高级语言程序设计作业 10/28
- 2024高级语言程序设计:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C
- 高级语言程序设计课程第四次作业:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C/homework/13298
- 学号:102400215
- 姓名:胡加乘
8.11编程练习
1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char fname[50];
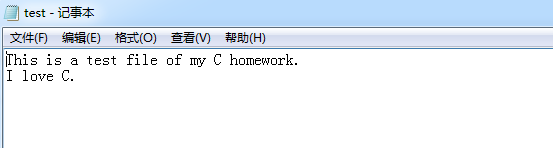
printf("Please enter filepath: ");
scanf("%s", fname);
fp = fopen(fname, "r");
if (!fp)
{
printf("Failed to open the file. Exit.\n");
exit(1);
}
int count = 0;
int ch;
while((ch = getc(fp)) != EOF)
count++;
fclose(fp);
printf("There are %d characters in this file.", count);
return 0;
}
2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
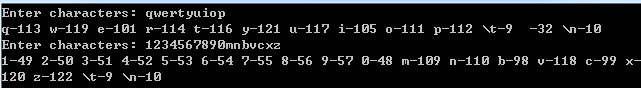
printf("Enter characters: ");
int ch;
int lineCounter = 0;
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
// normal characters.
if (ch >= ' ')
{
printf("%c-%d ", ch, ch);
continue;
}
// cmd characters (< 32)
switch (ch)
{
case '\n':
printf("\\n-10 ");
printf("\nEnter characters: ");
break;
case '\t':
printf("\\t-9 ");
break;
default:
printf("^%c-%d ", ch + 64, ch);
break;
}
// handle linebreak. (every 10 pairs)
lineCounter++;
if (lineCounter >= 10)
{
printf("\n");
lineCounter = 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
int upper = 0,
lower = 0;
printf("Enter text (Press Ctrl+Z to terminate): ");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if (isupper(ch))
upper++;
else if (islower(ch))
lower++;
}
printf("During this input,\nthere are %d upper characters\nand %d lower characters.", upper, lower);
return 0;
}

4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
int words = 0,
chars = 0;
bool wordon = false; // whether in the scope of a word.
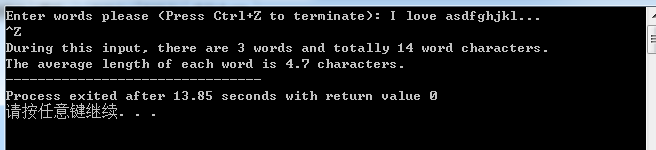
printf("Enter words please (Press Ctrl+Z to terminate): ");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if (isalpha(ch))
{
wordon = true;
chars++;
}
else // 只要输入不是字母的字符,就算一个单词结束了。
{
if (wordon)
{
wordon = false;
words++;
}
}
}
printf("During this input, there are %d words and totally %d word characters.\n"
"The average length of each word is %.1f characters.", words, chars, (double)chars / words);
return 0;
}
5
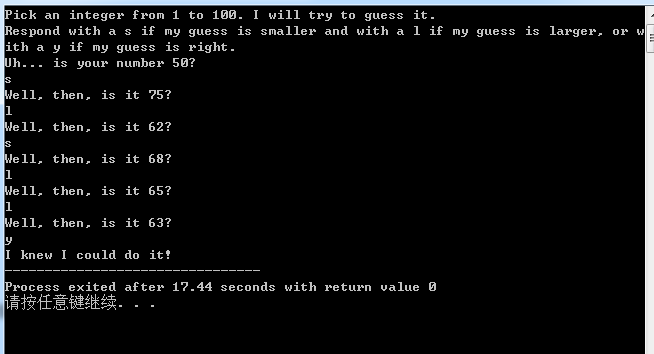
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main()
{
int guess = 50;
int start = 0,
end = 100;
printf("Pick an integer from 1 to 100. I will try to guess it.\n"
"Respond with a s if my guess is smaller and with a l if my guess is larger, or with a y if my guess is right.\n");
printf("Uh... is your number %d?\n", guess);
while (1)
{
switch (getchar())
{
case 'y':
goto guess_right;
case 's':
start = guess;
guess = (start + end) / 2;
break;
case 'l':
end = guess;
guess = (start + end) / 2;
break;
}
printf("Well, then, is it %d?\n", guess);
getchar(); // skip '\n' from buffer.
}
guess_right:
printf("I knew I could do it!");
return 0;
}
8
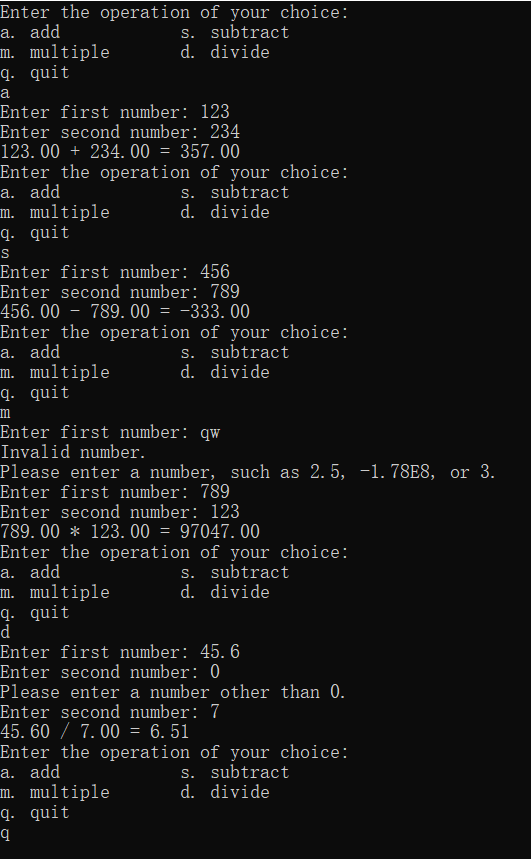
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdbool.h>
using namespace std;
float EnterNumber(const char* prompt, bool allowZero = true);
int main()
{
while (1)
{
printf("Enter the operation of your choice:\n"
"a. add s. subtract\n"
"m. multiple d. divide\n"
"q. quit\n");
char op;
do
{
op = getchar();
} while (op == '\n'); // 由于重复运行,上一轮末尾的回车会影响此轮的指令读取,因此需要吞掉\n。
if (op != 'a' && op != 's' && op != 'm' && op != 'd' && op != 'q')
{
printf("Invalid operation.\n");
continue;
}
if (op == 'q')
break;
float num1 = EnterNumber("Enter first number: ");
float num2 = EnterNumber("Enter second number: ", op != 'd');
switch (op)
{
case 'a':
printf("%.2f + %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 + num2);
break;
case 's':
printf("%.2f - %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 - num2);
break;
case 'm':
printf("%.2f * %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 * num2);
break;
case 'd':
printf("%.2f / %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, num1 / num2);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
float EnterNumber(const char* prompt, bool allowZero)
{
float num;
while (1)
{
printf("%s", prompt);
if (scanf_s("%f", &num))
{
// check zero.
if (!allowZero && fabs(num) < 1e-5)
{
printf("Please enter a number other than 0.\n");
continue;
}
return num;
}
while (getchar() != '\n'); // clear invalid characters in the buffer, until \n.
printf("Invalid number.\n");
printf("Please enter a number, such as 2.5, -1.78E8, or 3.\n");
}
}
9.11编程练习
1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double min(double x, double y)
{
return x < y ? x : y;
}
int main()
{
double num1 = 3.4,
num2 = 5.6;
printf("min(%.2f, %.2f): %.2f",
num1, num2, min(num1, num2));
return 0;
}

2、3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
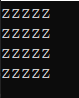
void chline(char ch, int i, int j);
int main()
{
chline('z', 5, 4);
return 0;
}
/* 打印指定字符j行i列。*/
void chline(char ch, int i, int j)
{
for (int row = 0; row < j; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < i; col++)
printf("%c", ch);
printf("\n");
}
}
4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double havg(double num1, double num2);
int main()
{
double num1 = 1.2,
num2 = 3.4;
printf("havg(%.2f, %.2f): %.2f",
num1, num2, havg(num1, num2));
return 0;
}
/* 返回两数的调和平均数(harmonic average)。*/
double havg(double num1, double num2)
{
num1 = 1 / num1;
num2 = 1 / num2;
double avg = (num1 + num2) / 2;
return 1 / avg;
}
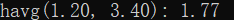
5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void larger_of(double* num1, double* num2);
int main()
{
double num1 = 14.5;
double num2 = 3.4;
printf("num1 = %.2f, num2 = %.2f\n",
num1, num2);
larger_of(&num1, &num2);
printf("After larger_of(), num1 = %.2f, num2 = %.2f\n",
num1, num2);
return 0;
}
void larger_of(double* p1, double* p2)
{
double val = *p1 > *p2
? *p1
: *p2;
*p1 = val;
*p2 = val;
}
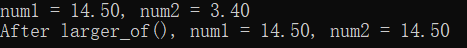
6
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void arrange(double* num1, double* num2, double* num3);
int main()
{
double num1 = 14.5;
double num2 = 3.4;
double num3 = 1.2;
printf("num1 = %.2f, num2 = %.2f, num3 = %.2f\n",
num1, num2, num3);
arrange(&num1, &num2, &num3);
printf("After arrange(), num1 = %.2f, num2 = %.2f, num3 = %.2f\n",
num1, num2, num3);
return 0;
}
void arrange(double* num1, double* num2, double* num3)
{
double min = __min(*num1, __min(*num2, *num3));
double max = __max(*num1, __max(*num2, *num3));
double mid = *num1 + *num2 + *num3 - min - max;
*num1 = min;
*num2 = mid;
*num3 = max;
}
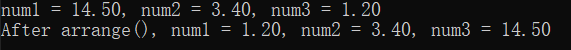
7
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int chpos(char ch);
int main()
{
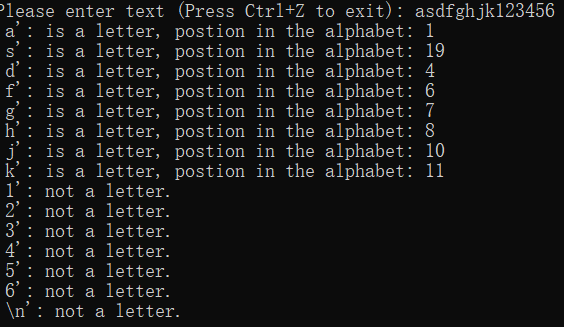
printf("Please enter text (Press Ctrl+Z to exit): ");
int ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if (ch != '\n')
printf("'%c': ", ch);
else
printf("'\\n': ");
int pos = chpos(ch);
if (pos == -1)
printf("not a letter.\n");
else
printf("is a letter, postion in the alphabet: %d\n", pos);
}
return 0;
}
int chpos(char ch)
{
if (isalpha(ch))
{
if (isupper(ch))
return ch - 65 + 1;
if (islower(ch))
return ch - 97 + 1;
}
return -1;
}
8
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double power(double n, int p, const char* reporter = NULL);
int main()
{
double n;
int exp;
while (1)
{
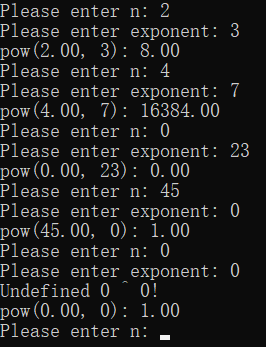
printf("Please enter n: ");
scanf_s("%lf", &n);
printf("Please enter exponent: ");
scanf_s("%d", &exp);
printf("pow(%.2f, %d): %.2f\n",
n, exp, power(n, exp, "Undefined 0 ^ 0!"));
}
return 0;
}
bool isZero(double d)
{
return fabs(d) < 1e-5;
}
double power(double n, int p, const char* reporter)
{
double ret = 1;
if (isZero(n) && p != 0) // 0 ^ n = 0 (n != 0)
return 0;
if (!isZero(n) && p == 0) // a ^ 0 = 1 (a != 0)
return 1;
if (isZero(n) && p == 0) // 0 ^ 0 = 1 (report undefined)
{
if (reporter)
printf("%s\n", reporter);
return 1;
}
if (p > 0) // pos
{
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++)
ret *= n;
}
else // neg
{
for (int i = 0; i < -p; i++)
ret *= n;
ret = 1 / ret;
}
return ret;
}
9
double power(double n, int p, const char* reporter)
{
double ret = 1;
if (isZero(n) && p != 0) // 0 ^ n = 0 (n != 0)
return 0;
if (!isZero(n) && p == 0) // a ^ 0 = 1 (a != 0)
return 1;
if (isZero(n) && p == 0) // 0 ^ 0 = 1 (report undefined)
{
if (reporter)
printf("%s\n", reporter);
return 1;
}
if (p > 0) // pos
{
double tmp = power(n, p / 2);
ret = (p % 2) == 0
? tmp * tmp
: tmp * tmp * n;
}
else // neg
{
ret = power(n, -p, reporter);
ret = 1 / ret;
}
return ret;
}
10
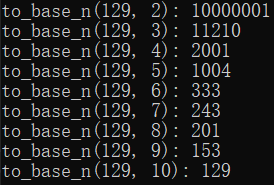
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
using namespace std;
void to_base_n(unsigned long n, int base);
int main()
{
unsigned long n = 129;
int base = 1;
while (base < 10)
{
printf("to_base_n(%lu, %d): ", n, ++base);
to_base_n(n, base);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
void to_base_n(unsigned long n, int base)
{
int r;
r = n % base;
if (n >= base)
to_base_n(n / base, base);
char c = r + '0'; // ascii码加法
putchar(c);
}
11
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
unsigned Fibonacci(unsigned i);
int main()
{
printf("前15个斐波那契数:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 35; i++)
printf("%lu ", Fibonacci(i));
return 0;
}
unsigned Fibonacci(unsigned i)
{
if (i >= 2)
return Fibonacci(i - 2) + Fibonacci(i - 1);
if (i == 0 || i == 1)
return 1;
}

总结
- 读取字符时需要注意缓冲区内是否有多余的字符,特别是
\n。 - 递归法求power。
- 个位数int转成同形式的char,如
7转成'7'的方法:int n = 7; char c = n + '0'; // 加上零的ascii码



