oracle 基础知识(十四)----索引扫描
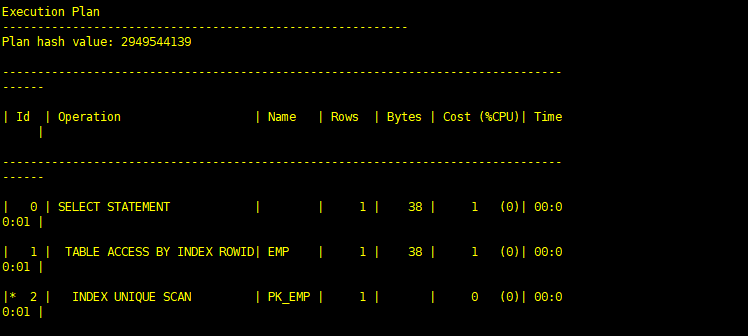
(1)索引唯一扫描(index unique scan)
通过唯一索引查找一个数值经常返回单个ROWID。如果该唯一索引有多个列组成(即组合索引),则至少要有组合索引的引导列参与到该查询中,如创建一个索引:create index idx_test on emp(ename, deptno, loc)。则select ename from emp where ename = ‘JACK’ and deptno = ‘DEV’语句可以使用该索引。如果该语句只返回一行,则存取方法称为索引唯一扫描。而select ename from emp where deptno = ‘DEV’语句则不会使用该索引,因为where子句种没有引导列。如果存在UNIQUE 或PRIMARY KEY 约束(它保证了语句只存取单行)的话,Oracle经常实现唯一性扫描。
为了方便查看设置执行计划为只显示执行计划
SQL> set autot traceonly exp; SQL> select * from scott.emp t where t.empno=10; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2949544139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("T"."EMPNO"=10) SQL>
(2)索引范围扫描(index range scan)
使用一个索引存取多行数据,同上面一样,如果索引是组合索引,而且select ename from emp where ename = ‘JACK’ and deptno = ‘DEV’ 语句返回多行数据,虽然该语句还是使用该组合索引进行查询,可此时的存取方法称为索引范围扫描。
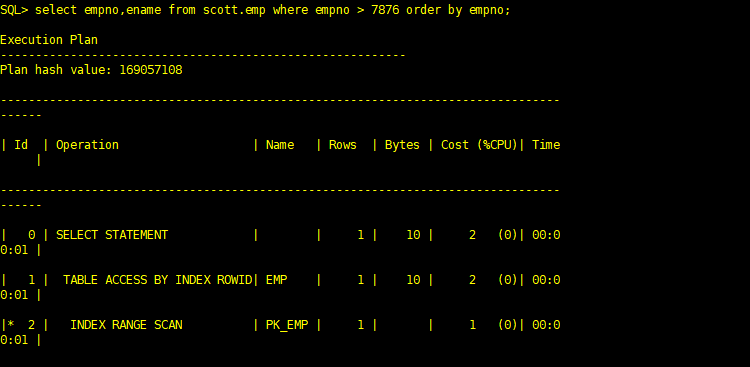
在唯一索引上使用索引范围扫描的典型情况下是在谓词(where限制条件)中使用了范围操作符(如>、<、<>、>=、<=、between)
SQL> select empno,ename from scott.emp where empno > 6666 order by empno; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 169057108 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 140 | 2 (0)| 00:0 0:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 14 | 140 | 2 (0)| 00:0 0:01 | |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | PK_EMP | 14 | | 1 (0)| 00:0 0:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("EMPNO">6666)
在非唯一索引上,谓词可能返回多行数据,所以在非唯一索引上都使用索引范围扫描。
使用index rang scan的3种情况:
(a) 在唯一索引列上使用了range操作符(> < <> >= <= between)。
(b) 在组合索引上,只使用部分列进行查询,导致查询出多行。
(c) 对非唯一索引列上进行的任何查询。
(3)索引全扫描(index full scan)
与全表扫描对应,也有相应的全Oracle索引扫描。在某些情况下,可能进行全Oracle索引扫描而不是范围扫描,需要注意的是全Oracle索引扫描只在CBO模式下才有效。 CBO根据统计数值得知进行全Oracle索引扫描比进行全表扫描更有效时,才进行全Oracle索引扫描,而且此时查询出的数据都必须从索引中可以直接得到。
SQL> create index big_emp on scott.emp(empno,ename); ---创建索引 Index created. SQL> select empno, ename from scott.emp order by empno,ename; 执行计划查看你 Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 322359667 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 140 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | INDEX FULL SCAN | BIG_EMP | 14 | 140 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
(4)索引快速扫描(index fast full scan)
扫描索引中的所有的数据块,与 index full scan很类似,但是一个显著的区别就是它不对查询出的数据进行排序,即数据不是以排序顺序被返回。在这种存取方法中,可以使用多块读功能,也可以使用并行读入,以便获得最大吞吐量与缩短执行时间。
测试表创建: ---资源来自>>
create table t as select * from dba_objects where 1=2; insert into t select * from dba_objects where object_id is not null; 创建一个索引 create index i_t_object_id on t(object_id); select object_id from t; set autot trace exp; -- 设置格式 查询:select object_id from t; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1601196873 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 89550 | 1136K| 336 (1)| 00:00:05 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| T | 89550 | 1136K| 336 (1)| 00:00:05 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- Note ----- - dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2) 这个好像走的是全表呀...由于我们需要查询的列为object_id,因此理论上只需要读取索引就应该可以返回所有数据,而此时为什么是全表扫描呢?这是因为NULL值与索引的特性所决定的。即null值不会被存储到B树索引。因此应该为表 t 的列 object_id 添加 not null 约束。 alter table t modify(object_id not null); 添加约束 再次查看 SQL> select object_id from t; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2036340805 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 89550 | 1136K| 53 (0)| 00:0 0:01 | | 1 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| I_T_OBJECT_ID | 89550 | 1136K| 53 (0)| 00:0 0:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ Note ----- - dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2) INDEX FAST FULL SCAN 类似于full table scan,使用该方式当在高速缓存中没有找到所需的索引块时,则根据db_file_multiblock_read_count的值进行多块读操 作。对于索引的分支结构只是简单的获取,然后扫描所有的叶结点。其结果是导致索引结构没有访问,获取的数据没有根据索引键的顺序排序。 INDEX FAST FULL SCAN使用multiblock_read,故产生db file scattered reads 事件

Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 431110666
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 89550 | 1136K| 194 (1)| 00:00:03
|
| 1 | INDEX FULL SCAN | I_T_OBJECT_ID | 89550 | 1136K| 194 (1)| 00:00:03
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
与INDEX FAST FULL SCAN所不同的是,INDEX FULL SCAN会完全按照索引存储的顺序依次访问整个索引树。当访问到叶结点之后,按照双向
链表方式读取相连节点的值。换言之,对于索引上所有的数据是按照有序的方式来读取的。如果索引块没有在高速缓存中被找到时,则需要从数
据文件中单块进行读取。对于需要读取大量数据的全索引扫描而言,这将使其变得低效。INDEX FULL SCAN使用single read,故产生
db file sequential reads事件。新版的Oracle支持db file parallel reads方式。
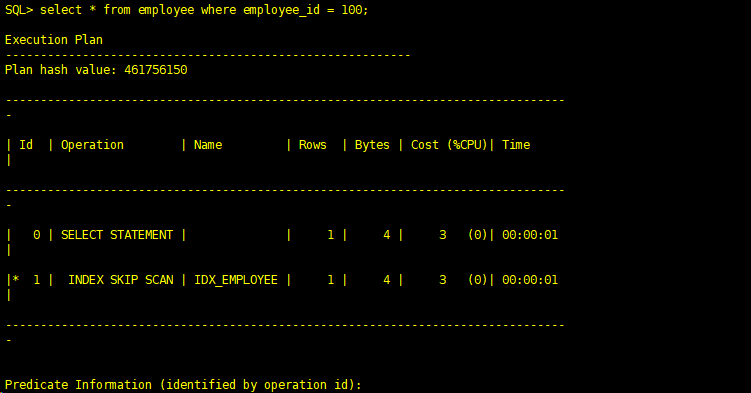
(5)索引跳跃扫描(INDEX SKIP SCAN)
INDEX SKIP SCAN,发生在多个列建立的复合索引上,如果SQL中谓词条件只包含索引中的部分列,并且这些列不是建立索引时的第一列时,就可能发生INDEX SKIP SCAN。这里SKIP的意思是因为查询条件没有第一列或前面几列,被忽略了。
例子来自于>>>
SQL> create table employee(gender varchar2(1),employee_id number); Table created. SQL> alter table employee modify(employee_id not null); Table altered. SQL> create index idx_employee on employee(gender,employee_id); Index created. SQL> begin for i in 5001..10000 loop insert into employee values ('M',i); end loop; commit; end; SQL> / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> begin for i in 1..5000 loop insert into employee values ('F',i); end loop; commit; end; SQL> / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> analyze table EMPLOYEE compute statistics for table for all columns for all indexes; Table analyzed. SQL> select * from employee where employee_id = 100; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 461756150 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 4 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | INDEX SKIP SCAN | IDX_EMPLOYEE | 1 | 4 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - access("EMPLOYEE_ID"=100) filter("EMPLOYEE_ID"=100) SQL>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号