Suspense组件
何时使用Suspense
在vue2.0时代我们必须使用条件(v-if或v-else)来检查我们的数据是否已加载并显示后备内容。
在vue3.0中内置了Suspense,因此我们不必担心何时加载数据并呈现相应的内容
Suspense是什么
Suspense组件作用是当你在进行一个异步加载时,先提供一些静态组件作为显示内容,然后当异步加载完毕时再显示
Suspense组件会暂停你的组件渲染,重现一个回落组件,直到满足条件为止。
Suspense的使用
Suspense组件是vue3推出的一个内置特殊组件,只是一个内置标签,不需要引入直接使用就可以,必须需要返回一个Promise,而不是json对象
Suspense组件是一个具有插槽的组件,是根据插槽机制来区分组件的,#default插槽内容是你需要渲染的异步组件(需要返回一个promise);#fallback是你指定的加载中的静态组件
defineComponent:defineComponent是用来解决在Typescript环境中,传统的Vue.extend无法对组件给出正确的类型判断,也就是说在Typescript环境中如果参数类型不正确时,用defineComponent()组件来进行包装函数
<template>
<div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {defineComponent} from "vue"
export default defineComponent ({
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<div>
<Suspense>
<template #default> <!--#default插槽内容是你需要渲染的异步组件(需要返回一个promise)-->
<async></async>
</template>
<template #fallback><!--#fallback是你指定的加载中的静态组件-->
loading...
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import async from "./components/async.vue"
export default {
components:{
async
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
async.vue
<template>
<div>
{{result}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {defineComponent} from "vue"
export default defineComponent ({
setup(){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve({result:'hello'})
},2000)
})
}
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
此时我们打开浏览器发现在前2秒,定时器还没有工作时加载的是指定的加载中的静态组件loading...,2秒钟过会才会加载出hello
Suspense组件使用步骤:
1>新建一个异步组件,需要返回一个promise
2>将异步组件包装在<template #default>标签中
3>在异步组件旁边添加一个兄弟组件标签为<template #fallback>
4>将两个组件包装在<Suspense>组件中
Suspense加载多个组件
我们新建一个async.vue组件
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in result" :key="index">{{item.title}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {defineComponent} from "vue"
import axios from "axios"
export default defineComponent ({
async setup(){
let data=await axios.get("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts?userId=2") //一个开源的接口地址
console.log(data)
return {result:data.data}
}
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<div>
<Suspense>
<template #default> <!--#default插槽内容是你需要渲染的异步组件(需要返回一个promise)-->
<async></async>
<async2></async2>
</template>
<template #fallback><!--#fallback是你指定的加载中的静态组件-->
loading...
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import async from "./components/async.vue"
import async2 from "./components/async2.vue"
export default {
components:{
async,
async2
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
此时页面会弹出一个警告

警告: Suspense是一个实验性的特性,它的API可能会改变slots,除非只有一个根节点
怎么解决:异步组件外增加一个div包裹(增加一个根节点)
<template>
<div>
<Suspense>
<template #default> <!--#default插槽内容是你需要渲染的异步组件(需要返回一个promise)-->
<div>
<async></async>
<async2></async2>
</div>
</template>
<template #fallback><!--#fallback是你指定的加载中的静态组件-->
loading...
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
此时就不会报错

如果我们一步请求失败会怎么办呢?
Suspense可以捕获组件错误
使用新的onErrorCaptured生命周期钩子来捕获此类错误并显示正确的错误信息
在vue.中,使用onErrorCaptured钩子函数,无论调用什么,此钩子函数会在捕获的组件的错误时运行,如果出现问题,我们可以将其余的suspense一起使用以渲染错误
app.vue
<template> <div> <div v-if="errMsg">{{errMsg}}</div> <Suspense v-else> <template #default> <!--#default插槽内容是你需要渲染的异步组件(需要返回一个promise)--> <div> <async></async> <async2></async2> </div> </template> <template #fallback><!--#fallback是你指定的加载中的静态组件--> loading... </template> </Suspense> </div> </template> <script> import async from "./components/async.vue" import async2 from "./components/async2.vue" import {onErrorCaptured,ref} from "vue" export default { components:{ async, async2 }, setup(){ let errMsg=ref(null); onErrorCaptured(e=>{ errMsg.value="出错了" return true //必须return true上传上去才能使用 }) return{errMsg} } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
此时我们把async2.vue中的地址写错,我们打开浏览器可以看到显示了错误信息,提示我们接口是错误的
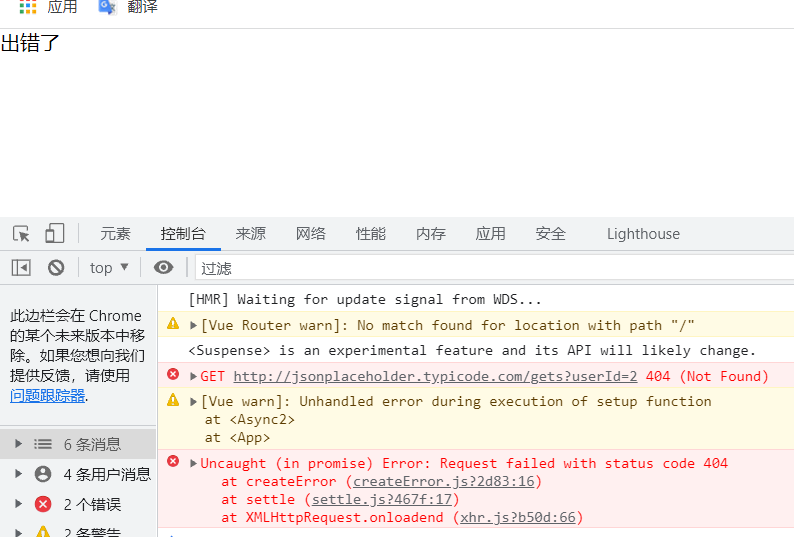
上面的示例中,我们显示的后备预显示的内容,直接解决了异步操作,如果出了什么问题被拒绝,使用onErrorCaptured钩子捕获错误,将其传递给errMsg属性并在模板中显示,而不是回退内容


