SpringCloud开发学习总结(三)—— 服务治理Eureka
在最初开始构建微服务系统的时候可能服务并不多,我们可以通过做一些静态配置来完成服务的调用。比如,有两个服务A和B,其中服务A需要调用服务B来完成一个业务操作时,为了实现服务B的高可用,不论采用服务端负载均衡还是客户端负载均衡,都需要手工维护服务B的具体实例清单。但是随着业务的发展,系统功能越来越复杂,相应的微服务应用也不断增加,我们的静态配置会变得越来越难以维护。并且面对不断发展的业务,我们的集群规模、服务的位置、服务的命名等都有可能发生变化,如果还是通过手工维护的方式,那么极易发生错误或是命名冲突问题。同事,对于这类静态内容的维护也必将消耗大量的人力。
为了解决上述问题,Spring Cloud Eureka 应运而生。Spring Cloud Eureka 是 Spring Cloud Netflix微服务套件中的一部分,它基于Netflix Eureka做了二次封装,主要负责完成微服务架构中的服务治理功能。它既包含了服务端组件,也包含了客户端组件,并且服务端与客户端均采用Java编写,所以Eureka主要适用于通过Java实现的分布式系统,或是与JVM兼容语言构建的系统。下面我们来构建一些简单实例,学习如何使用Eureka构建注册中心以及进行注册与发现服务。
一、搭建服务注册中心
首先,创建一个基础的Spring Boot工程,命名为eureka-server,并在pom.xml中引入必要的依赖内容,代码如下
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 4 <version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version> 5 <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> 6 </parent> 7 8 <dependencies> 9 <!-- Eureka服务端开始 --> 10 <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 11 <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId> 12 </dependency> 13 <!-- Eureka服务端结束 --> 14 </dependencies> 16 17 <dependencyManagement> 18 <dependencies> 19 <dependency> 20 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 21 <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> 22 <version>Edgware.SR2</version> 23 <type>pom</type> 24 <scope>import</scope> 25 </dependency> 26 </dependencies> 27 </dependencyManagement>
通过@EnableEurekaServer注解启动一个服务注册中心提供给其他应用进行对话。这一步非常简单,只需在一个普通的Spring Boot应用中添加这个注解就能开启此功能,比如下面的例子:
1 @EnableEurekaServer 2 @SpringBootApplication(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class})① 3 public class EurekaServerApplication { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args); 7 } 8 }
在默认设置下,该服务注册中心也会将自己作为客户端来尝试注册它自己,所以我们需要禁用它的客户端注册行为,只需在application.properties中增加如下配置:
1 server.port=1111 2 3 eureka.instance.hostname=localhost 4 eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false #由于该应用为注册中心,所以设置为false,代表不向注册中心注册自己 5 eureka.client.fetch-registry=false #由于注册中心的职责就是维护服务实例,它并不需要去检索服务,所以也设置为false 6 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
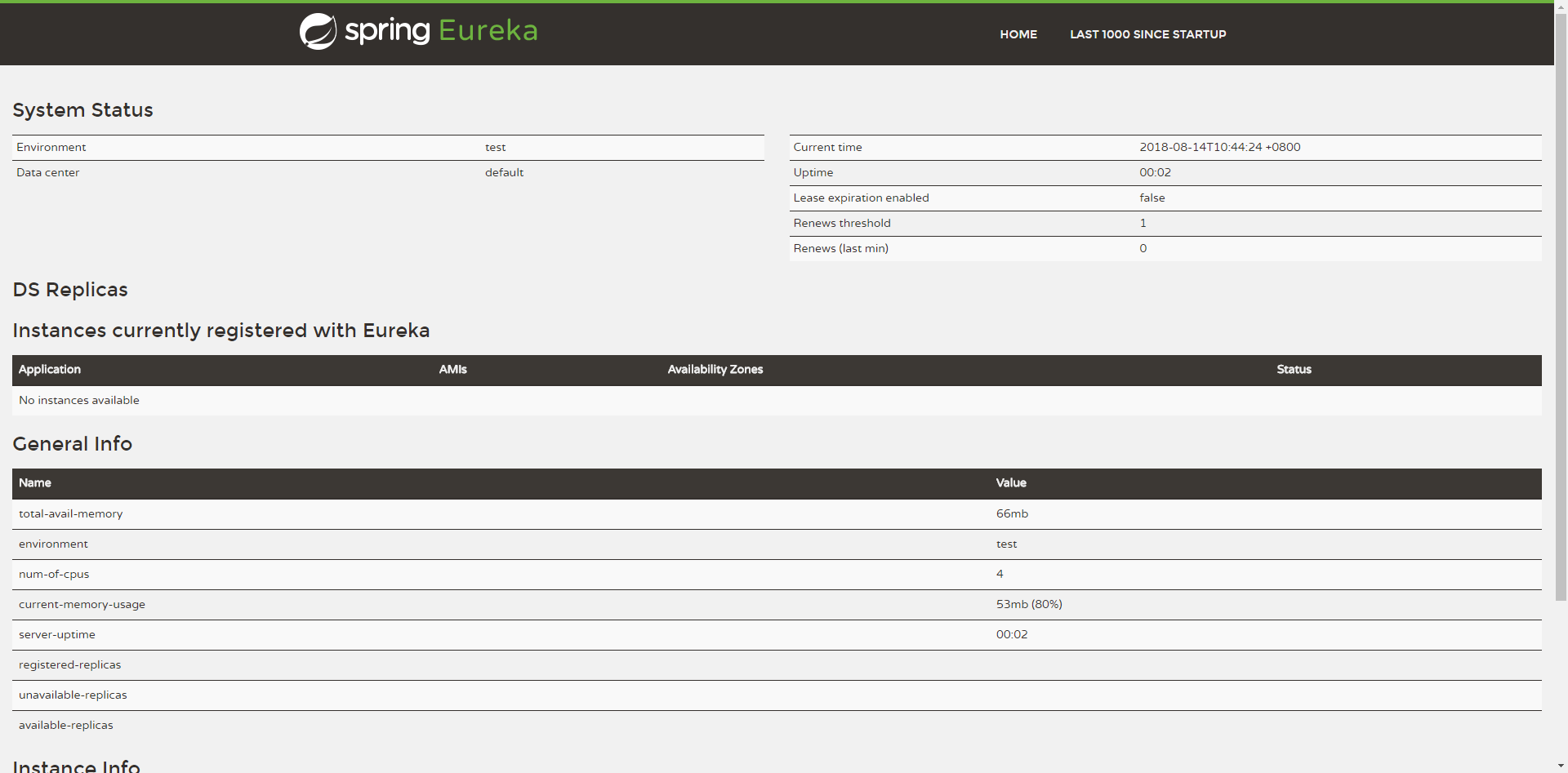
在完成了上面的配置后,启动应用并访问http://localhost:1111/。可以看到如下图所示的Eureka信息面板,其中Instances currently registered with Eureka栏是空的,说明该注册中心还没有注册任何服务。
二、注册服务提供者
在完成了服务注册中心的搭建之后,接下来我们尝试将一个既有的Spring Boot应用加入Eureka的服务治理体系中去。
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 4 <version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version> 5 <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> 6 </parent> 7 8 <properties> 9 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 10 <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> 11 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 12 </properties> 13 14 <dependencies> 15 <dependency> 16 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 17 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 18 </dependency> 19 <dependency> 20 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 21 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 22 </dependency> 23 <dependency> 24 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 25 <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId> 26 </dependency> 27 <dependency> 28 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 29 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 30 <scope>test</scope> 31 </dependency> 32 </dependencies> 33 <dependencyManagement> 34 <dependencies> 35 <dependency> 36 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 37 <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> 38 <version>Edgware.SR2</version> 39 <type>pom</type> 40 <scope>import</scope> 41 </dependency> 42 </dependencies> 43 </dependencyManagement>
接着添加/hello接口
1 @RestController 2 public class HelloController { 3 @RequestMapping("/hello") 4 public String hello() { 5 return "hello eureka"; 6 } 7 }
然后,在主类中通过加上@EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,激活Eureka对服务的发现
1 @EnableDiscoveryClient② 2 @SpringBootApplication 3 public class ProvideApplication { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 SpringApplication.run(ProvideApplication.class, args); 7 } 8 }
最后,我们需要在application.properties配置文件中,通过spring.application.name属性来为服务命名,比如命名为hello-service。再通过eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone属性来制定服务注册中心的地址,这里我们指定为上述构建的服务注册中心地址,完整配置如下所示:
1 server.port=8090 2 3 spring.application.name=hello-service 4 5 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:1111/eureka/
下面我们分别启动服务注册中心以及这里改造后的hello-service服务,通过访问Eureka的信息面板,在Instances currently registered with Eureka可以看到
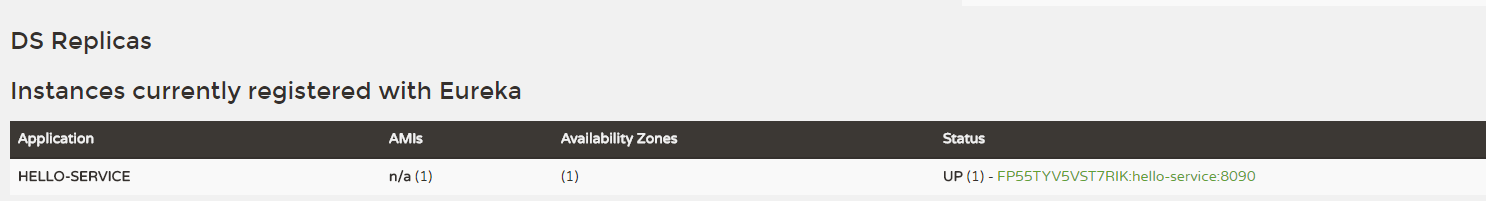
至此,服务注册成功!
注释一:springboot项目启动时,如果没有配置数据库配置,启动时会抛出如下异常。
Description:
Cannot determine embedded database driver class for database type NONE
Action:
If you want an embedded database please put a supported one on the classpath.
If you have database settings to be loaded from a particular profile you may
need to active it (no profiles are currently active).
因为springboot会自动注入数据源,而项目如果没有配,就会抛出该异常。
如果只是简单的想建个项目,并不需要数据库支持,那么可以添加exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class}不去注入数据源。
注释二:从Spring Cloud Edgware开始,@EnableDiscoveryClient 或@EnableEurekaClient 可省略。只需加上相关依赖,并进行相应配置,即可将微服务注册到服务发现组件上。
Spring Cloud为什么要这么设计/改进呢?
这是由于在实际项目中,我们可能希望实现“不同环境不同配置”的效果——例如:在开发环境中,不注册到Eureka Server上,而是服务提供者、服务消费者直连,便于调测;在生产环境中,我们又希望能够享受服务发现的优势——服务消费者无需知道服务提供者的绝对地址。为适应该需求,Spring Cloud Commons进行了改进
如不想将服务注册到Eureka Server,只需设置spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled=false ,或@EnableDiscoveryClient(autoRegister = false) 即可。


