); 55 } 56 } 57 58 class ThreadBBB extends Thread { 59 60 61 public void run() { 62 StaticService.methodB(); 63 } 64 }
运行结果:






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现