高级语言程序设计作业 11/18
- 2024高级语言程序设计:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C
- 高级语言程序设计课程第五次作业:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C/homework/13304
- 学号:102400215
- 姓名:胡加乘
11.13编程练习
1
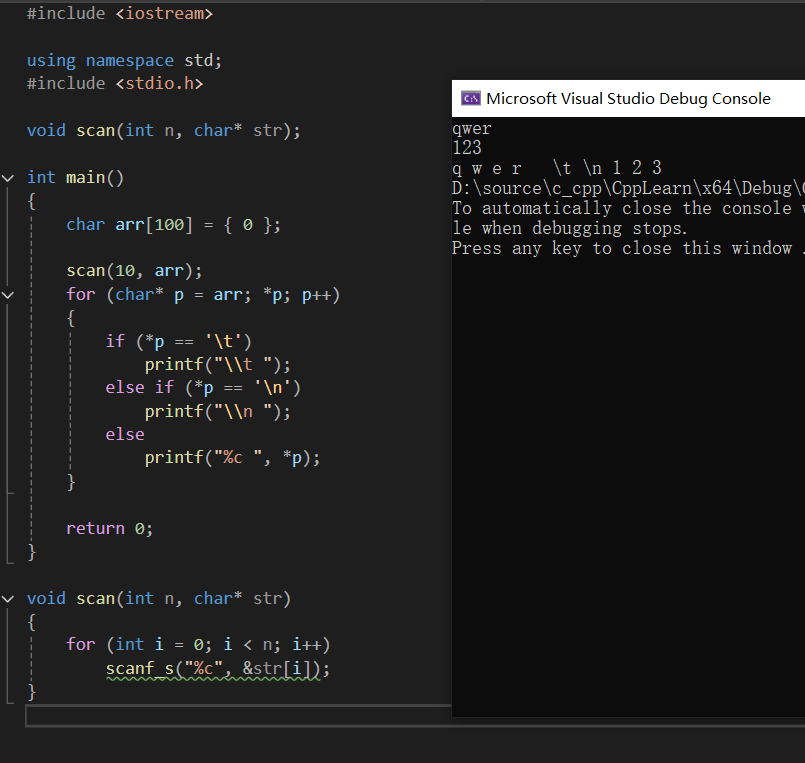
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
void scan(int n, char* str);
int main()
{
char arr[100] = { 0 };
scan(10, arr);
for (char* p = arr; *p; p++)
{
if (*p == '\t')
printf("\\t ");
else if (*p == '\n')
printf("\\n ");
else
printf("%c ", *p);
}
return 0;
}
void scan(int n, char* str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf_s("%c", &str[i]);
}
2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
void scan(int n, char* str);
int main()
{
char arr[100] = { 0 };
scan(10, arr);
for (char* p = arr; *p; p++)
{
if (*p == '\t')
printf("\\t ");
else if (*p == '\n')
printf("\\n ");
else
printf("%c ", *p);
}
return 0;
}
void scan(int n, char* str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char ch;
scanf_s("%c", &ch);
if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n')
break;
str[i] = ch;
}
}

3
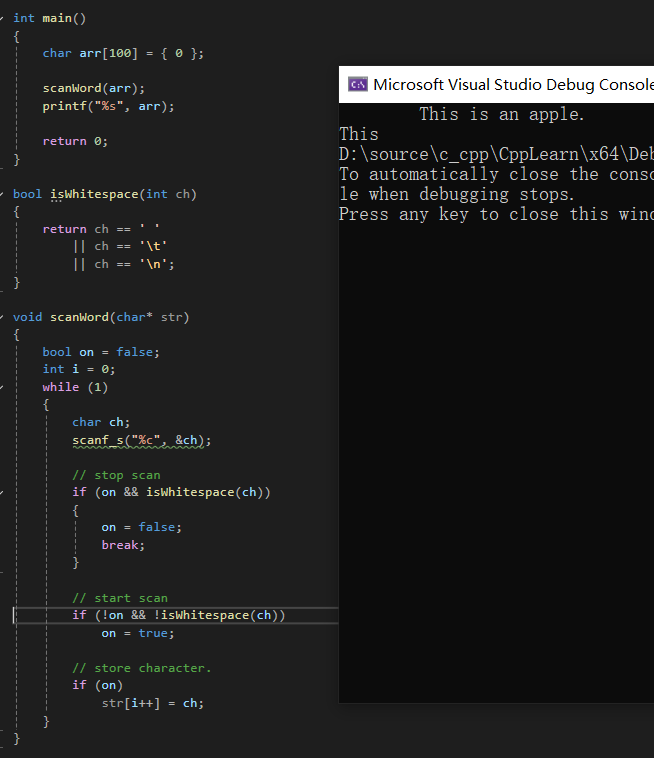
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
void scanWord(char* str);
int main()
{
char arr[100] = { 0 };
scanWord(arr);
printf("%s", arr);
return 0;
}
bool isWhitespace(int ch)
{
return ch == ' '
|| ch == '\t'
|| ch == '\n';
}
void scanWord(char* str)
{
bool on = false;
int i = 0;
while (1)
{
char ch;
scanf_s("%c", &ch);
// stop scan
if (on && isWhitespace(ch))
{
on = false;
break;
}
// start scan
if (!on && !isWhitespace(ch))
on = true;
// store character.
if (on)
str[i++] = ch;
}
}
6
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
int is_within(char ch, char* str);
int main()
{
char arr[100] = "Hello World!";
printf("%d\n", is_within('!', arr));
printf("%d\n", is_within('s', arr));
return 0;
}
int is_within(char ch, char* str)
{
for (char* p = str; *p; p++)
{
if (ch == *p)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}

7
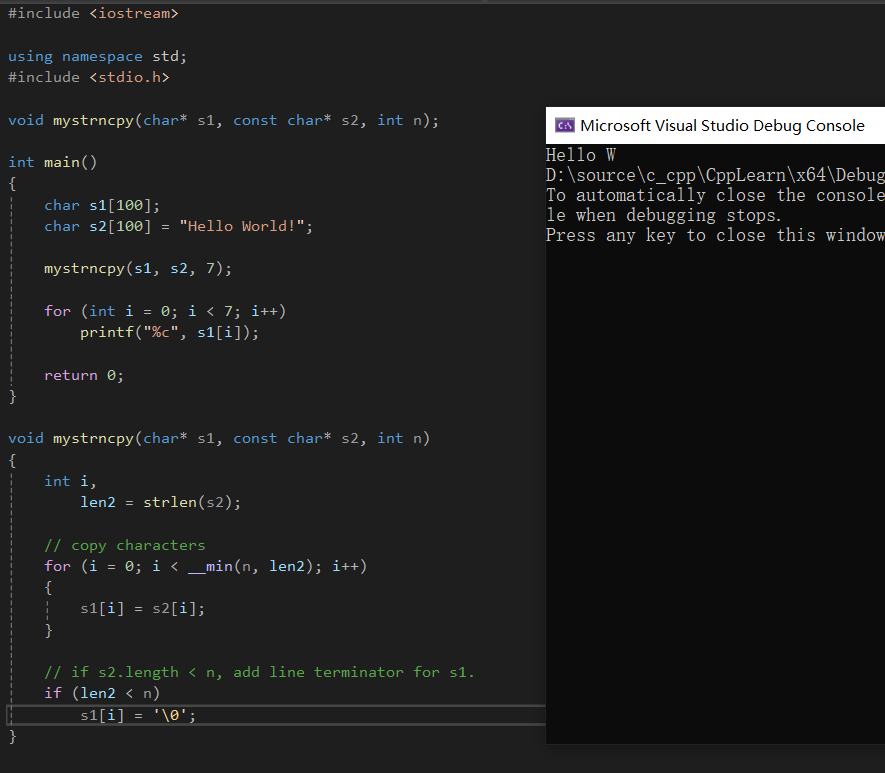
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
void mystrncpy(char* s1, const char* s2, int n);
int main()
{
char s1[100];
char s2[100] = "Hello World!";
mystrncpy(s1, s2, 7);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("%c", s1[i]);
return 0;
}
void mystrncpy(char* s1, const char* s2, int n)
{
int i,
len2 = strlen(s2);
// copy characters
for (i = 0; i < __min(n, len2); i++)
{
s1[i] = s2[i];
}
// if s2.length < n, add line terminator for s1.
if (len2 < n)
s1[i] = '\0';
}
12.9编程练习
1
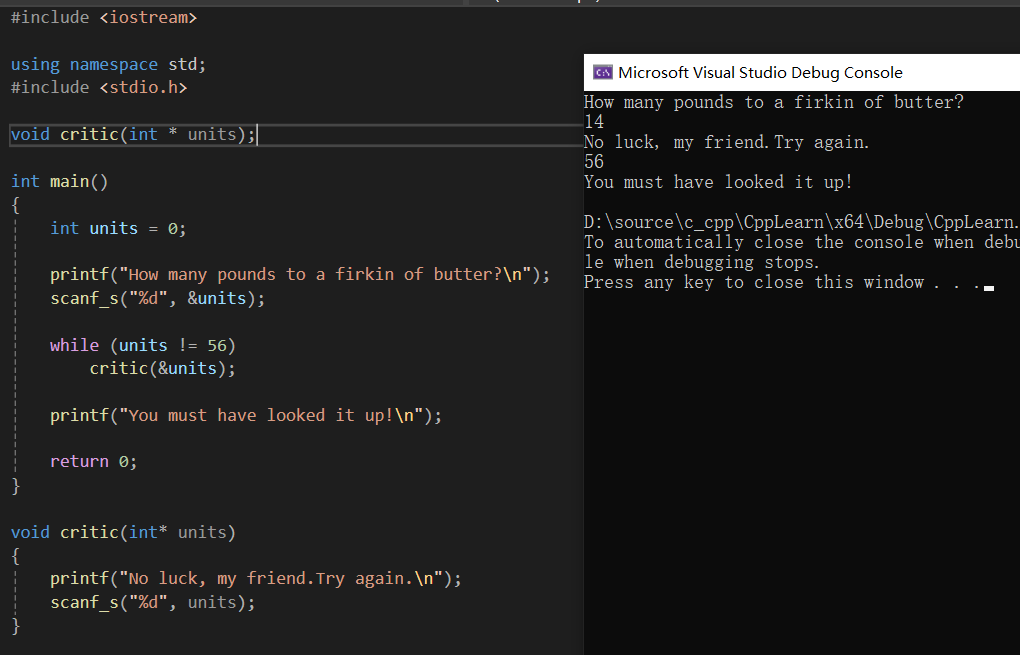
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
void critic(int * units);
int main()
{
int units = 0;
printf("How many pounds to a firkin of butter?\n");
scanf_s("%d", &units);
while (units != 56)
critic(&units);
printf("You must have looked it up!\n");
return 0;
}
void critic(int* units)
{
printf("No luck, my friend.Try again.\n");
scanf_s("%d", units);
}
2
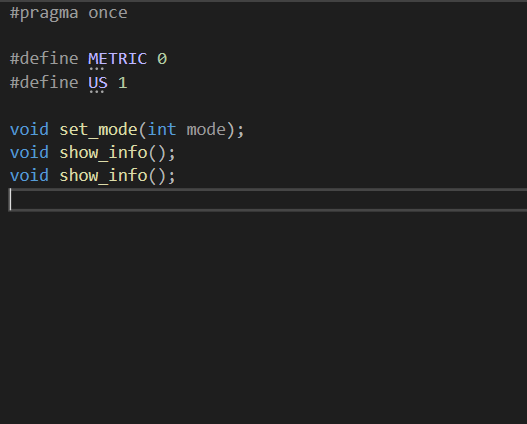
#pragma once
#define METRIC 0
#define US 1
void set_mode(int mode);
void show_info();
void show_info();
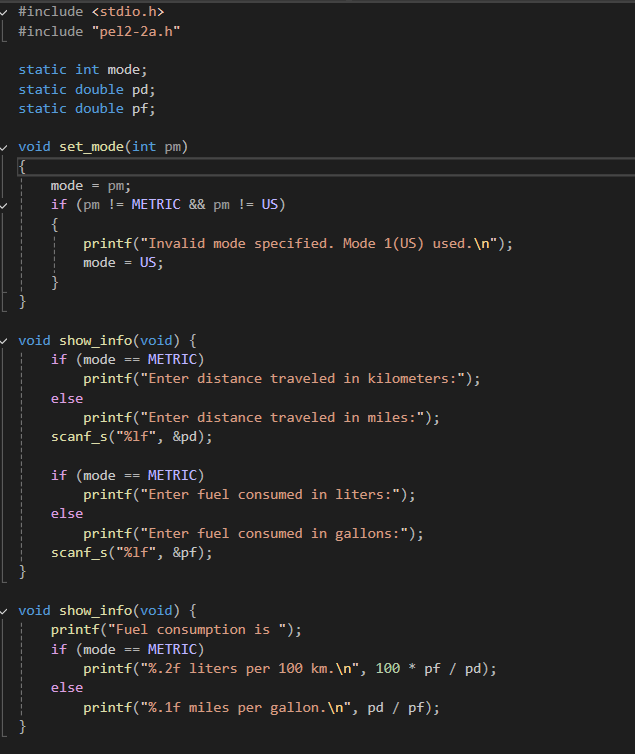
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pel2-2a.h"
static int mode;
static double pd;
static double pf;
void set_mode(int pm)
{
mode = pm;
if (pm != METRIC && pm != US)
{
printf("Invalid mode specified. Mode 1(US) used.\n");
mode = US;
}
}
void show_info(void) {
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometers:");
else
printf("Enter distance traveled in miles:");
scanf_s("%lf", &pd);
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters:");
else
printf("Enter fuel consumed in gallons:");
scanf_s("%lf", &pf);
}
void show_info(void) {
printf("Fuel consumption is ");
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("%.2f liters per 100 km.\n", 100 * pf / pd);
else
printf("%.1f miles per gallon.\n", pd / pf);
}
3
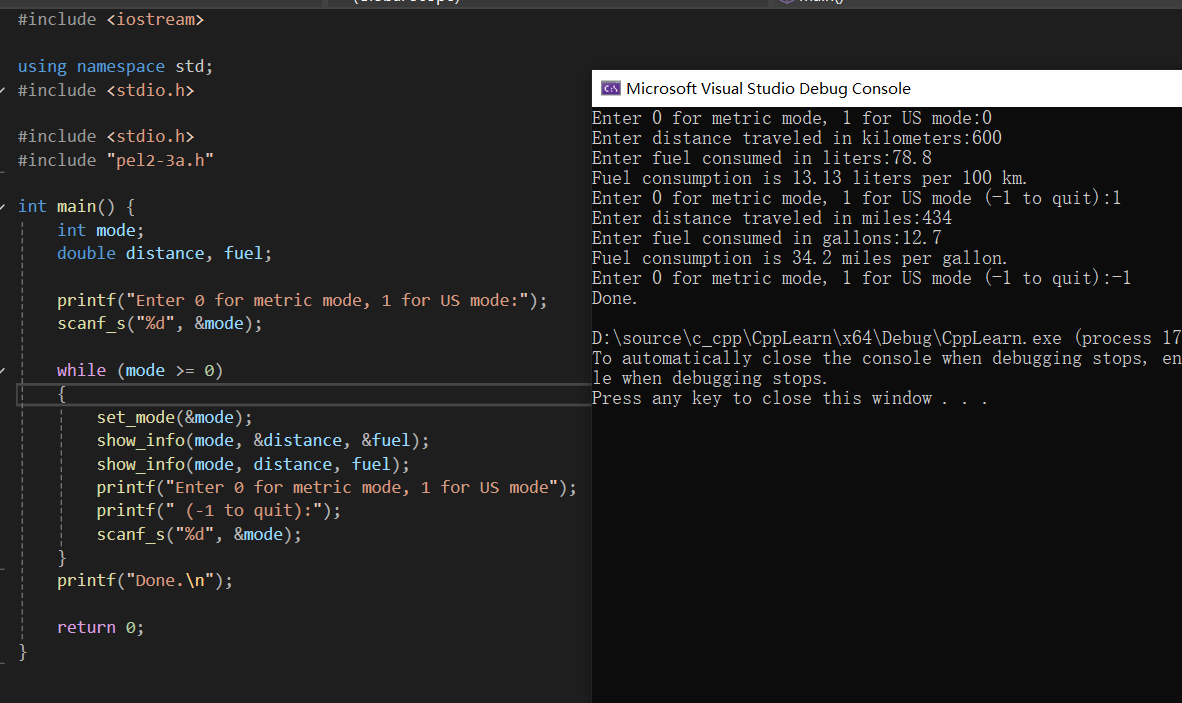
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pel2-3a.h"
int main() {
int mode;
double distance, fuel;
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode:");
scanf_s("%d", &mode);
while (mode >= 0)
{
set_mode(&mode);
show_info(mode, &distance, &fuel);
show_info(mode, distance, fuel);
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode");
printf(" (-1 to quit):");
scanf_s("%d", &mode);
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
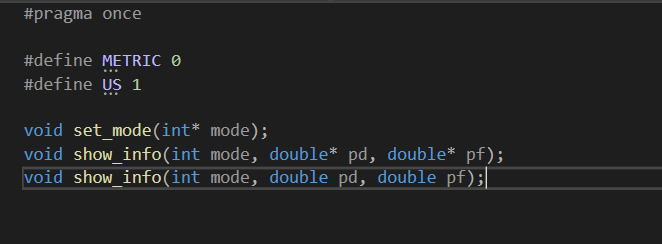
#pragma once
#define METRIC 0
#define US 1
void set_mode(int* mode);
void show_info(int mode, double* pd, double* pf);
void show_info(int mode, double pd, double pf);
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pel2-3a.h"
void set_mode(int* mode)
{
if (*mode != METRIC && *mode != US)
{
printf("Invalid mode specified. Mode 1(US) used.\n");
*mode = US;
}
}
void show_info(int mode, double* pd, double* pf)
{
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometers:");
else
printf("Enter distance traveled in miles:");
scanf_s("%lf", pd);
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters:");
else
printf("Enter fuel consumed in gallons:");
scanf_s("%lf", pf);
}
void show_info(int mode, double pd, double pf)
{
printf("Fuel consumption is ");
if (mode == METRIC)
printf("%.2f liters per 100 km.\n", 100 * pf / pd);
else
printf("%.1f miles per gallon.\n", pd / pf);
}

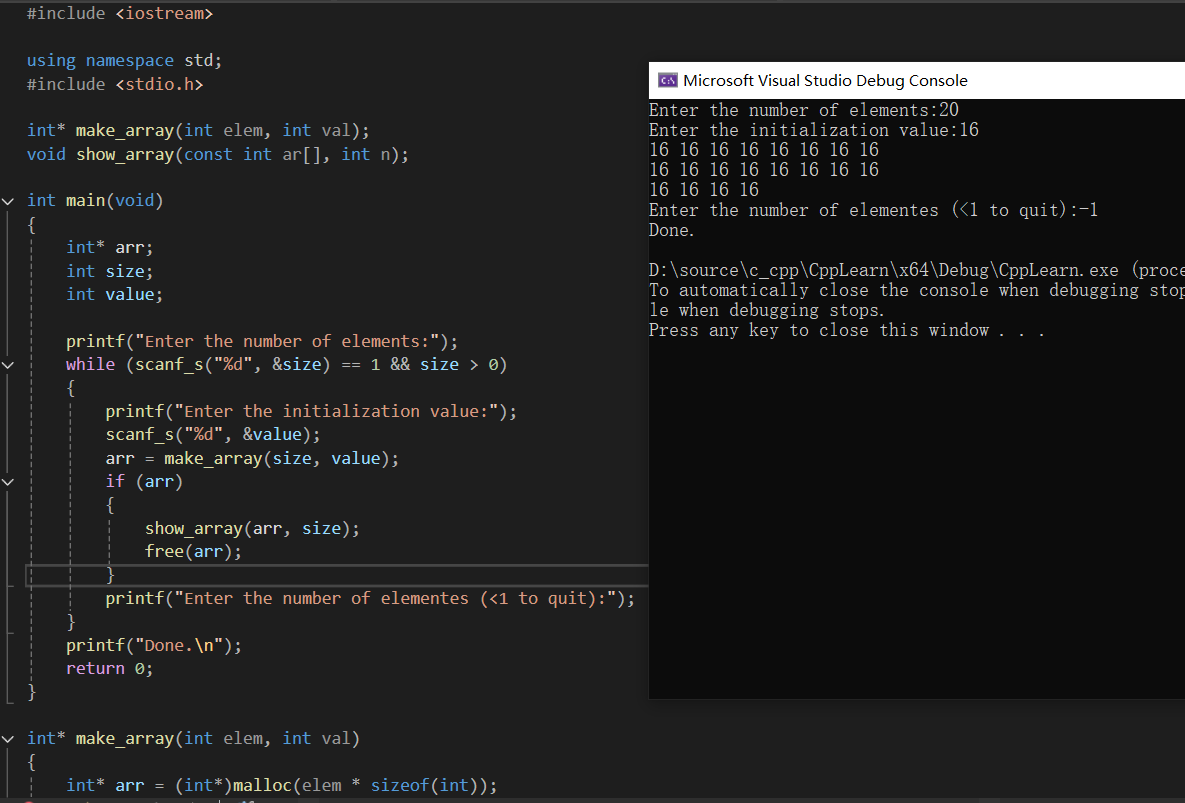
8
#include <stdio.h>
int* make_array(int elem, int val);
void show_array(const int ar[], int n);
int main(void)
{
int* arr;
int size;
int value;
printf("Enter the number of elements:");
while (scanf_s("%d", &size) == 1 && size > 0)
{
printf("Enter the initialization value:");
scanf_s("%d", &value);
arr = make_array(size, value);
if (arr)
{
show_array(arr, size);
free(arr);
}
printf("Enter the number of elementes (<1 to quit):");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
int* make_array(int elem, int val)
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(elem * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < elem; i++)
arr[i] = val;
return arr;
}
void show_array(const int ar[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d%s", ar[i], (i + 1) % 8 == 0 ? "\n" : " ");
}
putchar('\n');
}
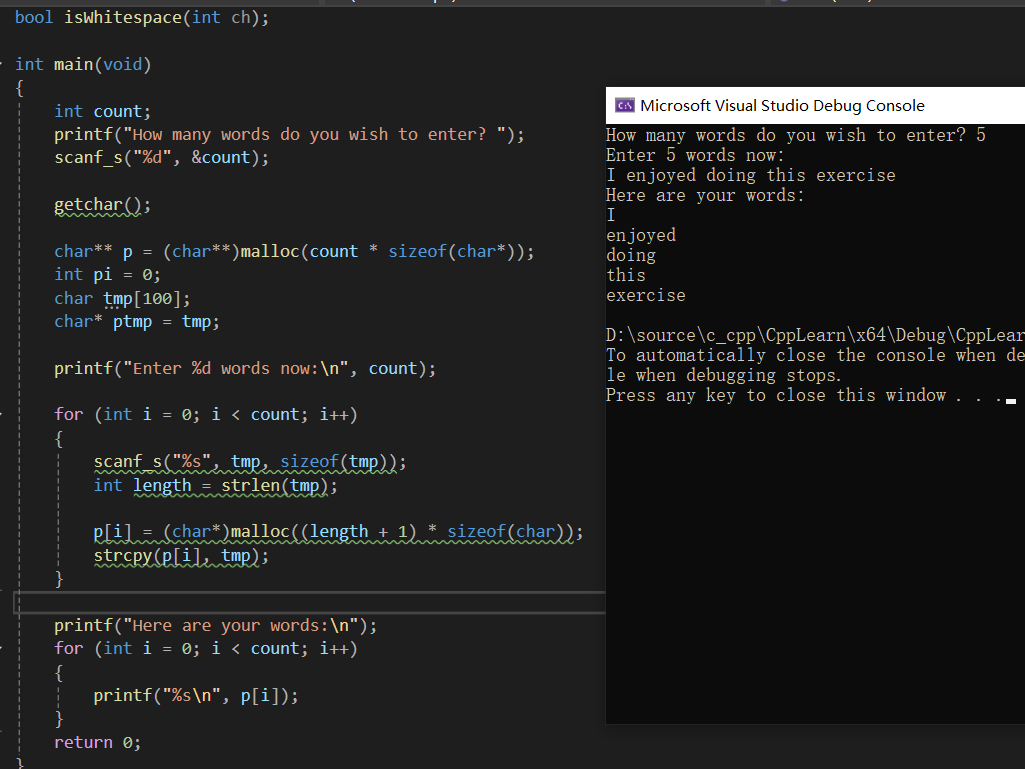
9
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int count;
printf("How many words do you wish to enter? ");
scanf_s("%d", &count);
getchar();
char** p = (char**)malloc(count * sizeof(char*));
int pi = 0;
char tmp[100];
char* ptmp = tmp;
printf("Enter %d words now:\n", count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
scanf_s("%s", tmp, sizeof(tmp));
int length = strlen(tmp);
p[i] = (char*)malloc((length + 1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(p[i], tmp);
}
printf("Here are your words:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("%s\n", p[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
free(p[i]);
free(p);
return 0;
}
总结和收获
- 学习了
extern关键字 - 学习了
malloc()和free()函数


