Window Pains
Description
Boudreaux likes to multitask, especially when it comes to using his computer. Never satisfied with just running one application at a time, he usually runs nine applications, each in its own window. Due to
limited screen real estate, he overlaps these windows and brings whatever window he currently needs to work with to the foreground. If his screen were a 4 x 4 grid of squares, each of Boudreaux's windows would be represented by the following 2 x 2 windows:
When Boudreaux brings a window to the foreground, all of its squares come to the top, overlapping any squares it shares with other windows. For example, if window 1 and then window 2 were brought to the foreground, the resulting representation
would be:
. . . and so on . . .
Unfortunately, Boudreaux's computer is very unreliable and crashes often. He could easily tell if a crash occurred by looking at the windows and seeing a graphical representation that should not occur if windows were being brought to the foreground correctly. And this is where you come in . . .
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
If window 4 were then brought to the foreground: |
|
Unfortunately, Boudreaux's computer is very unreliable and crashes often. He could easily tell if a crash occurred by looking at the windows and seeing a graphical representation that should not occur if windows were being brought to the foreground correctly. And this is where you come in . . .
Input
Input to this problem will consist of a (non-empty) series of up to 100 data sets. Each data set will be formatted according to the following description, and there will be no blank lines separating data
sets.
A single data set has 3 components:
After the last data set, there will be a single line:
ENDOFINPUT
Note that each piece of visible window will appear only in screen areas where the window could appear when brought to the front. For instance, a 1 can only appear in the top left quadrant.
A single data set has 3 components:
- Start line - A single line:
START - Screen Shot - Four lines that represent the current graphical representation of the windows on Boudreaux's screen. Each position in this 4 x 4 matrix will represent the current piece of window showing in each square. To make input easier, the list of numbers
on each line will be delimited by a single space.
- End line - A single line:
END
After the last data set, there will be a single line:
ENDOFINPUT
Note that each piece of visible window will appear only in screen areas where the window could appear when brought to the front. For instance, a 1 can only appear in the top left quadrant.
Output
For each data set, there will be exactly one line of output. If there exists a sequence of bringing windows to the foreground that would result in the graphical representation of the windows on Boudreaux's
screen, the output will be a single line with the statement:
THESE WINDOWS ARE CLEAN
Otherwise, the output will be a single line with the statement:
THESE WINDOWS ARE BROKEN
THESE WINDOWS ARE CLEAN
Otherwise, the output will be a single line with the statement:
THESE WINDOWS ARE BROKEN
Sample Input
START 1 2 3 3 4 5 6 6 7 8 9 9 7 8 9 9 END START 1 1 3 3 4 1 3 3 7 7 9 9 7 7 9 9 END ENDOFINPUT
Sample Output
THESE WINDOWS ARE CLEAN THESE WINDOWS ARE BROKEN
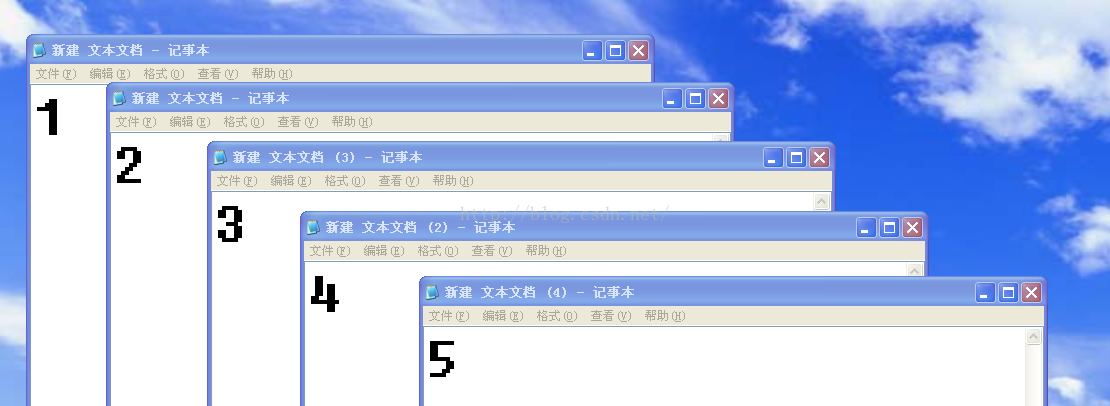
给你一个4*4的电脑屏幕 现在有9个面积为2*2的应用 分别是四个相同的数 编号1-9 电脑屏幕不够大 当你看一个应用的时候可能就会覆盖其他的应用 所以有些应用只能看见一部分(不懂的话就多点开应用试试)按顺序点应用 最早点的应该是被覆盖在最下面的应用 最晚点的在表面 比如下面的图 点击的顺序就是 1 2 3 4 5
现在给你一个电脑界面 问你是否能够按一定的顺序点击应用 让电脑屏幕显现出这种情况
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;//列出16个方格中可能出现的数 {1,0,0,0}表示只可能出现数字1
int s[4][4][4]={ {{1,0,0,0},{1,2,0,0},{2,3,0,0},{3,0,0,0}},{{1,4,0,0},{1,2,4,5},{2,3,5,6},{3,6,0,0}},{{4,7,0,0},{4,5,7,8},{5,6,8,9},{6,9,0,0}},{{7,0,0,0},{7,8,0,0},{8,9,0,0},{9,0,0,0}}};
int map[110][110];
int vis[110][110];
int die[1010]; //处于最表面的应用他的“入度”应该为0 建立应用界面之间的边 接下来用拓扑排序计算
void topo()
{
queue<int>q;
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++)
{
if(die[i]==0)
{
q.push(i);
die[i]=-1;
}
}
int ans=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int first=q.front();
q.pop();
ans++;
for(int j=1;j<=9;j++ )
{
if(vis[first][j]==1)
{
die[j]--;
}
if(die[j]==0)
{
q.push(j);
die[j]=-1;
}
}
}
if(ans==9)
{
printf("THESE WINDOWS ARE CLEAN\n");
}
else
{
printf("THESE WINDOWS ARE BROKEN\n");
}
}
int main()
{
char word1[100],word2[100];
while(scanf("%s",word1)!=EOF)
{
if(strcmp(word1,"ENDOFINPUT")==0)
break;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(die,0,sizeof(die));
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
if(s[i][j][k]==0)
break;
if(vis[map[i][j]][s[i][j][k]]==0&&map[i][j]!=s[i][j][k])
{
vis[map[i][j]][s[i][j][k]]=1;
die[s[i][j][k]]++;
}
}
}
}
scanf("%s",word2);
topo();
}
return 0;
}
编程五分钟,调试两小时...


