3个例子详解C++ 11 中push_back 和 emplace_back差异
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/b83bc460/,欢迎阅读最新内容!
cpp11 push_back and emplace_back
Guide
case1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class A
{
public:
A (int x_arg) : x (x_arg) { std::cout << "A (x_arg)\n"; }
A () { x = 0; std::cout << "A ()\n"; }
A (const A &rhs) noexcept { x = rhs.x; std::cout << "A (A &)\n"; }
A (A &&rhs) noexcept { x = rhs.x; std::cout << "A (A &&)\n"; }
~A() { std::cout << "~A ()\n"; }
private:
int x;
};
void test_emplace_back_1()
{
// For emplace_back constructor A (int x_arg) will be called.
// And for push_back A (int x_arg) is called first and
// move A (A &&rhs) is called afterwards
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call emplace_back:\n";
a.emplace_back(0);
// (1) direct object creation inside vector
}
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call push_back:\n";
a.push_back(1);
// (1) create temp object and
// (2) then move copy to vector and
// (3) free temp object
}
}
/*
call emplace_back:
A (x_arg)
~A ()
call push_back:
A (x_arg)
A (A &&)
~A ()
~A ()
*/
see 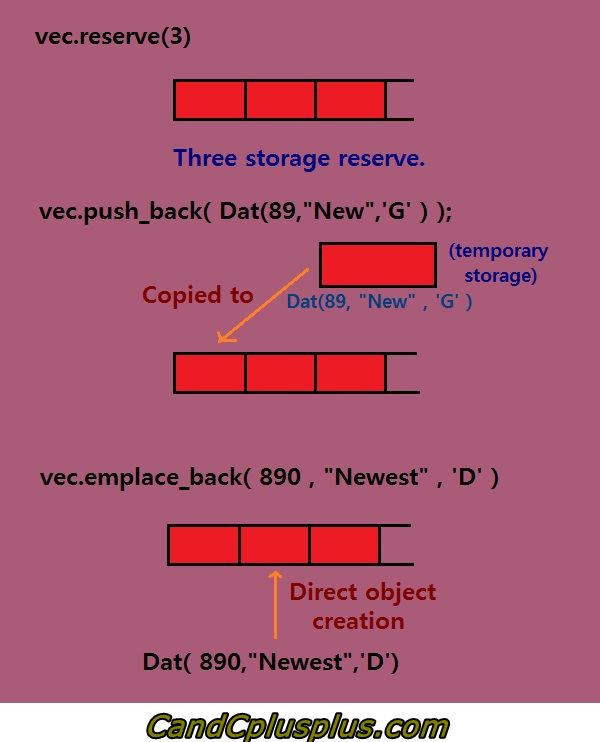
image from c-difference-between-emplace_back-and-push_back-function
case2
void test_emplace_back_2()
{
// emplace_back and push_back for `A(0)`, it's same.
// A (int x_arg) is called first and
// move A (A &&rhs) is called afterwards
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call emplace_back:\n";
a.emplace_back(A(0));
// (1) create temp object and
// (2) then move copy to vector and
// (3) free temp object
}
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call push_back:\n";
a.push_back(A(1));
// (1) create temp object and
// (2) then move copy to vector and
// (3) free temp object
}
}
/*
call emplace_back:
A (x_arg)
A (A &&)
~A ()
~A ()
call push_back:
A (x_arg)
A (A &&)
~A ()
~A ()
*/
case 3
void test_emplace_back_3()
{
// emplace_back and push_back for `A obj(0)`, it's same.
// A (int x_arg) is called first and
// copy constructor A (A &) is called afterwards
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call emplace_back:\n";
A obj(0);
a.emplace_back(obj);
// copy constructor to vector
}
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call push_back:\n";
A obj(1);
a.push_back(obj);
// copy constructor to vector
}
}
/*
call emplace_back:
A (x_arg)
A (A &)
~A ()
~A ()
call push_back:
A (x_arg)
A (A &)
~A ()
~A ()
*/
Reference
- push-back-vs-emplace-back
- c-difference-between-emplace_back-and-push_back-function
- push_back and emplace_back
History
- 20190422: created.
Copyright
- Post author: kezunlin
- Post link: https://kezunlin.me/post/b83bc460/
- Copyright Notice: All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 unless stating additionally.



