【论文阅读】ICRA2021: VDB-EDT An Efficient Euclidean Distance Transform Algorithm Based on VDB Data Struct
参考与前言
Summary: 浩哥推荐的一篇 无人机下的建图 and planning实验
Type: ICRA
Year: 2021
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.04419
youtube presentation video:https://youtu.be/Bojh6ylYUOo
代码链接:https://github.com/zhudelong/VDB-EDT
1. Motivation
Eucliden distance transform EDT 对于机器人运动规划是很重要的,但是生成EDT 是比较费时的一件事,同时需要时刻更新并维护这样一个地图,本篇文章主要 通过优化数据结构和distance transform的过程来提升EDT算法的速度
在本文中,我们采用了树结构进行 hashing-based EDTs,主要是在做规划时发现 最优轨迹其实值需要考虑一定范围的障碍物, full distance information其实对于规划来说是冗余的,所以实际free部分都是一个值。These regions can then be efficiently encoded by a few number of tree nodes. Such a property is called spatial coherency, which can help further reduce memory consumption.
Benefiting from the fast index and caching systems, VDB achieves a much faster random access speed than Octree and also exhibits a competitive performance with the voxel hashing.
Contribution
- the first time introduce the VDB data structure for distance field representation, which significantly reduces the memory consumption of EDT.
- we propose a novel algorithm to facilitate distance transform procedure and significantly improve the running speed of conventional EDT algorithms.
2. Method
首先是问题定义,一个典型的distance transform问题 可以表达为如下公式:
其中,Mf是指free space,Mo是被占据空间,x为在grid map M中的坐标,目标函数f表示xi到xj之间的距离,目标是搜索对于每个xi都找其最近的xj作为距离
随后问题有了d(x) 后 我们就走到了 要找到一条安全的路径,则问题可表述为如下:
其中,dmax是最大的transform distance,xs起点,xf终点,alpha为balance coefficient,g<theta主要是限制两个连续点之间产生较大的角度,平滑轨迹用的。目标函数中 前者为路径长度的cost,后者为避障的cost
2.1 数据结构
主要是介绍了VDB结构,由Museth[25] 提出的。It sufficiently exploits the sparsity of volumetric data, and employs a variant of B+ tree [32] to represent the data hierarchically.
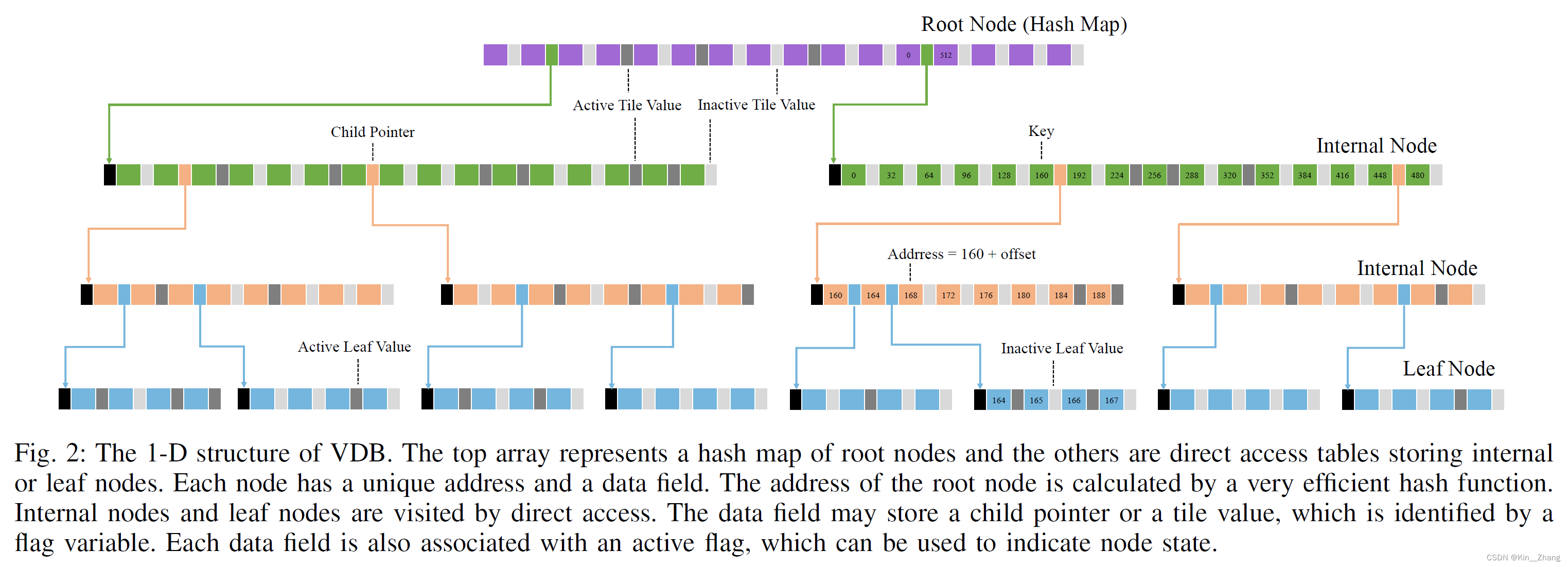
下图是1D结构下的VDB,其和B+的几个特性是一致的,root node为索引,由hashmap建立,下面为internal node 和 leaf node保存了数据。也有本质上的不同:
it encodes values in internal nodes, called tile value. The tile value and child pointer exclusively use the same memory unit, and a flag is additionally leveraged to identify the different cases. A tile value only takes up tens of bits memory but can represent a large area in the distance field, which is the key feature leveraged to improve memory efficiency.
B+是一种平衡tree,在数据库中常用,主要原因是对于树结构的查询,程序加载子节点都需要进行一次磁盘IO,磁盘IO 比 读内存IO要慢 所以多叉的B+ tree可以减少I/O的次数
参考:b站视频 “索引”的原理 4min 建议感兴趣的可以再查询进阶数据结构书籍了解 实际上代码是直接openvdb库直接构建的
- VDB: the branching factors are very large and variable, making the tree shallow and wide
- Octree-based: deep and narrow, thus not fast enough for distance transform.
2.2 VDB-EDT
感觉这个看文中会比较好 主要是针对伪代码的解释
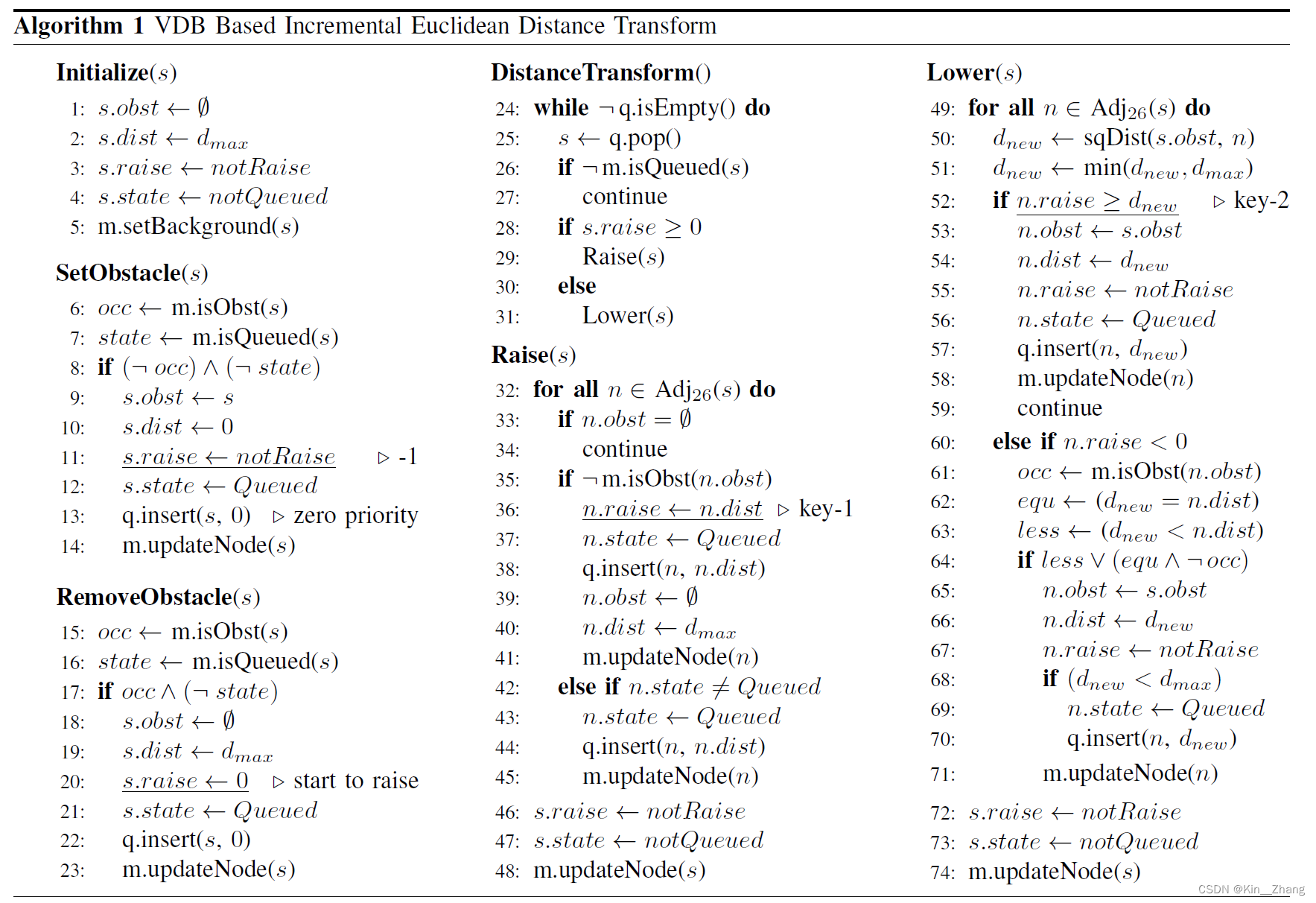
The distance field represented by VDB is essentially a sparse volumetric grid, and each field point is represented by a grid cell s indexed by a 3-D coordinate.

更新部分code:
void VDBMap::update_occmap(FloatGrid::Ptr grid_map, const tf::Vector3 &origin, XYZCloud::Ptr xyz)
{
auto grid_acc = grid_map->getAccessor();
auto tfm = grid_map->transform();
openvdb::Vec3d origin3d(origin.x(), origin.y(), origin.z());
openvdb::Vec3d origin_ijk = grid_map->worldToIndex(origin3d);
for (auto point = xyz->begin(); point != xyz->end(); ++point) {
openvdb::Vec3d p_xyz(point->x, point->y, point->z);
openvdb::Vec3d p_ijk = grid_map->worldToIndex(p_xyz);
openvdb::Vec3d dir(p_ijk - origin_ijk);
double range = dir.length();
dir.normalize();
// Note: real sensor range should stractly larger than sensor_range
bool truncated = false;
openvdb::math::Ray<double> ray(origin_ijk, dir);
// openvdb::math::DDA<openvdb::math::Ray<double>, 0> dda(ray, 0., std::min(SENSOR_RANGE, range));
// if (START_RANGE >= std::min(SENSOR_RANGE, range)){
// continue;
// }
openvdb::math::DDA<openvdb::math::Ray<double>, 0> dda(ray, 0, std::min(SENSOR_RANGE, range));
// decrease occupancy
do {
openvdb::Coord ijk(dda.voxel());
float ll_old;
bool isKnown = grid_acc.probeValue(ijk, ll_old);
float ll_new = std::max(L_MIN, ll_old+L_FREE);
if(!isKnown){
grid_distance_->dist_acc_->setValueOn(ijk);
} // unknown -> free -> EDT initialize
else if(ll_old >= 0 && ll_new < 0){
grid_distance_->removeObstacle(ijk);
} // occupied -> free -> EDT RemoveObstacle
grid_acc.setValueOn(ijk, ll_new);
dda.step();
} while (dda.time() < dda.maxTime());
// increase occupancy
if ((!truncated) && (range <= SENSOR_RANGE)){
for (int i=0; i < HIT_THICKNESS; ++i) {
openvdb::Coord ijk(dda.voxel());
float ll_old;
bool isKnown = grid_acc.probeValue(ijk, ll_old);
float ll_new = std::min(L_MAX, ll_old+L_OCCU);
if(!isKnown){
grid_distance_->dist_acc_->setValueOn(ijk);
} // unknown -> occupied -> EDT SetObstacle
else if(ll_old < 0 && ll_new >= 0){
grid_distance_->setObstacle(ijk);
} // free -> occupied -> EDT SetObstacle
grid_acc.setValueOn(ijk, ll_new);
dda.step();
}
} // process obstacle
} // end inserting
/* commit changes to the open queue*/
}
3. 实验及结果
各个阈值对时间的影响,其中对比了几个baseline方法如下:
- A commonly-used general EDT [18] (denoted without -Ex suffix)
- the proposed algorithm (denoted with -Ex suffix).
- Two implementations based on the array and VDB data structures to compare their memory efficiency (denoted with Arr- and VDB- prefix, respectively)
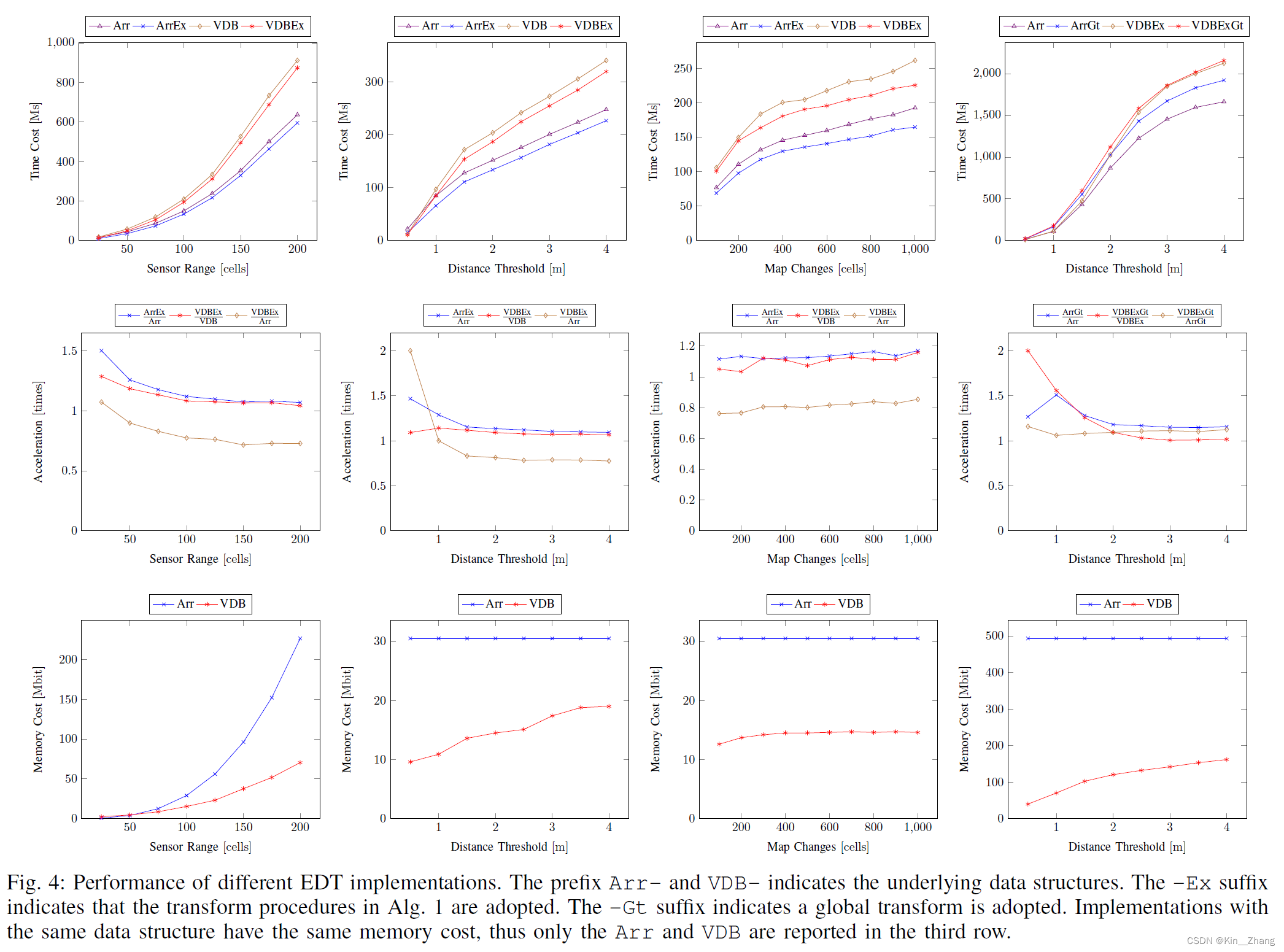
可以看到 在时间上-Ex 的耗时都比无Ex的快,虽然VDB的速度上比arr的还是慢了一点 10%-25%,但是从memeory cost上确实节约了30-60%的 Herein, the increment of time cost is inevitable, as VDB is based on tree structures and has a slower random access speed than the array-based implementation
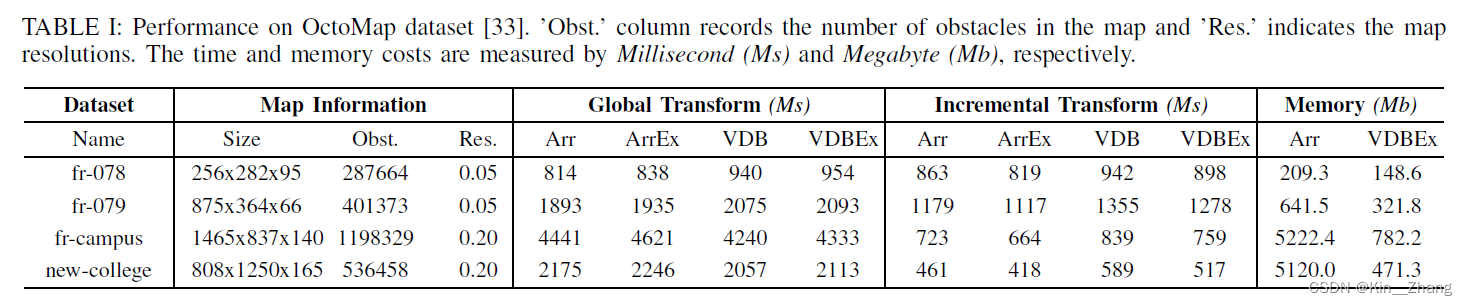
同样表格是在数据集上的表现,在global 和 incremental transform会慢一点,但是在memory上省了不少
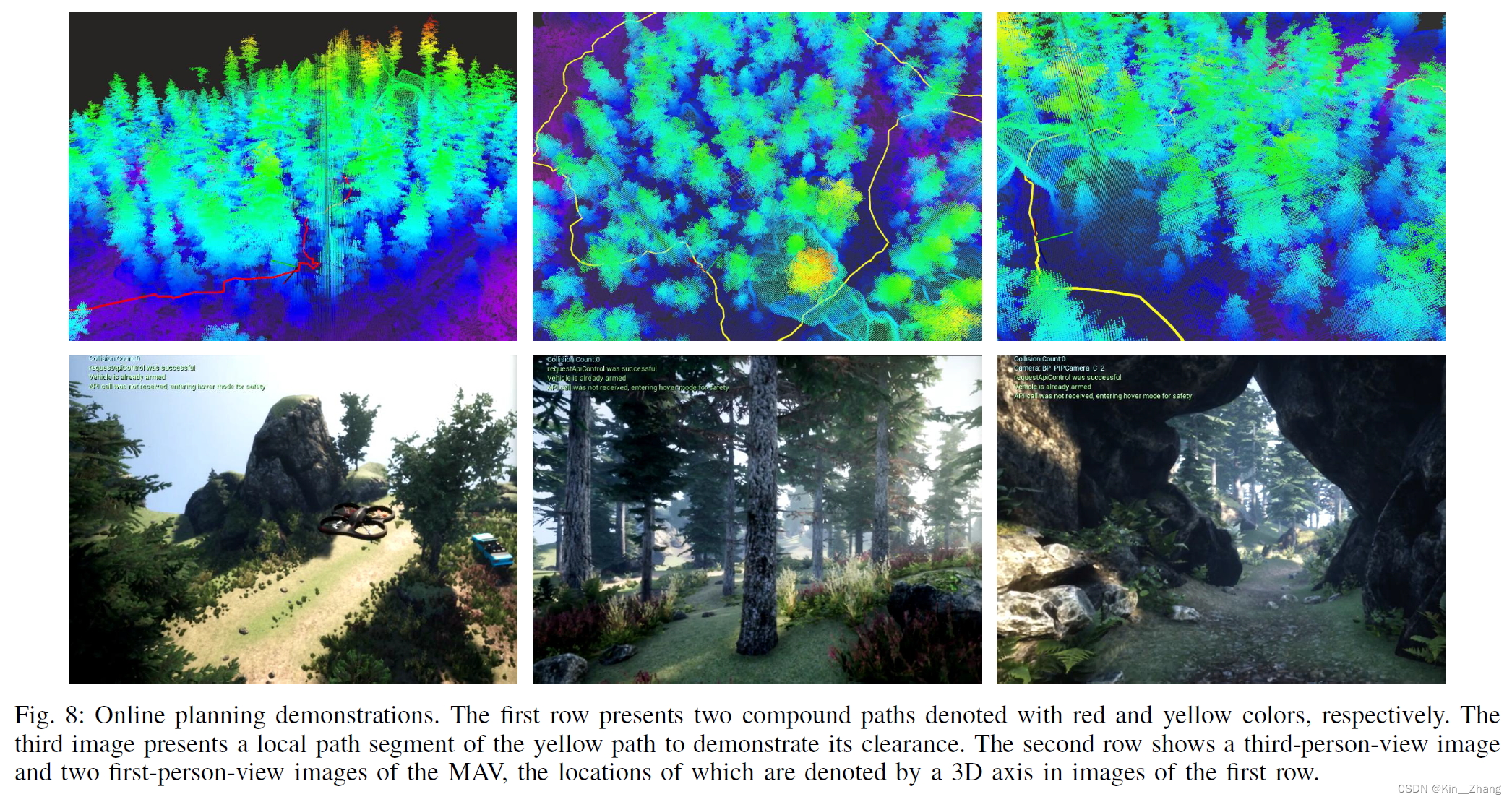
还有一个就是无人机在仿真环境中建图并有planning效果:

4. Conclusion
提出了一种VDB-EDT算法去解决 distance transform problem. The algorithm is implemented based on a memory-efficient data structure and a novel distance transform procedure, which significantly improves the memory and runtime efficiency of EDTs.
这项工作突破了通常的EDT的限制,也可以为后面基于VDB-based mapping, distance transform and safe motion planning的研究进行使用
赠人点赞 手有余香 😆;正向回馈 才能更好开放记录 hhh



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】