05 文本处理工具-分析文本的工具wc、sort、uniq)20210202 (四)

useradd -u 306 -g -mysql -d /data/mysql -s sbin/nologin/ -r mysql
chmod 600 file
chown -R .mysql dir
chgrp mysql dir
r 4
w 2
x1
umask
file=666-umask=奇数+1,偶数不变
dir=777-umask
setfacl -Rm u:apach:rwx /data(#R递归)
setfacl -Rb /data (#R递归)
vim
[15:49:58 root@centos8 ~]#cat /etc/issue \S Kernel \r on an \m
$表示换行
[15:55:06 root@centos8 ~]#cat 11.txt 11111 aaaaa AAAA[15:55:14 root@centos8 ~]#cat 11.txt -E $1111 $aaaa AAAA[15:55:26 root@centos8 ~]#
大A可以看看里面有什么内容
[16:03:27 root@centos8 ~]#cat -A 11.txt 1^I2^I3^I4^I5^I^M$ ^M$ aaaaa^M$ A^IA^IA^IA^M$
1.收集文本统计数据 wc
-l 只计数行数 -w 只计数单词总数 -c 只计数字节总数 -m 只计数字符总数 -L 显示文件中长行的长度
范例1:
1 [root@centos8 ~]# cat title.txt(#汉字的字节数比英文的多) 2 ceo mage coo zhang cto 老王 3 [root@centos8 ~]# cat title1.txt 4 ceo mage coo zhang cto wang 5 [root@centos8 ~]# wc title.txt 6 1 6 31 title.txt 7 [root@centos8 ~]# wc title1.txt 8 1 6 28 title1.txt 9 [root@centos8 ~]#
-l 只计数行数
[root@centos8 ~]# ll title.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 31 Feb 2 13:46 title.txt [root@centos8 ~]# ll title1.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 28 Feb 2 13:46 title1.txt [root@centos8 ~]# wc -l title.txt 3 title.txt [root@centos8 ~]# wc -l title1.txt 3 title1.txt [root@centos8 ~]# cat title1.txt |wc -l(#通过管道只统计行数,不显示文本名) 3
#通过管道只统计行数,不显示文本名
-L 显示文件中长行的长度
1 [root@centos8 ~]# cat title1.txt 2 ceo mage 3 coo zhang (#红色字体那个是最长的,空格也要占字节数)
4 cto wang 5 [root@centos8 ~]# wc -L title1.txt 6 9 title1.txt
范例2:显示文件中长行的长度
[root@centos8 ~]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 887248 0 887248 0% /dev tmpfs 916500 0 916500 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 916500 9536 906964 2% /run tmpfs 916500 0 916500 0% /sys/fs/cgroup (#最长的一行) /dev/sda2 104806400 5428896 99377504 6% / /dev/sda3 52403200 398400 52004800 1% /data /dev/sda1 1038336 240836 797500 24% /boot tmpfs 183300 1180 182120 1% /run/user/42 tmpfs 183300 0 183300 0% /run/user/0 [root@centos8 ~]# df |wc -L 62
范例3:统计行数
[02:34:54 root@CentOS8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|wc -l 8 [02:35:38 root@CentOS8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|wc -c 17 [02:35:44 root@CentOS8 ~]#
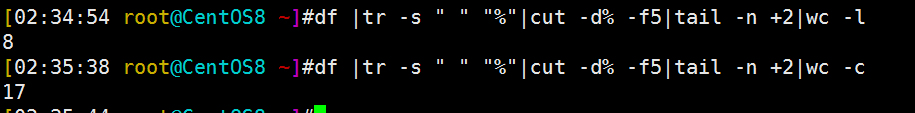
统计行数8行,字节数17个
2.文本排序 sort
-c: 显示每行重复出现的次数 -d: 仅显示重复过的行 -u: 仅显示不曾重复的行
-c: 显示每行重复出现的次数 -d: 仅显示重复过的行 -u: 仅显示不曾重复的行
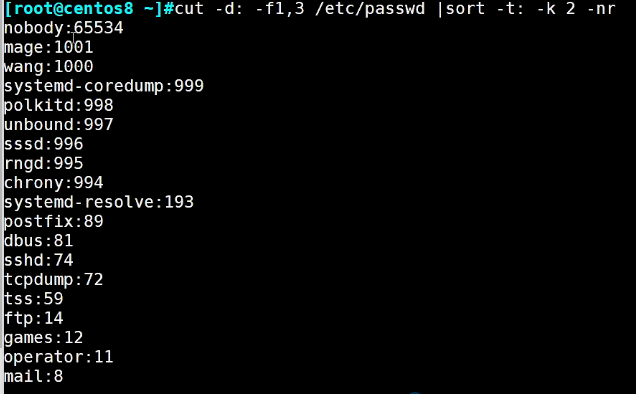
[root@rocky8 ~]#cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd
[roott@rocky8 ~]#cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd|sort -t: -k2 -nr
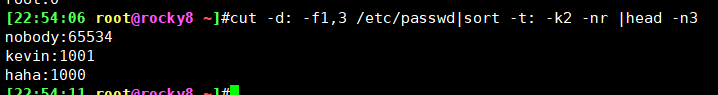
[root@rocky8 ~]#cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd|sort -t: -k2 -nr |head -n3
取值成功
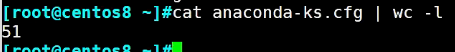
范例1:
1 [root@centos8 ~]# ll 2 total 16 3 -rw-------. 1 root root 1489 Jan 11 16:41 anaconda-ks.cfg 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1778 Jan 11 17:12 initial-setup-ks.cfg 5 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 28 Feb 2 13:46 title1.txt 6 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 31 Feb 2 13:46 title.txt 7 [root@centos8 ~]# df| tr -s ' ' '%'|cut -d% -f5|sort -nr|head -1 8 24 9 [root@centos8 ~]# df | tr -s " " %|cut -d% -f5|tr -d '[:alpha:]' | sort(#去掉USE字母的排序) 10 11 0 12 0 13 0 14 0 15 1 16 1 17 2 18 24 19 6 20 [root@centos8 ~]# df | tr -s " " %|cut -d% -f5| sort(#未去掉字母的排序) 21 0 22 0 23 0 24 0 25 1 26 1 27 2 28 24 29 6 30 Use
范例2:生成十个数随机排序
[root@centos8 ~]# seq 10|sort -R 7 8 6 1 10 3 5 4 9 2 [root@centos8 ~]# seq 10|sort -R 5 6 3 4 2 1 8 10 9 7
范例3:取出分区利用率中利用率最高的那个值
1 [02:50:59 root@CentOS8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2 2 0 3 0 4 1 5 0 6 3 7 17 8 1 9 0 10 [02:51:00 root@CentOS8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|sort -nr 11 17 12 3 13 1 14 1 15 0 16 0 17 0 18 0 19 [02:51:12 root@CentOS8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|sort -nr|head -n1 20 17
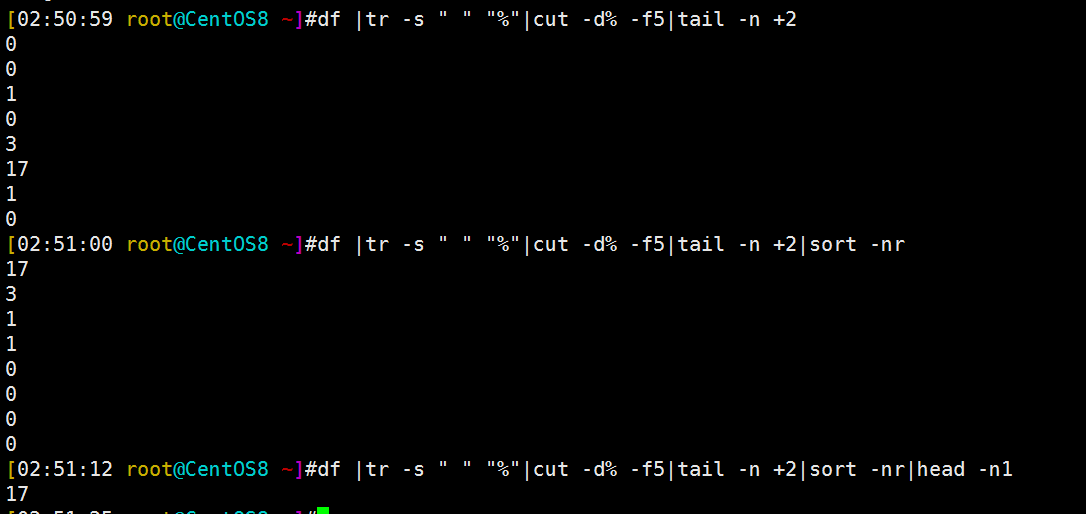
[root@rocky8 ~]#df |tr -s " " "%"|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|sort -nr|head -n1
19
[root@rocky8 ~]#df |tr -s ' ' %|cut -d% -f5|tail -n +2|sort -nr|head -n1
19
3.去重uniq
-c: 显示每行重复出现的次数 -d: 仅显示重复过的行 -u: 仅显示不曾重复的行
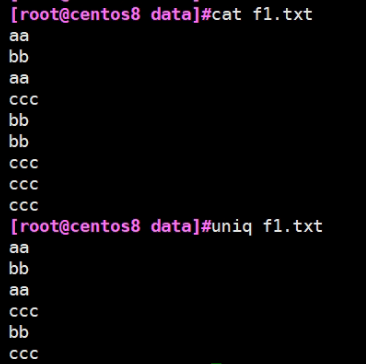
1.查看 2.去重 3.仅显示不曾重复的行 4.显示每行重复出现的次数
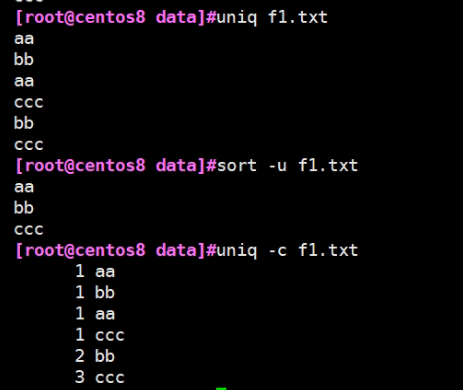
常见组合 #sort a.xtx |uniq -c
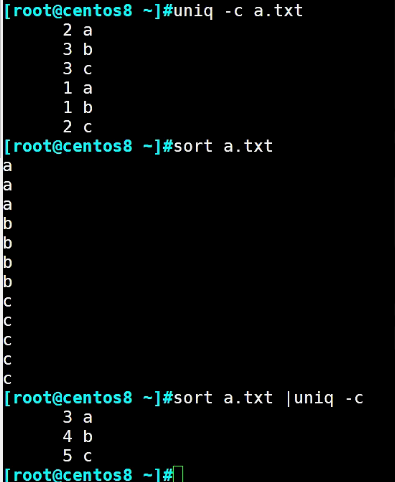
实战案例:
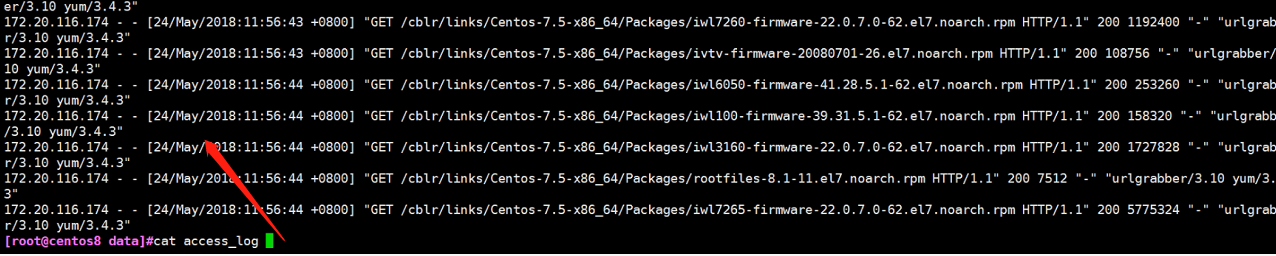
1.查看日志内容 #cat access_log
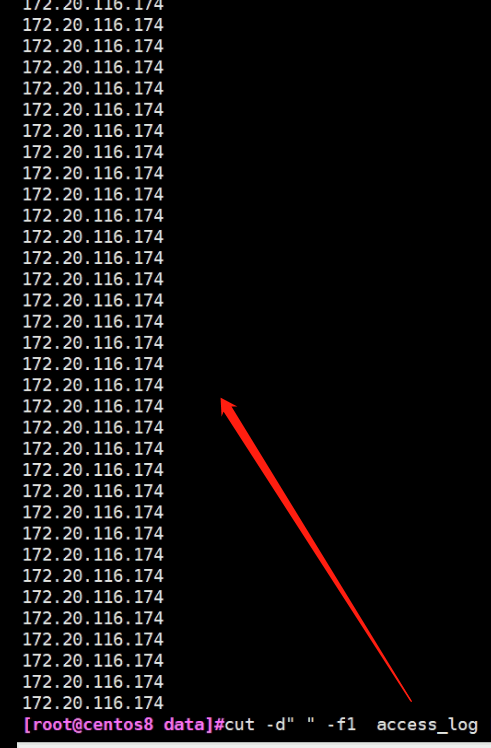
2.取这个日志的第一列 #cut -d" " -f1 access_log
3.排序 #cut -d" " -f1 access_log |sort
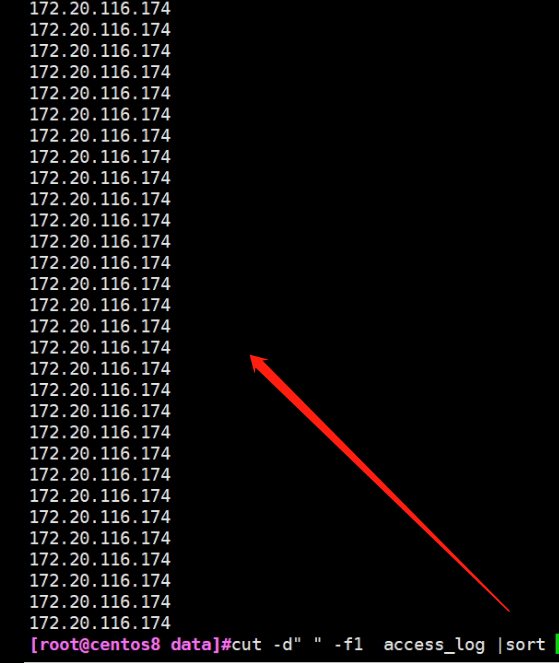
4.排完序之后,同样的内容在一起了
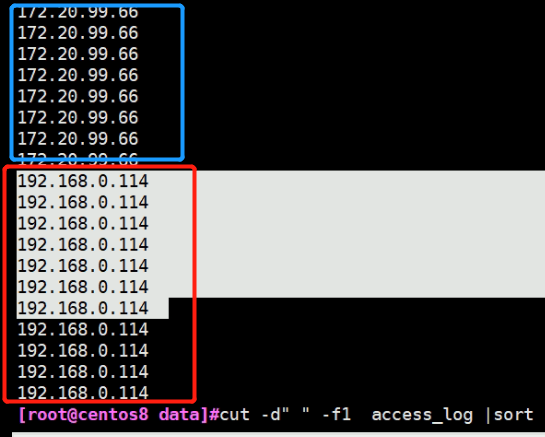
5.统计次数] #cut -d" " -f1 access_log |sort |uniq -c
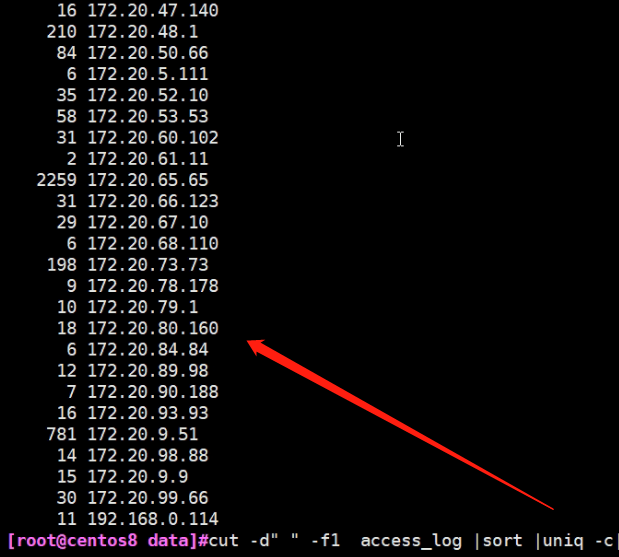
6.统计结果出来了,但是有点乱,需要再次排序
#cut -d" " -f1 access_log |sort |uniq -c|sort -nr (#r是倒序排列)
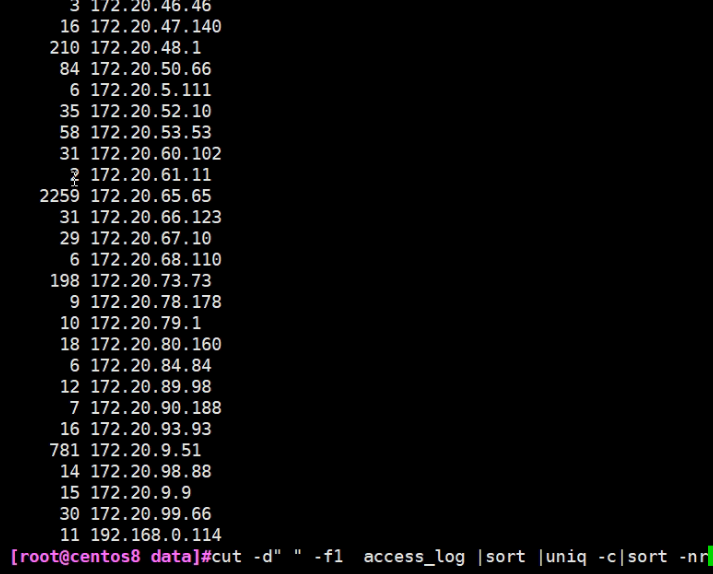
7.做下对比,第一行倒序排列的结果
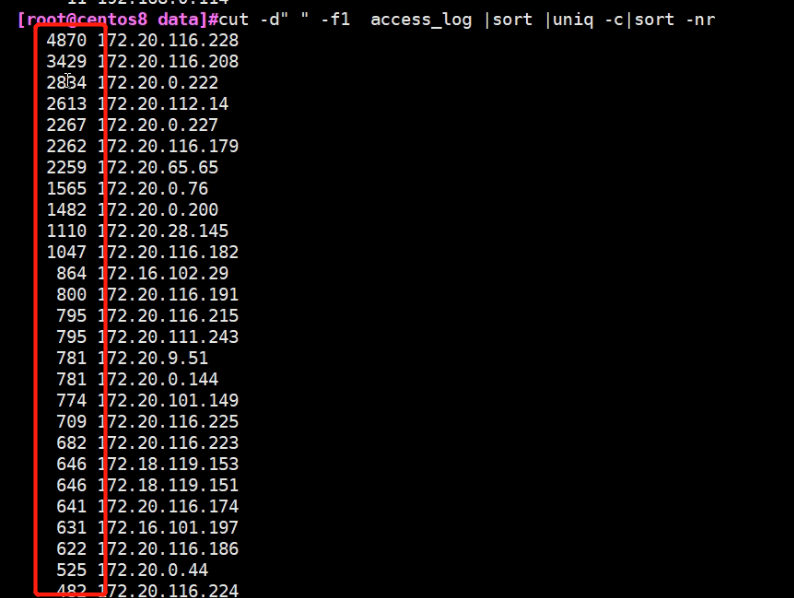
8.最后取前三名
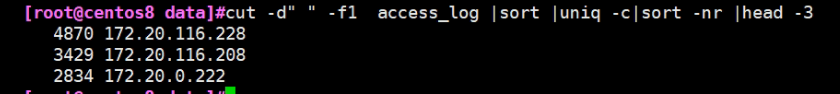
[root@centos8 data]#cut -d" " -f1 access_log |sort |uniq -c|sort -nr |head -3 4870 172.20.116.228 3429 172.20.116.208 2834 172.20.0.222
范例2:统计每个IP访问最高的前三名
访问记录记录到日志文件中
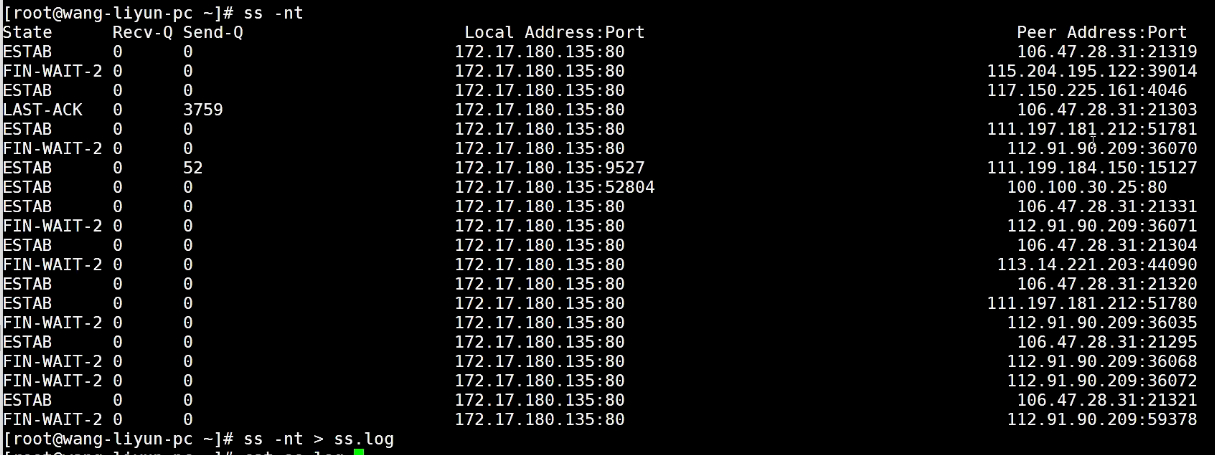
查看 ss.log文件
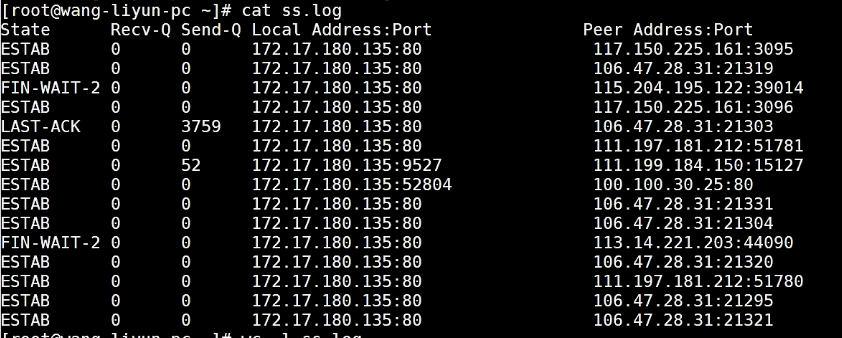
统计一下有82行

取值前三

另外一种简洁写法:
[root@rocky8 ~]#tail -n +2 ss.log | tr -s ' ' : |cut -d:-f6 |soft |uniq -c | sort -nr |head -n3

范例3:
1.创建2个文件查看结果
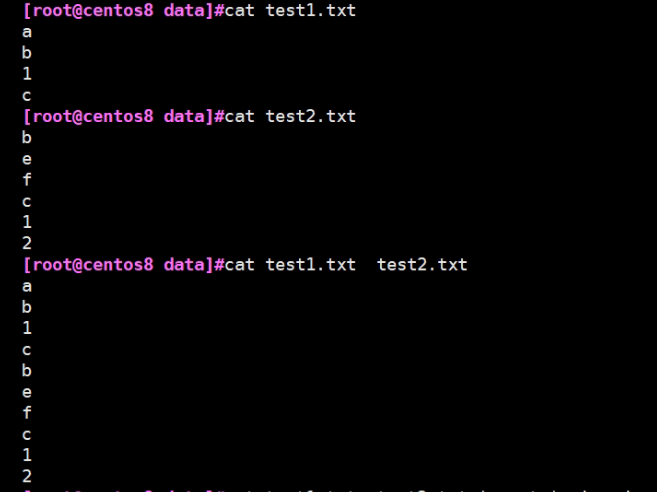
2.显示这2个文件中重复的内容
[root@centos8 data]#cat test1.txt test2.txt | sort |uniq -d 1 b c
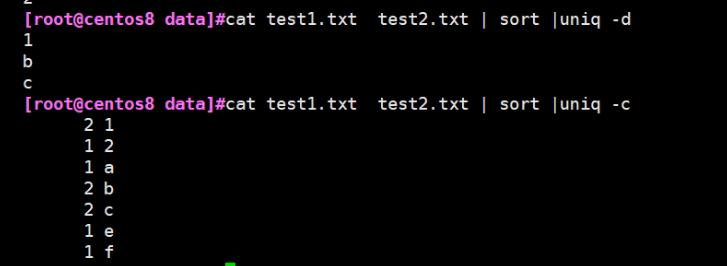
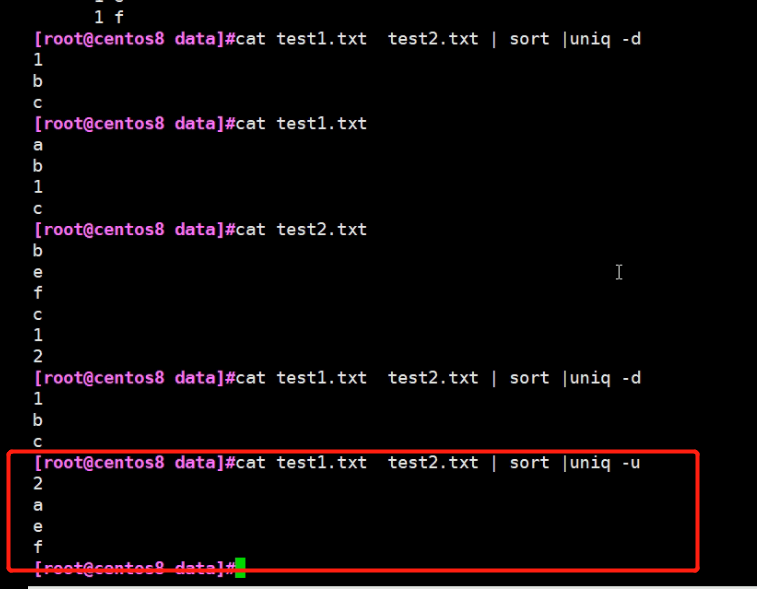
3.另外:找出不同的行 #cat test1.txt test2.txt | sort |uniq -u
[root@centos8 data]#cat test1.txt test2.txt | sort |uniq -u 2 a e f
合并多个文件paste
12:30:01 root@centos8 ~]#vim title.txt
[12:34:10 root@centos8 ~]#ls
anaconda-ks.cfg install_mysql5.7.sh title.txt
[12:34:34 root@centos8 ~]#mv title.txt name.txt
[12:34:43 root@centos8 ~]#ls
anaconda-ks.cfg install_mysql5.7.sh name.txt
[12:34:52 root@centos8 ~]#vim title.txt
[12:35:40 root@centos8 ~]#cat title.txt name.txt
ceo
coo
cto
mage
zhang
wang
xu
[12:35:58 root@centos8 ~]#mv name.txt emp.txt
[12:37:28 root@centos8 ~]#paste -s title.txt emp.txt
ceo coo cto
mage zhang wang xu
[12:37:51 root@centos8 ~]#cat title.txt
ceo
coo
cto
[12:38:53 root@centos8 ~]#cat name.txt (#移走了,所以name就没了)
cat: name.txt: No such file or directory
[12:38:59 root@centos8 ~]#cat emp.txt
mage
zhang
wang
xu
20211006renew~



