TEXT CLASSIFICATION WITH TORCHTEXT
本文译自PYTORCH官网TEXT系列。本节主要利用torchtext中的文本分类数据集,包括:

这个例子展示了如何利用这些TextClassfication数据集中的一个来训练监督学习算法。
用ngrams加载数据
一个ngrams包特性被用来捕获一些关于本地词序的部分信息。在实际应用中,双字元(bi-gram)或三字元(tri-gram)作为词组比只使用一个词更有益处。例如:

TextClassfication 数据集支持ngrams方法。通过设定ngrams为2,数据集中的text将包含单个单词和bi-grams字符串。
import torch import torchtext from torchtext.datasets import text_classification NGRAMS = 2 import os if not os.path.isdir('./.data'): os.mkdir('./.data') train_dataset, test_dataset = text_classification.DATASETS['AG_NEWS']( root='./.data', ngrams=NGRAMS, vocab=None) BATCH_SIZE = 16 device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
定义模型
模型由EmbeddingBag层和线性层组成。nn.EmbeddingBag计算embedding包的均值。不同的文本长度是不同的。nn.EmbeddingBag无需padding,因为文本长度在offsets已保存。
此外,因为nn.EmbeddingBag动态累加嵌入的平均值,nn.EmbeddingBag动可以提高性能和记忆效率来处理tensor序列。
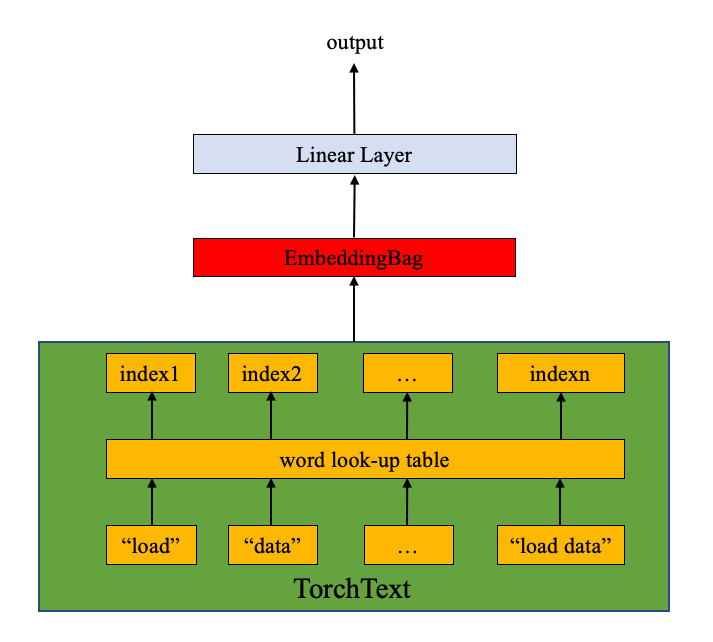
一个例子
AG_NEWS数据集含有四个标签,因此类别数为4。

vocab大小等于vocab长度(包括单词和ngrams)。类别数目等于标签数,在AG_NEWS这个例子中为4。

批量生成
由于文本长度不同,一个定制的generate_batch()用来生成批量和offsets。该函数传到collate_fn里面吗(不会用collate_fn函数的参考这里->)。collate_fn的输入为:batch_size大小的列表,将其大包围mini-batch。整个文本输入批量被整理为list,并连接作为单一tensor作为nn.EmbeddingBag的输入。offset是一个tensor表征文本tensor中队里序列的起始索引。Label是tensor保留了整个文本的标签。
def generate_batch(batch): label = torch.tensor([entry[0] for entry in batch]) text = [entry[1] for entry in batch] offsets = [0] + [len(entry) for entry in text] # torch.Tensor.cumsum returns the cumulative sum # of elements in the dimension dim. # torch.Tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]).cumsum(dim=0) offsets = torch.tensor(offsets[:-1]).cumsum(dim=0) text = torch.cat(text) return text, offsets, label
函数定义与模型训练评估
推荐pytorch boys利用torch.utils.data.DataLoader来整,并且并行处理也方便(a tutorial is here)。我们利用DataLoader来加载AG_NEWS数据集并用来训练/评估。
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader def train_func(sub_train_): # Train the model train_loss = 0 train_acc = 0 data = DataLoader(sub_train_, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, collate_fn=generate_batch) for i, (text, offsets, cls) in enumerate(data): optimizer.zero_grad() text, offsets, cls = text.to(device), offsets.to(device), cls.to(device) output = model(text, offsets) loss = criterion(output, cls) train_loss += loss.item() loss.backward() optimizer.step() train_acc += (output.argmax(1) == cls).sum().item() # Adjust the learning rate scheduler.step() return train_loss / len(sub_train_), train_acc / len(sub_train_) def test(data_): loss = 0 acc = 0 data = DataLoader(data_, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, collate_fn=generate_batch) for text, offsets, cls in data: text, offsets, cls = text.to(device), offsets.to(device), cls.to(device) with torch.no_grad(): output = model(text, offsets) loss = criterion(output, cls) loss += loss.item() acc += (output.argmax(1) == cls).sum().item() return loss / len(data_), acc / len(data_)
划分数据集并训练模型
因为原始AG_NEWS数据没有验证集,将训练集分为训练/验证集合,比例为0.95/0.05。利用pytorch库中的 torch.utils.data.dataset.random_spllt实现。利用CrossEntropyLoss集合 nn.LogSoftmax() and nn.NLLLoss() 在一个类里。对于训练C个类别的分类任务是有用的。SGD作为优化器。初始学习率为4.0。StepLR用来调整学习率。
import time from torch.utils.data.dataset import random_split N_EPOCHS = 5 min_valid_loss = float('inf') criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=4.0) scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, 1, gamma=0.9) train_len = int(len(train_dataset) * 0.95) sub_train_, sub_valid_ = \ random_split(train_dataset, [train_len, len(train_dataset) - train_len]) for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS): start_time = time.time() train_loss, train_acc = train_func(sub_train_) valid_loss, valid_acc = test(sub_valid_) secs = int(time.time() - start_time) mins = secs / 60 secs = secs % 60 print('Epoch: %d' %(epoch + 1), " | time in %d minutes, %d seconds" %(mins, secs)) print(f'\tLoss: {train_loss:.4f}(train)\t|\tAcc: {train_acc * 100:.1f}%(train)') print(f'\tLoss: {valid_loss:.4f}(valid)\t|\tAcc: {valid_acc * 100:.1f}%(valid)')
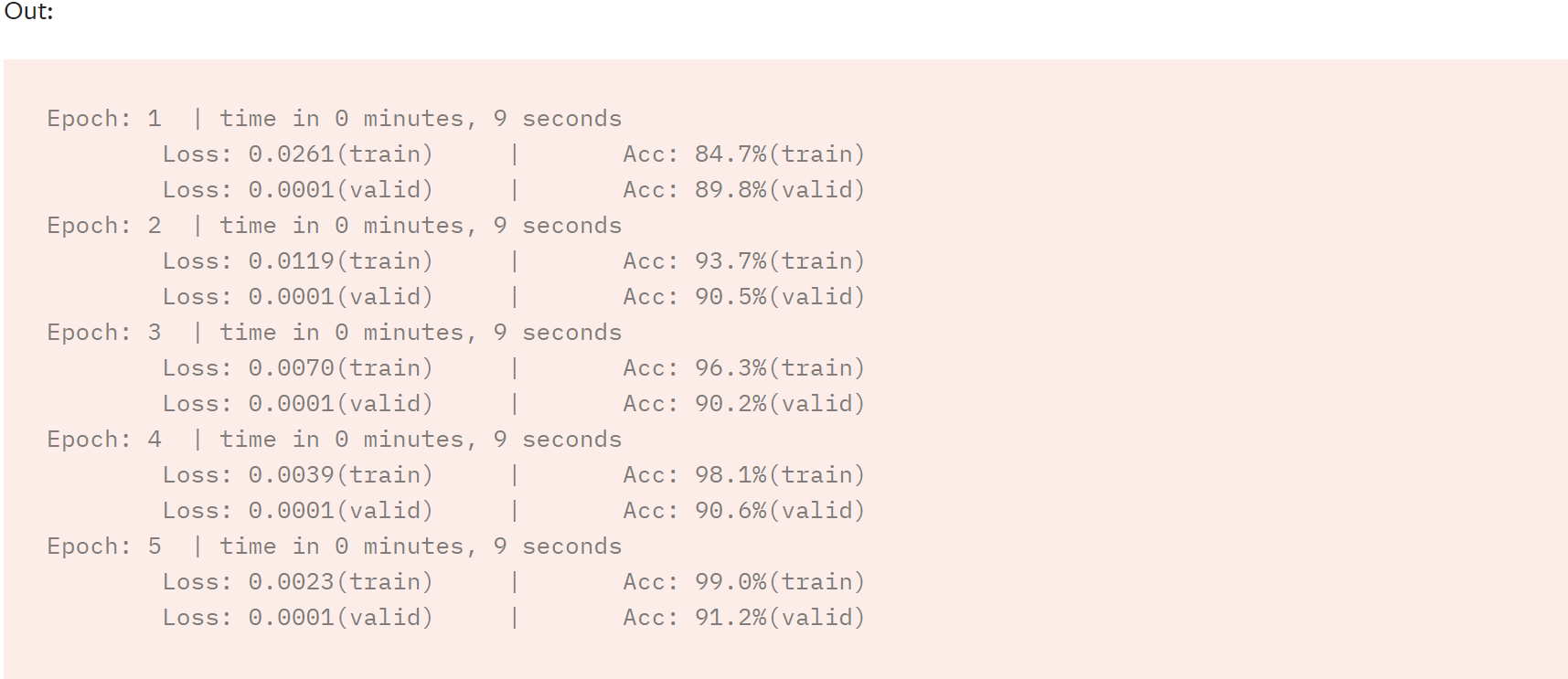
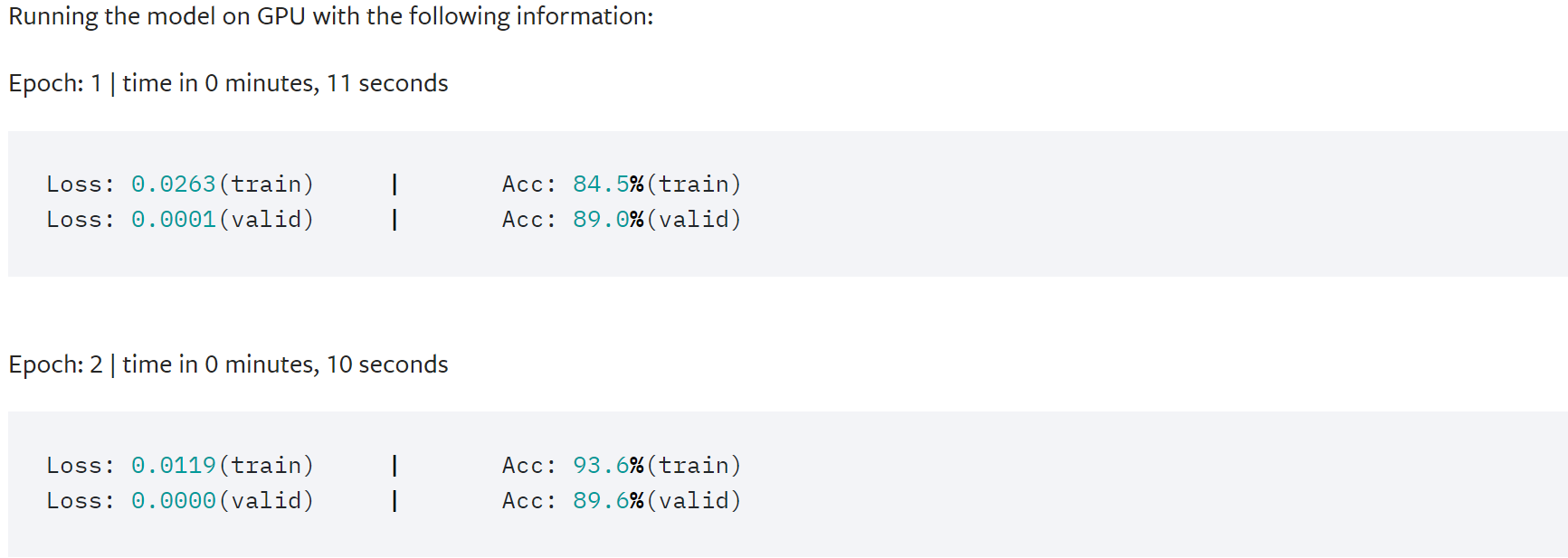
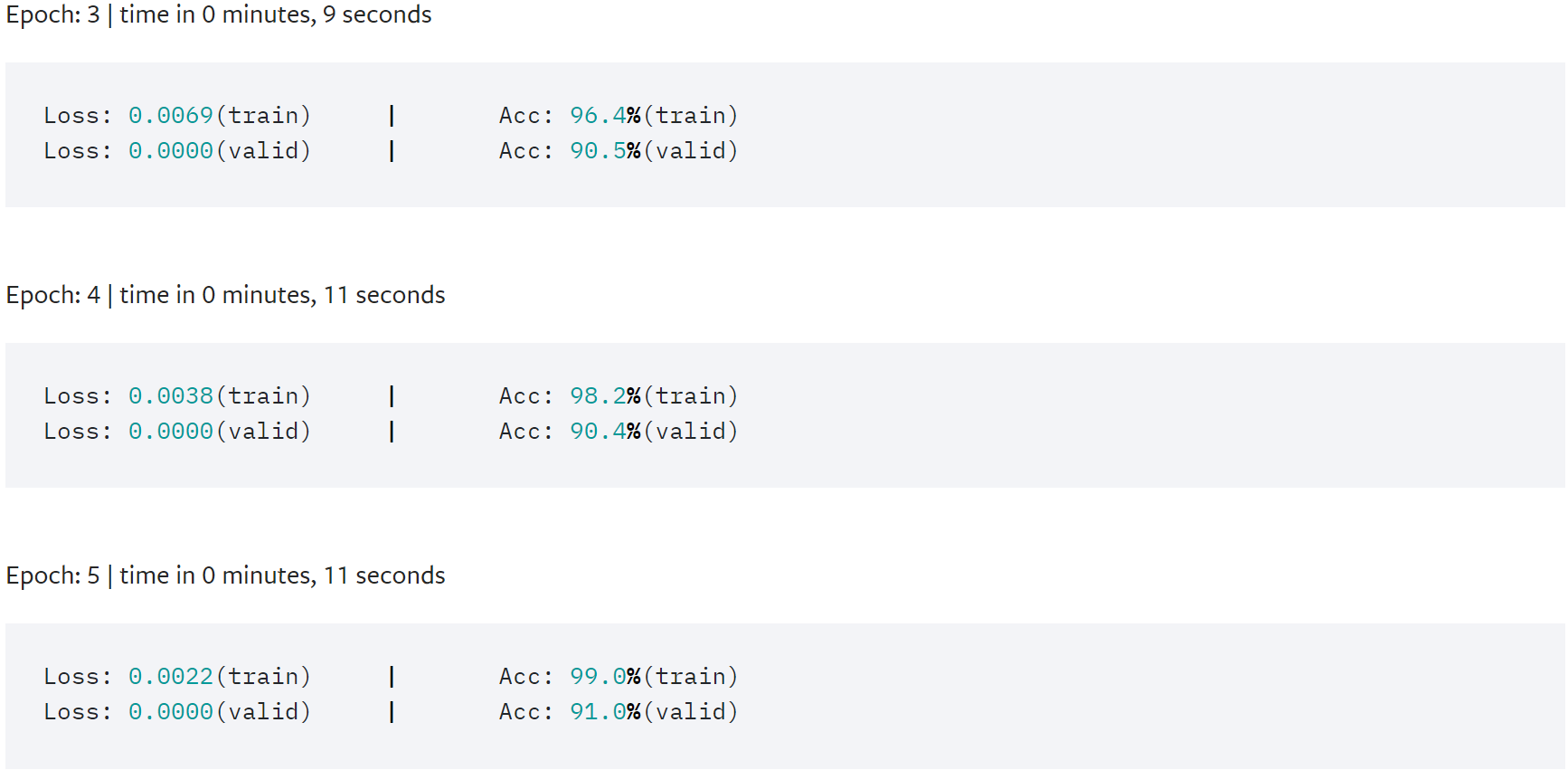
利用测试集评估
print('Checking the results of test dataset...') test_loss, test_acc = test(test_dataset) print(f'\tLoss: {test_loss:.4f}(test)\t|\tAcc: {test_acc * 100:.1f}%(test)')

随机进行测试
利用最好的模型进行测试,标签信息:
import re from torchtext.data.utils import ngrams_iterator from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer ag_news_label = {1 : "World", 2 : "Sports", 3 : "Business", 4 : "Sci/Tec"} def predict(text, model, vocab, ngrams): tokenizer = get_tokenizer("basic_english") with torch.no_grad(): text = torch.tensor([vocab[token] for token in ngrams_iterator(tokenizer(text), ngrams)]) output = model(text, torch.tensor([0])) return output.argmax(1).item() + 1 ex_text_str = "MEMPHIS, Tenn. – Four days ago, Jon Rahm was \ enduring the season’s worst weather conditions on Sunday at The \ Open on his way to a closing 75 at Royal Portrush, which \ considering the wind and the rain was a respectable showing. \ Thursday’s first round at the WGC-FedEx St. Jude Invitational \ was another story. With temperatures in the mid-80s and hardly any \ wind, the Spaniard was 13 strokes better in a flawless round. \ Thanks to his best putting performance on the PGA Tour, Rahm \ finished with an 8-under 62 for a three-stroke lead, which \ was even more impressive considering he’d never played the \ front nine at TPC Southwind." vocab = train_dataset.get_vocab() model = model.to("cpu") print("This is a %s news" %ag_news_label[predict(ex_text_str, model, vocab, 2)])



