【仿真】Carla介绍与基本使用 [1] (附代码 基础版)
0. 参考与前言
主要介绍无人驾驶的仿真环境CARLA,开源社区维护,以下为相关参考链接:
-
Carla官方文档 建议后续找的时候 先按好版本号,有些功能/api 是新版本里有的,Carla官方github
-
Youtube Python+Window 0.9.5 主要是用Carla环境,使用TensorFlow搭建简单的自我学习自动驾驶车辆【虽然到最后还是没看到学成功的车到底长啥样】
-
知乎正在更新中的关于Carla较全面的介绍链接
-
简易安装见:张聪明的CSDN【压缩包安装法】
此系列为张聪明三次使用carla,终于开始写记录 认认真真搞一次
第一次:是因为 Youtube Python+Window 0.9.5 ,然后当时在windows上没发运行就不了了之了,具体问题见当初在Github issue链接
第二次:是打算用Carla跑ROS联通,但是很快就... 没搞了 有其他活
第三次:也是这次... Autoware的连接,当然就包括ROS了,其实不难查到Carla有一个专门的分支是用autoware内核的,但是呢... 介于我们还要上实车,所以就相当于remap到autoware的topic上了,但是这次因为要设置NPC玩家的轨迹以便验证每个步骤的流程【识别、OpenPlanner的行驶】所以就刚好认认真真看一次顺便做个笔记
这个系列同步在cnblog和csdn上进行更新,相关专栏和分类链接如下,有用的话 点个小赞,正向反馈~ 👍
- CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39537898/category_11562137.html
- cnblog: https://www.cnblogs.com/kin-zhang/category/2096236.html
更新日志:
20221107:重新链一下代码,感觉上一版代码有些乱
20220527:重置 删除相关notion外链等 添加相关图片和对应链接
20220525:进行了一次较为大的改动,重组了一下目录 和 一些内容;去掉了一些原文的大段英文
20210420:第一版说明发布,总结了CARLA的基本使用
1. CARLA 世界组成
这一点在 引用3. Carla较全面的介绍 进行了介绍,所以我就写点 我的note/补充
首先是交互形式:Client-Server,所以当时我提出windows上无法运行成功时有人回复:是否是2000口没有开(但后续我确认过开了还是不行)就类似于IP握手连接的感觉?所以应该是可以在主机直接连接到其他跑仿真主机的host_ip的 => 后面事实证明2000口被其他的占用了,我-port=3000就成功了 hhhh
主要核心
仅进行一些简单介绍,对整体有个概念,如果没有到用上的时候,没有做说明的,可以暂时不用深入了解
- Traffic manager. 类似于一个车辆管理器,更多详情见 [3] NPC管理/Traffic Manager ,‼️ 建议后续进行了解
- Sensors. 车辆上的传感器,可以进行设置,CARLA内置有不少的传感器(LiDAR, Camera, Depth, DVS, Radar等等)
- Recorder. 内置的一个记录工具,和rosbag异曲同工,更多详情见 [9] replay用法
- ROS bridge and Autoware implementation. 和ROS相关的一些bridge,可以直接看github ros-bridge的用法
- Open assets. 城镇的一些贴图之类的,assets,如果不走UE4 源码编译,基本不会用上,0.9.13里进行了更新,可以修改一些贴图,更多建议自己探索
- Scenario runner. 场景生成器,类似于做算法测试时希望能生成特定场景的功能。更多详情可以看看CARLA办的排行榜比赛 [7] Carla leaderboard 排行榜,0.9.11/12 好像引入了openscenario的格式进行设置
2. 头文件设置
一般最好的学习方式是直接先看一下官方的示例,一般用压缩包安装法打开后,整体文件夹的位置如下,可以看到 PythonAPI/examples 文件夹下有很多示例
➜ CARLA tree -L 1
.
├── CarlaUE4
├── CarlaUE4.sh
├── CHANGELOG
├── Co-Simulation
├── Dockerfile
├── Engine
├── HDMaps
├── Import
├── ImportAssets.sh
├── LICENSE
├── Manifest_DebugFiles_Linux.txt
├── Plugins
├── PythonAPI
│ ├── carla
│ ├── examples
│ ├── python_api.md
│ ├── tutorials
│ └── util
├── README
├── Tools
└── VERSION
然后打开时可以看到基本上所有的开头都有这样一段code,其实原因是因为carla有自己的python api库,可以通过此进行定位导入
# -- coding:UTF-8 --
#!/usr/bin/env python
import glob
import os
import sys
import time
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
每个文件请复制这个到头,或者按照下面所示添加库到自己的路径中,注意以下演示的是py2的 一定要根据自己的CARLA版本和py版本进行设置哈!!!
CARLA pip libaray
0.9.13及后的都可以通过pip install
pip3 install carla
0.9.12及以下的【引用3. 提到的方法把carla内置于python库当中去】 注意修改自己的CARLA文件夹、版本号和Python 版本号
cd ~/CARLA_0.9.11/PythonAPI/carla/dist/
unzip carla-0.9.11-py2.7-linux-x86_64.egg -d carla-0.9.11-py2.7-linux-x86_64
cd carla-0.9.11-py2.7-linux-x86_64
gedit setup.py
然后复制这段到setup.py里
from distutils.core import setup
setup(name='carla',
version='0.9.11',
py_modules=['carla'],
)
最后install一下就行
pip install -e ~/CARLA_0.9.11/PythonAPI/carla/dist/carla-0.9.11-py2.7-linux-x86_64
后话
看到有同学要这个.egg文件,其实CARLA甚至可以不用py37运行也可以的,主要就是找到这样一个对应的py库就行
https://pypi.org/simple/carla/ 在这里 你可以下载到任何python版本下的对应的CARLA版本的py库,对于whl的话 可以直接进行pip install的操作,我随便演示一下:
pip install carla-0.9.3-cp27-cp27mu-manylinux1_x86_64.whl
3. 初步探索
此章节主要参照官方文档的first step里的内容,学有余力者可直接阅读英文原版文档,之中会添加一些自己的使用经验和碎碎念
如果觉得 1st, 2nd 太啰嗦了 可以直接阅读完整代码:https://gitee.com/kin_zhang/carla-python-api/blob/develop/tutorial/tutorial_spawn_car.py 一般情况下 可以直接看懂 因为我把注释也复制过去了 hhh
1st - World and Client
# 这里是连接Carla 服务器
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(10.0) # seconds
# 读取现在开启的Carla里的世界信息
world = client.get_world()
读取世界信息的操作呢,主要是为了后面能
world.get_map()拿到世界地图world.spawn_actor在世界内生成NPC或自己的车world.get_blueprint_library()在世界读blueprint的库里都有些啥 加车加传感器world.get_random_location_from_navigation()就是他名字写的那样
那么这些点后面的 我们应该从哪里得知呢?→ 跳转官方文档链接
2nd - Actors and blueprints
关于world能得到的所有的蓝图见此链接,我们先试着生成一辆车
# get blueprint library
blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library()
# 你可以在上面给的链接中找到 你想添加的东西
ego_vehicle_bp = blueprint_library.find('vehicle.audi.a2')
# 给我们的车加上特定的颜色
ego_vehicle_bp.set_attribute('color', '0, 0, 0')
关于第二点,是在find里找到添加的东西,建议打开网页然后CTRL+F,然后搜索关键字,比如
- 如果你想添加的是传感器那么一般以sensor开头,sensor.sensor_type(传感器.传感器类型)
sensor.lidar.ray_cast就是激光雷达,sensor.other.collision就是碰撞检测的【具体是啥呢 咱也不用管】 - 如果是车呢,一般就是vehicle开头,
vehicle.audi.a2就是奥迪A2的车型
Attributes have an carla.ActorAttributeType variable. It states its type from a list of enums. Also, modifiable attributes come with a list of recommended values.
这句话是指 每一个blueprint呢都是有附加的东西的,比如颜色?你可以看看关于attibute的类型有哪些
-
知道了在BP的库链接里能看到,每一个find里面都有它自身附带的属性;可以获取或设置attribute

看完了怎么去找到blueprint,那么怎么把他加入到world并跟踪其状态,包括位置、信息(如果是传感器的话 就会有传感器的一系列消息 比如相机会有图片、激光雷达会有点云)
The world object is responsible of spawning actors and keeping track of these. Spawning only requires a blueprint, and a carla.Transform stating a location and rotation for the actor.
也就是我们已经有了blueprint那么只需要给出transform就OK啦!
# 设置固定点,和他的朝向应该是怎样的
transform = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=-9, y=80, z=2), carla.Rotation(yaw=180))
# 随机的获取世界中的一个点,这一行你也可以在spwan_npc.py中看到
spawn_points = world.get_map().get_spawn_points()
# 然后把之前的blueprint填入第一个参数中,transform填入第二个参数中
actor = world.spawn_actor(ego_vehicle_bp, transform)
map.get_spawn_points()for vehicles. Returns a list of recommended spawning points.world.get_random_location()for walkers. Returns a random point on a sidewalk. This same method is used to set a goal location for walkers.
官方文档的这个章节有详细的讲解怎么添加传感器到车上,行人的轨迹等。基于我的需求 我就写到这里了,噢 还有个部分就是创建出来的NPC你在退出的时候要销毁,不然... 就会有很多很多很多NPC只能关闭Carla本身去销毁,而且后续也容易出BUG
然后这里就是运行完后直接CTRL+C停止脚本的同时,执行销毁
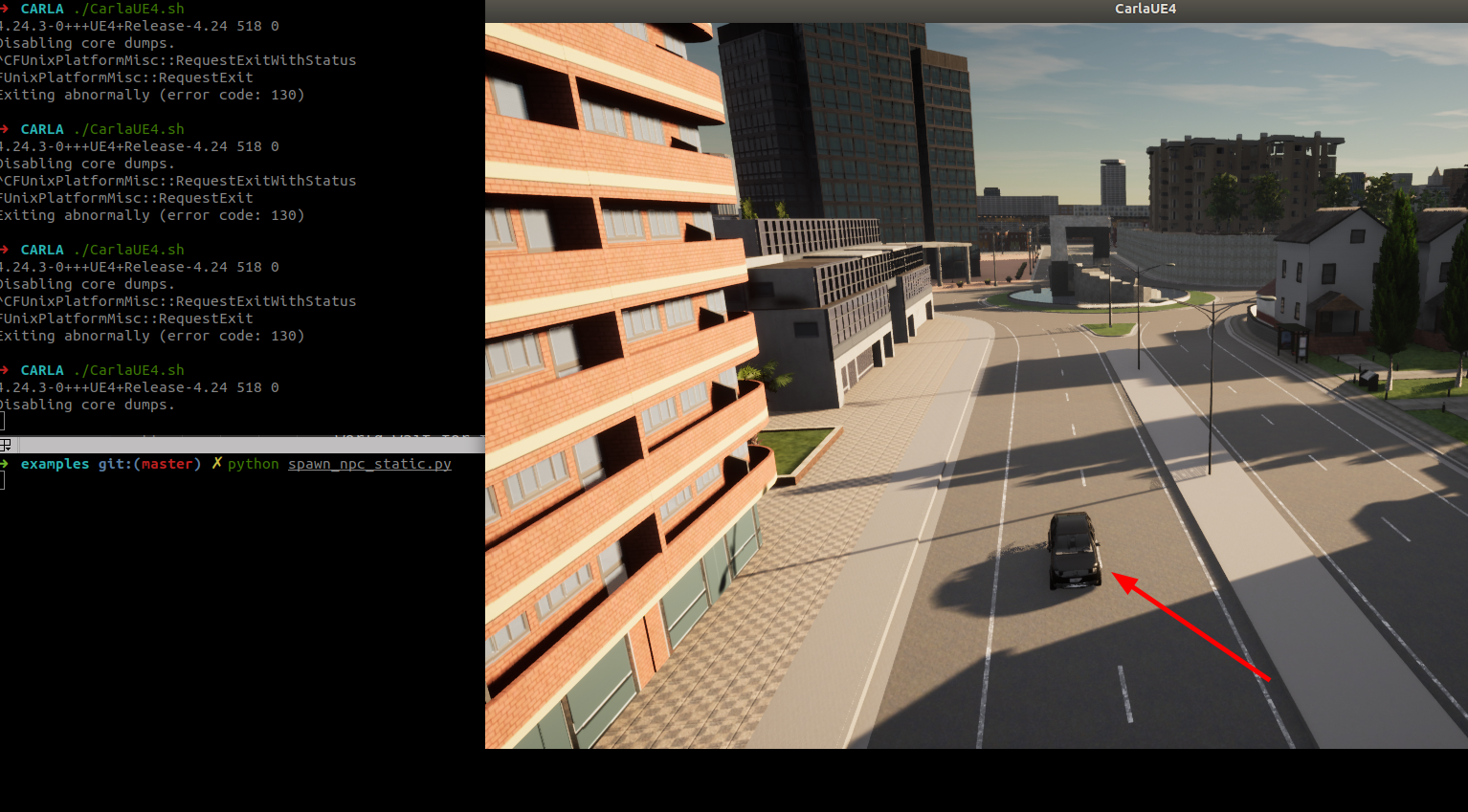
按照下面的代码及位置生成车辆
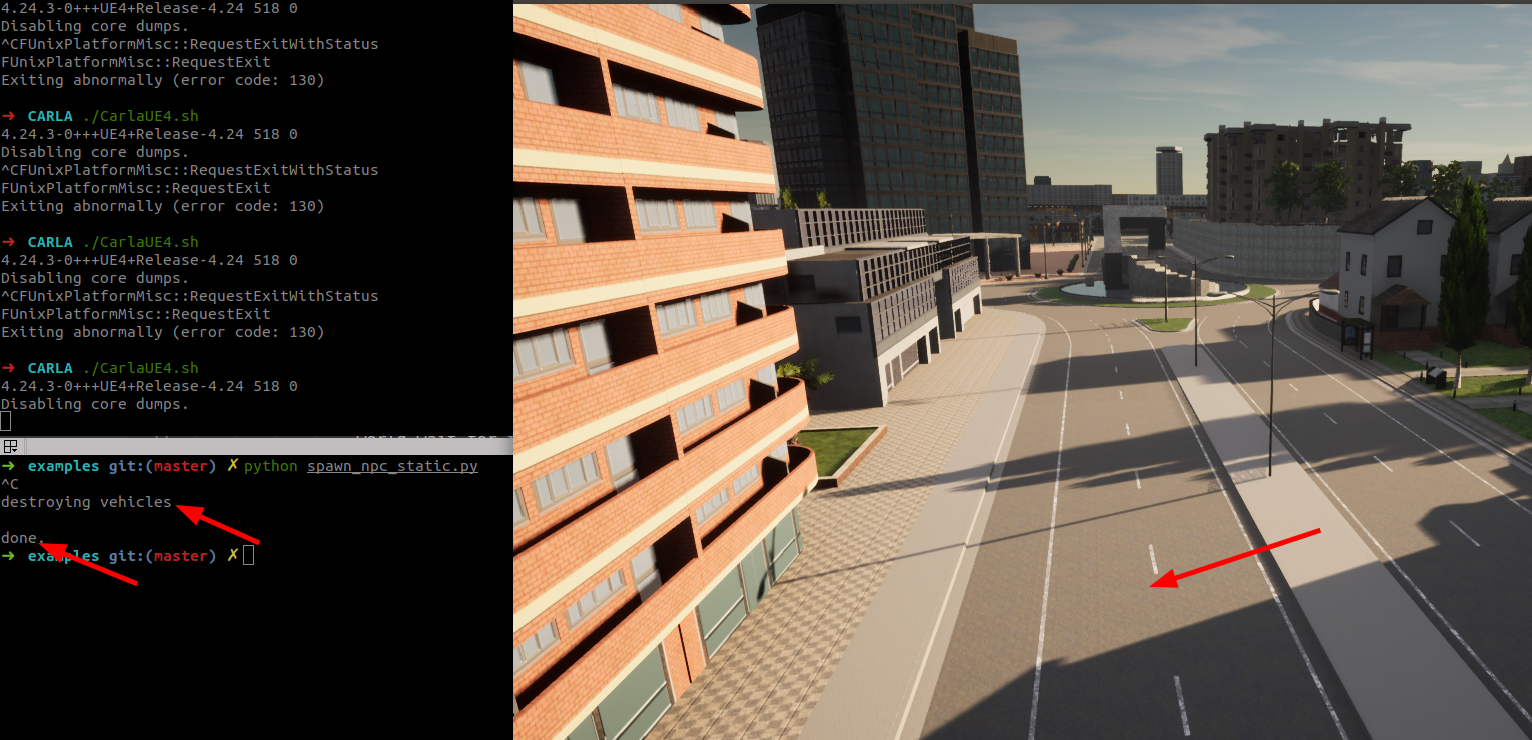
停止运行并,销毁车辆
可以直接阅读完整代码:https://gitee.com/kin_zhang/carla-python-api/blob/develop/tutorial/tutorial_spawn_car.py
关于生成我们已经清楚了【可以留个作业:怎么生成走路的行人,也就是制作重复行人过马路的场景 .gif图如下,会再下次再贴代码讲】那么在使用过程中我们可能需要设置行人过马路或者突然横穿马路的情景,在这里,我们继续实现前者以便验证一些感知、规划算法等

根据以上提供的完整代码后,再阅读下面的模块 就应该能知道 放置位置啦!
首先关于这一点还有一些知识,但也就是官网上的,主要呢就是说 整个actor的状态你都是可以知道的;当你生成了很多actors后,可以使用
# 读取现在开启的Carla里的世界信息
world = client.get_world()
# 前提是你定义的client.get_world()是赋给了叫world的变量哈
# 这样就拿到了这个世界里所有actor的信息
actor_list = world.get_actors()
我们可以看到图片中是运行的结果,如果你只想关注vehicle可以actor_list.filter('vehicle.*') 而图片中我是抽取了限速标志 看看所有限速标志的位置即其id号
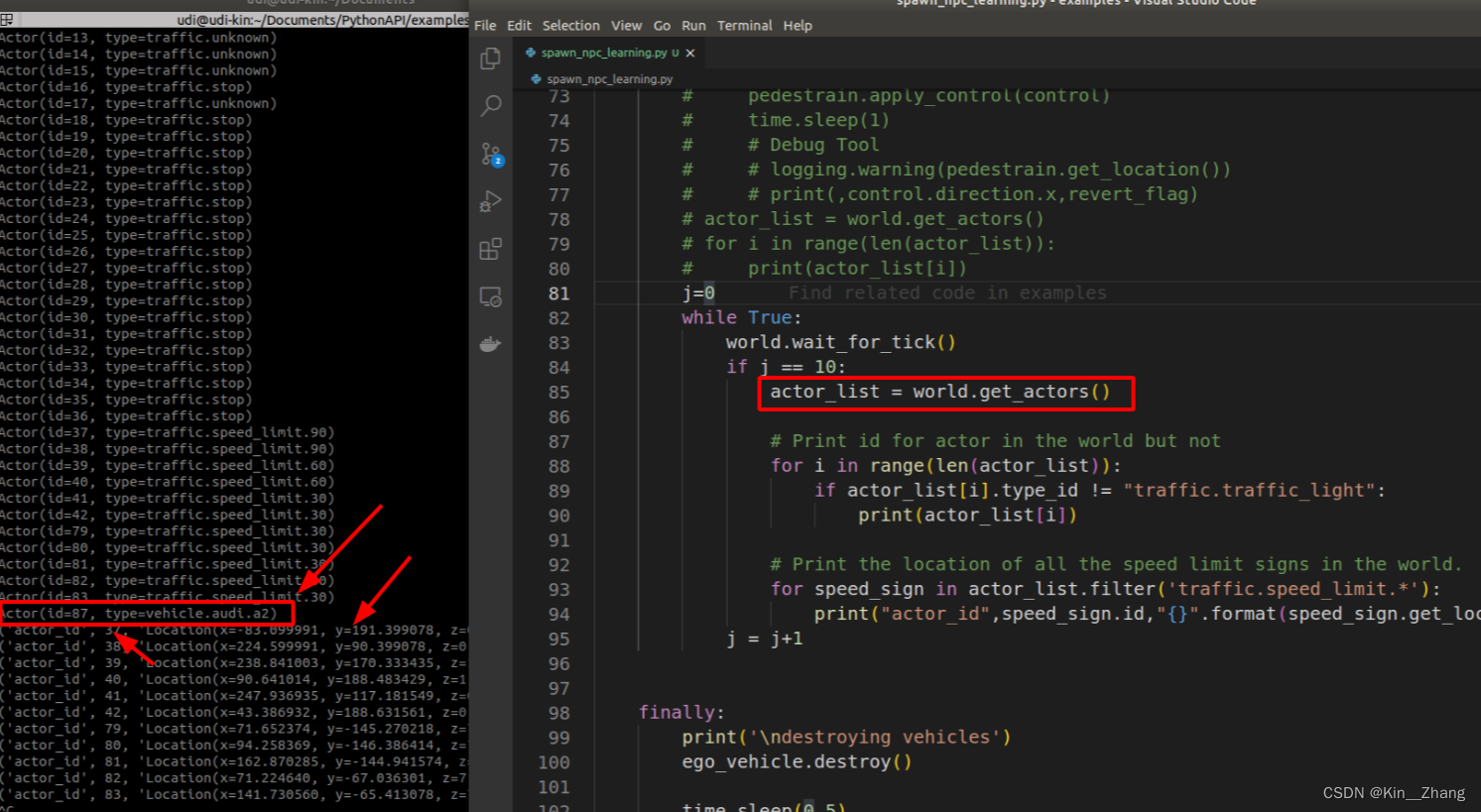
那么我是怎么知道他的是type_id而不是type呢?【别问 问就是我... 以为是type然后报错了 然后就去官网,有一说一官网的文档写的那叫一个好,前提是你入门了这个..】 Python API reference
打开文档后我们可以看到如图所示的然后就知道了一个actor所包含的东西,往下翻还可以看到为什么我能拿到他的位置因为Methods里面有:Getters都有些啥
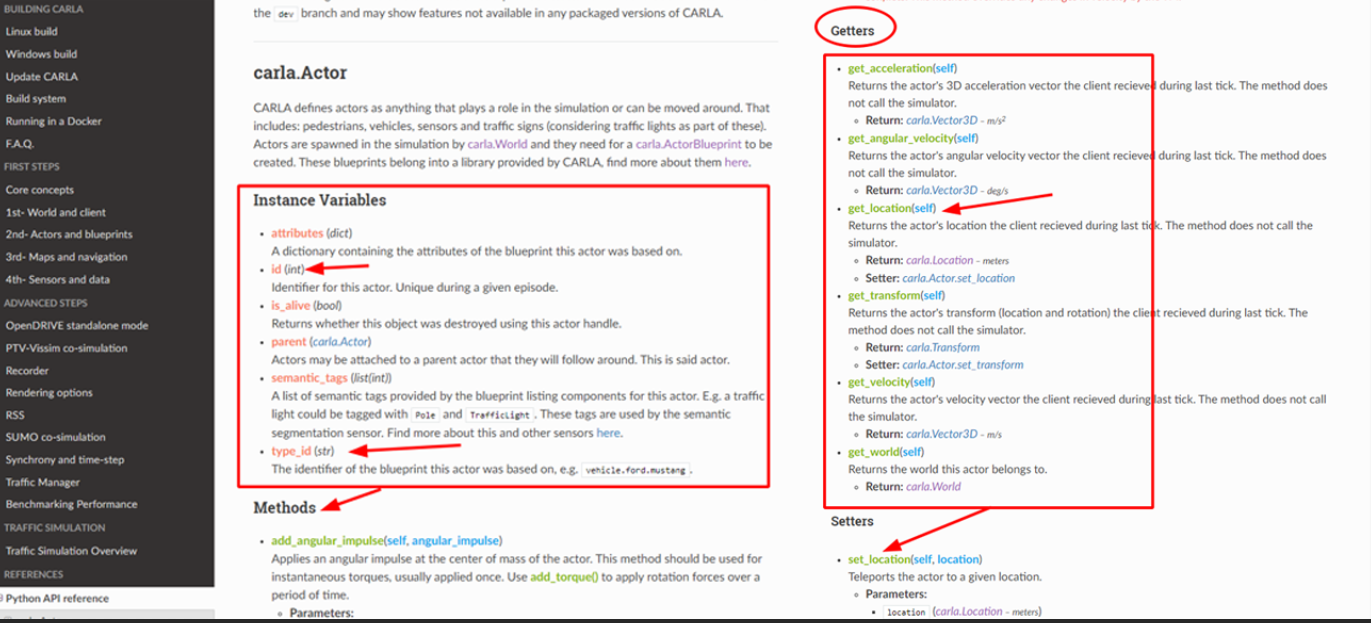
同时还可以设置一些参数,注意输入的数据格式即可,比如你可以先生成车辆,再把车辆set_location
说了Actors的操作后,我们还需要强调一点前面提到过的,destory销毁这些,不然你仅仅退出,这个actor还是会在这个地图里的,如果下一个位置你还是在这里生成车辆
所以一定要记得destroyed_sucessfully = actor.destroy() # Returns True if successful 这个destory命令 在运行后,特别是针对于在Carla中用学习来不断创造场景的
当然你还可以设置你的视野,所以你可以绑定你的视野,或者是... 绑定相机的位置 到司机的位置
spectator = world.get_spectator()
transform = vehicle.get_transform()
spectator.set_transform(carla.Transform(transform.location + carla.Location(z=50),
carla.Rotation(pitch=-90)))
读取交通灯的状态
#Get the traffic light affecting a vehicle
if vehicle_actor.is_at_traffic_light():
traffic_light = vehicle_actor.get_traffic_light()
甚至是改变交通灯的状态【上帝模式】
#Change a red traffic light to green
if traffic_light.get_state() == carla.TrafficLightState.Red:
traffic_light.set_state(carla.TrafficLightState.Green)
traffic_light.set_set_green_time(4.0)
3rd - Maps and navigation
啊 后悔,太晚才看这个点... 写到这里还是再次建议大家看官方文档比较好,如果对英文阅读没有什么障碍的话,文档的语言都很简单放心 不像论文那样,字都认识连起来不知道啥意思【没错说我自己呢】
在上面的例子中,我们可以在client后建立世界的时候,加载自己想要的地图
try:
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(2.0)
world = client.load_world('Town01') #load Town 01 Map
world = reload_world() #reload the same map as world have
| Town | Summary |
|---|---|
| Town01 | A basic town layout with all "T junctions". |
| Town02 | Similar to Town01, but smaller. |
| Town03 | The most complex town, with a 5-lane junction, a roundabout, unevenness, a tunnel, and much more. Essentially a medley. |
| Town04 | An infinite loop with a highway and a small town. |
| Town05 | Squared-grid town with cross junctions and a bridge. It has multiple lanes per direction. Useful to perform lane changes. |
| Town06 | Long highways with many highway entrances and exits. It also has a Michigan left. |
| Town07 | A rural environment with narrow roads, barely non traffic lights and barns. |
| Town10HD | A city environment with with different environments such as an avenue or a promenade, and more realistic textures. |
更多关于城镇路线俯视图图片可以跳转此处查看
对于地图的格式,其实如果要在其他地方用的话,是可以直接提取地图里的waypoint点的,准确点是根据OpenDRIVE 1.4的标准来看,也就是说其实在Carla世界里是不需要建图、定位,直接导航即可,The traffic signs defined in the OpenDRIVE file are translated into CARLA as landmark objects that can be queried from the API. In order to facilitate their manipulation, there have been several additions to it.
- carla.Landmark objects represent the OpenDRIVE signals. The attributes and methods describe the landmark, and where it is effective.
- carla.LandmarkOrientation states the orientation of the landmark with regards of the road's geometry definition.
- carla.LandmarkType contains some common landmark types, to ease translation to OpenDRIVE types.
- A carla.Waypoint can get landmarks located a certain distance ahead of it. The type of landmark can be specified.
- The carla.Map retrieves sets of landmarks. It can return all the landmarks in the map, or those having an ID, type or group in common.
- The carla.World acts as intermediary between landmarks, and the carla.TrafficSign and carla.TrafficLight that embody them in the simulation.
下面我们可以试着读取一下地图里有的waypoint,world.get_map().generate_waypoints(distance) 如果是老版本可能是world.map().generate_waypoints(distance) 或者是没有这个功能
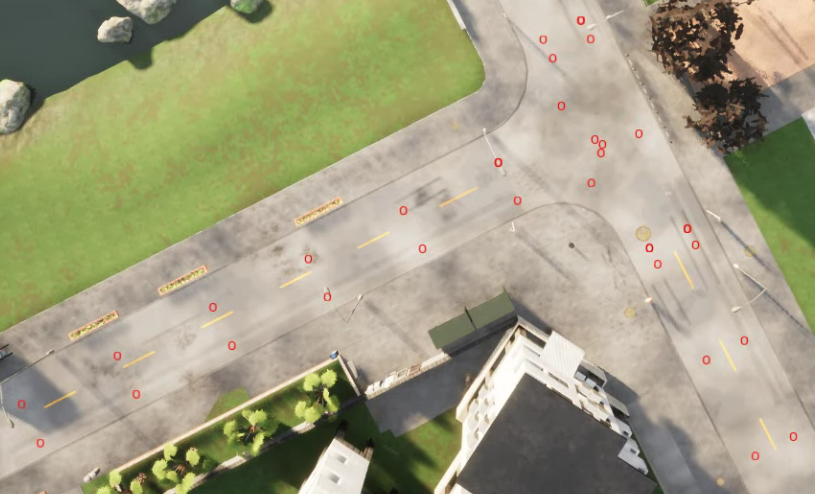

waypoint点显示图 Town01下的
def main():
try:
SpawnActor = carla.command.SpawnActor
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(2.0)
world = client.load_world('Town01')
distance = 10 #waypoint的间距
waypoints = world.get_map().generate_waypoints(distance)
for w in waypoints:
world.debug.draw_string(w.transform.location, 'O', draw_shadow=False,
color=carla.Color(r=255, g=0, b=0), life_time=120.0,
persistent_lines=True)
while True:
world.wait_for_tick()
finally:
print('\ndestroying vehicles')
time.sleep(0.5)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
print('\ndone.')
这样一来如果在Carla里面去实现什么,根本不需要再用大采样的方式了,采样只需在两个waypoint与可达点范围内即。至此我们已经知道怎样获取waypoint了,可以试一试manual_control.py内,获取我们车的位置所处的waypoint甚至是lane_id,判断是否在junction里等一系列
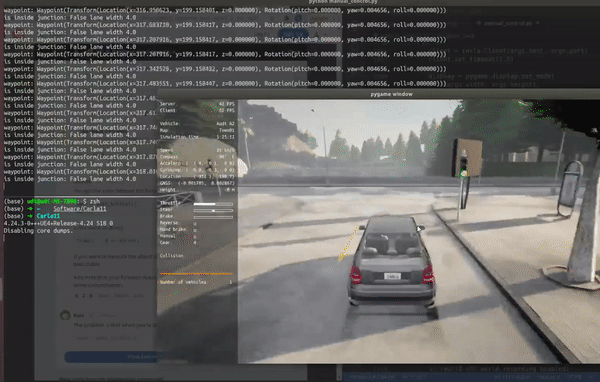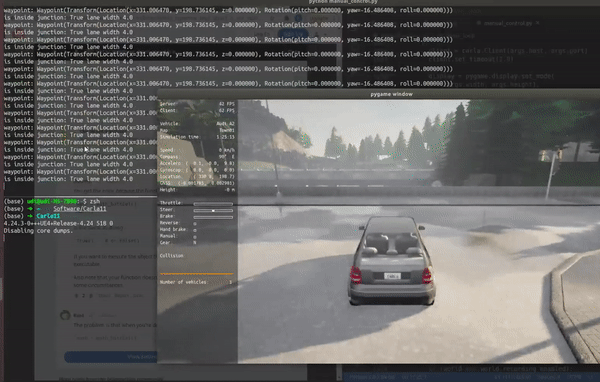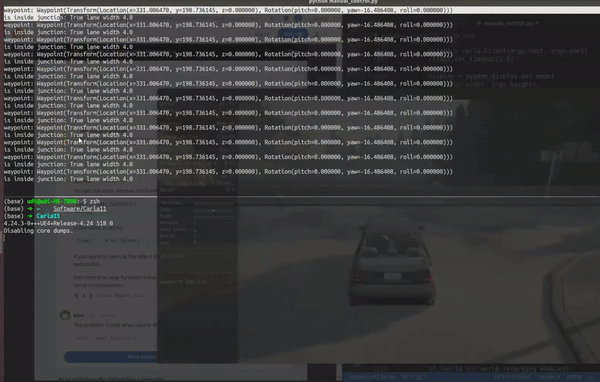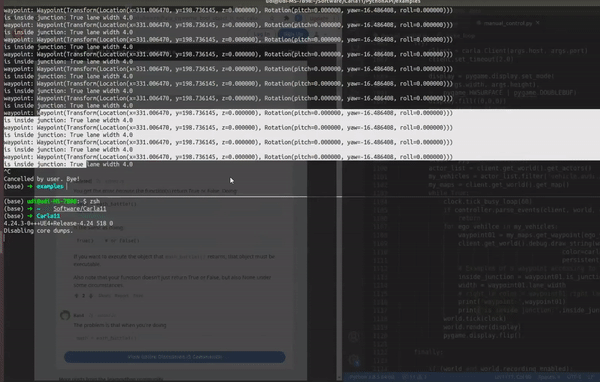
运行演示gif 判断是否到了交叉路口处
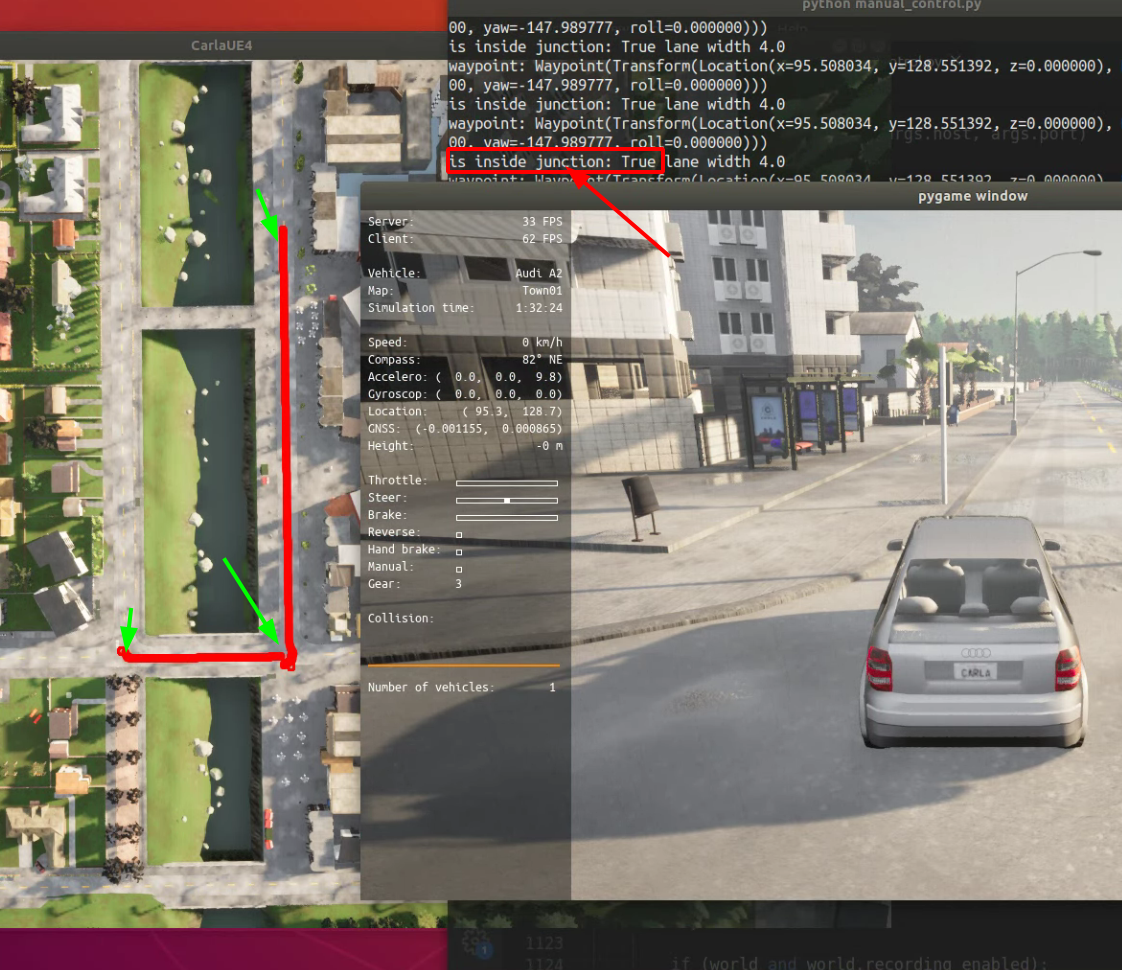
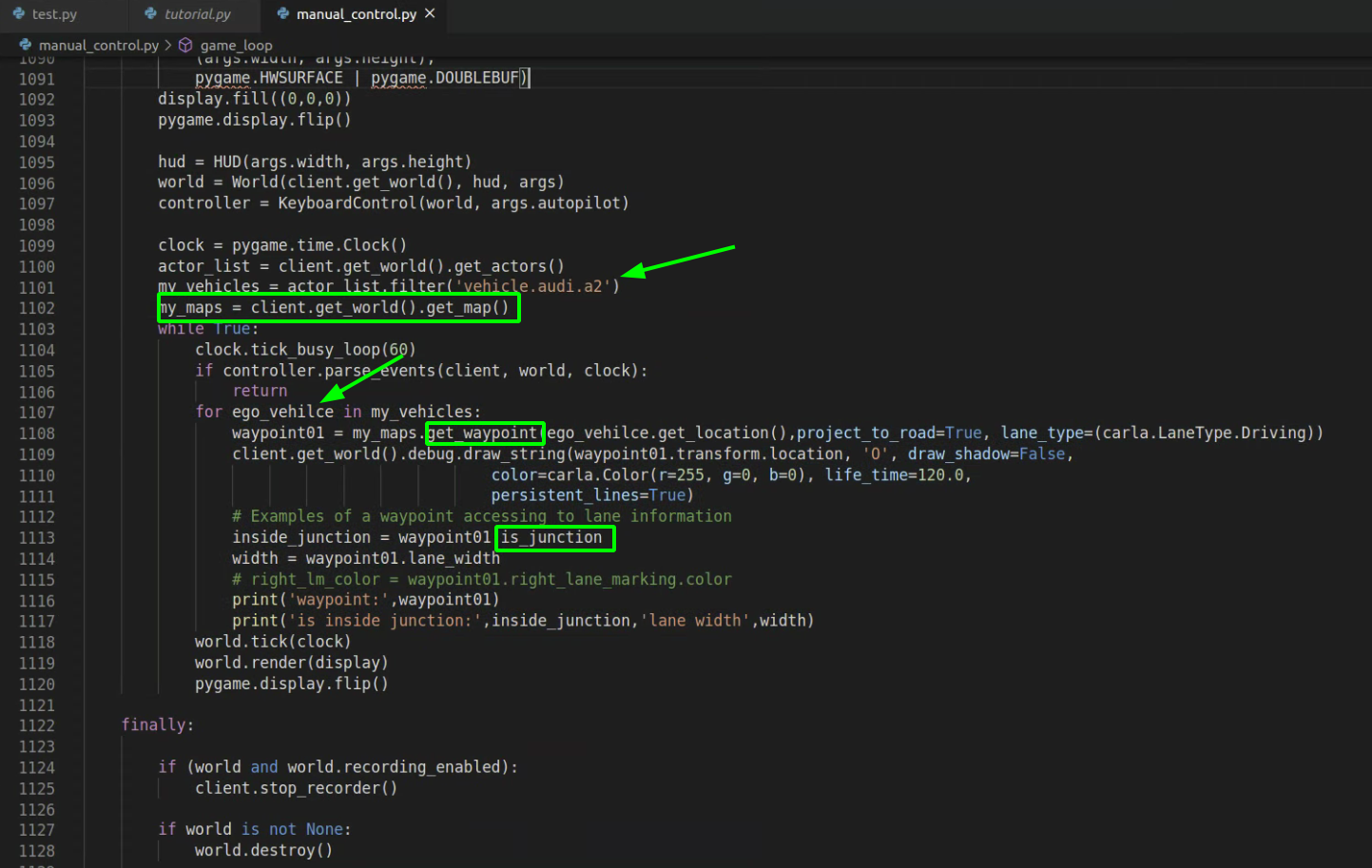
运行判断的示意图
for ego_vehilce in my_vehicles:
waypoint01 = my_maps.get_waypoint(ego_vehilce.get_location(),project_to_road=True, lane_type=(carla.LaneType.Driving))
client.get_world().debug.draw_string(waypoint01.transform.location, 'O', draw_shadow=False,
color=carla.Color(r=255, g=0, b=0), life_time=120.0,
persistent_lines=True)
# Examples of a waypoint accessing to lane information
inside_junction = waypoint01.is_junction
width = waypoint01.lane_width
# right_lm_color = waypoint01.right_lane_marking.color
print('waypoint:',waypoint01)
print('is inside junction:',inside_junction,'lane width',width)
插入的位置与前置条件:
- 需要一开始把自己的车型定下来,或者看好actor_id然后再到另一个py脚本找这个对应的id
- 一定要记得get_map()这样才有前面提到的一些操作
- waypoint其下也有判断,点击此处官方文档进行了解
- is_junction其实在官方的3st这个节下写错了应该是没有()不然会报错bool no callback
4th. Sensors and data
这一节主要是告诉大家怎么将现有的车上安装 传感器,和传感器的数据格式,其实在manual_control.py和tutorial.py里面都有... 看着看着也就会模仿了,比如RGB相机的,怎么看有什么呢?前面提到了blueprint大集合官方文档:https://carla.readthedocs.io/en/latest/bp_library/ 然后CTRL+F 输入sensor就可以看到所有的传感器类型即其输出的信息
# 找到传感器的蓝图
# Find the blueprint of the sensor.
blueprint = world.get_blueprint_library().find('sensor.camera.rgb')
# Modify the attributes of the blueprint to set image resolution and field of view.
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_x', '1920')
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_y', '1080')
blueprint.set_attribute('fov', '110')
# Set the time in seconds between sensor captures
blueprint.set_attribute('sensor_tick', '1.0')
# 设置传感器位置,attach to的vehicle
transform = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=0.8, z=1.7))
sensor = world.spawn_actor(blueprint, transform, attach_to=my_vehicle)
# 接收传感器的数据
# do_something() will be called each time a new image is generated by the camera.
sensor.listen(lambda data: do_something(data))
...
# This collision sensor would print everytime a collision is detected.
def callback(event):
for actor_id in event:
vehicle = world_ref().get_actor(actor_id)
print('Vehicle too close: %s' % vehicle.type_id)
sensor02.listen(callback)
至于这个 留个作业可以是【当然如果考虑同步时间的话 可能有些困难建议 可以再往下读一篇 CARLA时间设置】
自己设置一个收集照片 Lidar 信息的npc玩家 来收集自己的数据集,答案在代码在 这里 link me,完整解释在这里:【仿真】Carla之收集数据脚本 [7] (附完整代码)
4. 总结
- Carla原来比我想的强大太多了,主要是关于地图的定义也很明确,传感器类型,等等等等简直了... 太适合做学习类的了
- 感觉下来学习Carla最重要的就是看官方文档而不是百度,首先明确自己想要干什么,比如设置速度,设置位置,你就要知道actor.get_location()或者是actor.set_location()这些都可以在blueprint那里面看到每一个blueprint下都有什么属性
- 以上,也算是给自己做一个笔记了,后续可能会继续学习怎么建立学习的环境(看到github上其实有很多挺棒的,但是版本都比较老了)
赠人点赞 手有余香 😆;正向回馈 才能更好开放记录 hhh


