简单分析BeanPostProcessor
1. 什么是BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是一个接口,有两个方法,分别是:Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object var1, String var2) throws BeansException 和 Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object var1, String var2) throws BeansException;
Spring Bean的生命周期中,在为Bean实例化,装配好属性后,会调用上下文中所有的BeanPostProcessor对象的两个方法为其初始化;
2. 一个小例子
分别创建三个类,分别是接口类、接口类的实现类,和BeanPostProcessor的实现类。
1 package com.khlin.my.test; 2 3 public interface WelcomeService { 4 5 void welcome(); 6 }
1 package com.khlin.my.test; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; 4 5 public class WelcomeServiceImpl implements WelcomeService, InitializingBean { 6 7 public void init() { 8 System.out.println("init."); 9 } 10 11 public void welcome() { 12 System.out.println("Welcome to Spring."); 13 } 14 15 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { 16 System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet."); 17 } 18 }
1 package com.khlin.my.test; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; 4 import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; 5 6 public class LoginProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 7 8 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { 9 System.out.println("login successfully."); 10 return o; 11 } 12 13 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { 14 System.out.println("logout successfully."); 15 return o; 16 } 17 }
在applicationContext.xml里实例化对应的Bean.
1 <bean id="welcomeService" class="com.khlin.my.test.WelcomeServiceImpl" init-method="init"/> 2 <bean id="loginProcessor" class="com.khlin.my.test.LoginProcessor"/>
再写一个启动类
1 package com.khlin.my.test; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class IOCTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); 10 System.out.println("context 启动成功"); 11 WelcomeService messageService = context.getBean(WelcomeService.class); 12 messageService.welcome(); 13 } 14 }
启动main方法,输出如下:

调用顺序分别为:
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization
InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet
init方法
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization
3. 实现原理
我们来看一下Spring启动一个上下文的时候,都做了啥。这里不作详细的源码解读。
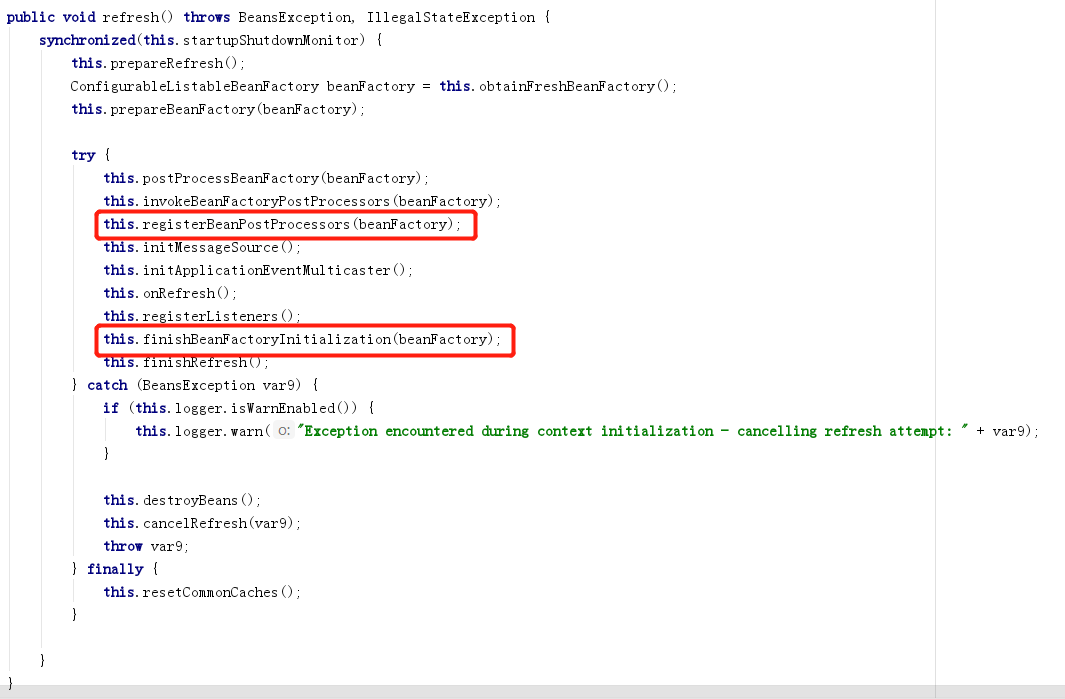
可以看到上下文ApplicationContext持有一个BeanFactory。在第一个红框,将所有的BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory。
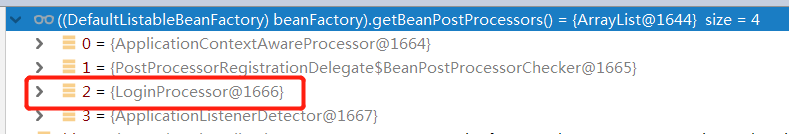
调试代码,可以看到注册后保存在BeanFactory的beanPostProcessors集合里。
再来看第二个红框,finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 这个方法会对Bean进行初始化。
在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory这个类的protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)方法里,可以看到invokeInitMethods方法被夹在BeanPostProcessor两个方法的中间。

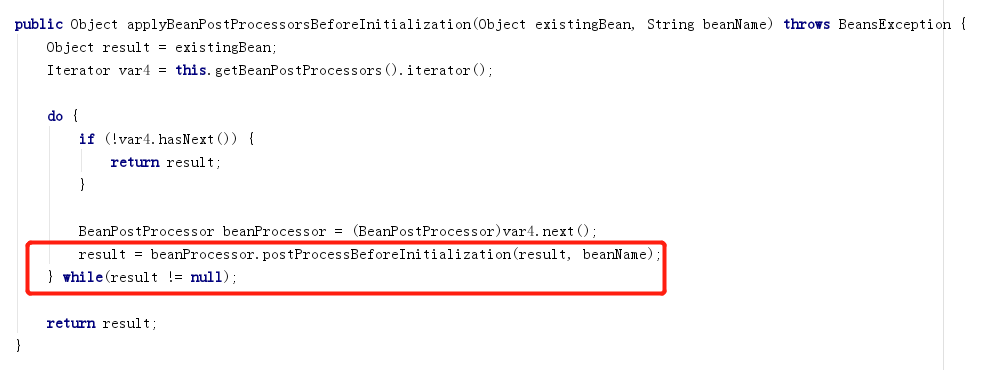
在applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization和applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法中,会遍历所有注册的BeanBeanProcessor并调用方法。
每个BeanPostProcessor可以返回处理后的对象,如果返回null,会导致遍历中断,可能有些BeanPostProcessor无法处理,这点要注意。
InitMethod有两种方式,一种是在配置文件中加上init-method属性并指定对应的方法,另一种是实现InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法。
可以看到是优先调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,再调用init-method指定的方法,这与我们的输出顺序一致。

4. 总结
Spring Bean的生命周期,在初始化阶段的调用顺序为:
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization
InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet
init方法
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization
如果有一个BeanPostProcessor返回null,会导致遍历的中断,可能有些BeanPostProcessor无法调用。因此一般不返回null.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现