python常用功能
1. 获取昨天日期
引入datetime模块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | import datetimedef getYesterday(): today = datetime.date.today() #返回当前本地日期# oneday = datetime.timedelta(day=1) #两个日期对象的最小间隔 oneday = datetime.date.resolution #两个日期对象的最小间隔 yesterday = today - oneday return yesterdayprint(getYesterday())#2020-10-17 |
2. 计算每个月天数
1 2 3 | import calendar #导入日历模块monthRange = calendar.monthrange(2020,10) #当月的天数print(monthRange) #输出当月的天数# (3, 31) |
3. 字符串大小转换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | str = "https://www.cnblogs.com/kevin.hou"print(str.upper()) #把所字符中的小写字母转换成大写字母print(str.lower()) #把所有字符中的大写字母转换成小写字母print(str.capitalize()) #把第一个字母转化为大写字母,其余小写print(str.title()) #把每个单词的第一个字母转化为大写,其余小写# HTTPS://WWW.CNBLOGS.COM/KEVIN.HOU# https://www.cnblogs.com/kevin.hou# Https://www.cnblogs.com/kevin.hou# Https://Www.Cnblogs.Com/Kevin.Hou |
4. 字符串判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | #测试实例1print("测试实例1")str = "runoob.com" #print(str.isalnum()) #判断所有的字符都是数字或者字母print(str.isalpha()) #判断所有的字符都是字母print(str.isdigit()) #判断所有的字符都是数字print(str.islower()) #判断所有的字符都是小写print(str.isupper()) #判断所有的字符都是大写print(str.istitle()) #判断所有的单词都是首字母大写,像标题print(str.isspace()) #判断所有的字符都是空白字符、\t、\n、\rprint("----------------------------------")#测试实例2print("测试实例2")str = "Bake corN"print(str.isalnum()) #判断所有的字符都是数字或者字母print(str.isalpha()) #判断所有的字符都是字母print(str.isdigit()) #判断所有的字符都是数字print(str.islower()) #判断所有的字符都是小写print(str.isupper()) #判断所有的字符都是大写print(str.istitle()) #判断所有的单词都是首字母大写,像标题print(str.isspace()) # 测试实例1# False# False# False# True# False# False# False# ----------------------------------# 测试实例2# False# False# False# False# False# False# False |
5. 生成日历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #引入日历模块import calendar#输入指定年月yy = int(input("输入年份:"))mm = int(input("输入月份:"))#显示日历print(calendar.month(yy, mm))# 输入年份:2020# 输入月份:10# October 2020# Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su# 1 2 3 4# 5 6 7 8 9 10 11# 12 13 14 15 16 17 18# 19 20 21 22 23 24 25# 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | 输入年份:2020输入月份:11 November 2020Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1516 17 18 19 20 21 2223 24 25 26 27 28 2930 |
6. 简单计算器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | def add(x,y): """相加""" return x+ydef subtract(x,y): """相减""" return x-ydef multiply(x,y): """相乘""" return x*ydef divide(x,y): """相除""" return x/y#用户输入print("选择运算:")print("1、相加")print("2、相减")print("3、相乘")print("4、相除")choice = input("输入你的选择(1/2/3/4):")num1 = int(input("输入第一个数字:"))num2 = int(input("输入第二个数字:"))if choice == '1': print(num1, "+", num2, "=", add(num1, num2))elif choice == '2': print(num1, "-", num2 ,"=", subtract(num1, num2))elif choice == '3': print(num1, "*", num2, "=", multiply(num1, num2))elif choice == '4': if num2 !=0: print(num1, "/", num2, "=", divide(num1, num2)) else: print("分母不能为0")else: print("非法输入") |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | 选择运算:1、相加2、相减3、相乘4、相除输入你的选择(1/2/3/4):1输入第一个数字:2输入第二个数字:32 + 3 = 5选择运算:1、相加2、相减3、相乘4、相除输入你的选择(1/2/3/4):2输入第一个数字:3输入第二个数字:53 - 5 = -2选择运算:1、相加2、相减3、相乘4、相除输入你的选择(1/2/3/4):3输入第一个数字:4输入第二个数字:54 * 5 = 20选择运算:1、相加2、相减3、相乘4、相除输入你的选择(1/2/3/4):4输入第一个数字:8输入第二个数字:48 / 4 = 2.0 |
7. 最小公倍数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | #定义函数def lcm(x,y): #获取最大的数 if x > y: greater = x else: greater = y while(True): if ((greater % x ==0) and (greater % y ==0)): lcm = greater break greater += 1 return lcm#获取用户输入num1 = int(input("输入第一个数字:"))num2 = int(input("输入第一个数字:"))print(num1, "和", num2, "的最小公倍数为", lcm(num1, num2))# 输入第一个数字:3# 输入第一个数字:5# 3 和 5 的最小公倍数为 15 |
8. 最大公约数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | def hcf(x,y):"""该函数返回两个数的最大公约数"""#获取最小值 if x > y: smaller = y else: smaller = x for i in range(1, smaller +1): if ((x % i ==0) and (y % i == 0)): hcf = i return hcf#用户输入两个数字num1 = int(input("输入第一个数字:"))num2 = int(input("输入第二个数字:"))print(num1, "和", num2, "的最大公约数为", hcf(num1, num2)) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | 输入第一个数字:1输入第二个数字:21 和 2 的最大公约数为 1输入第一个数字:3输入第二个数字:53 和 5 的最大公约数为 1 |
9. 十进制转二进制、十六进制、八进制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | #获取输入十进制数dec = int(input("输入数字:"))print("十进制数为:", dec)print("转换为二进制为:", bin(dec))print("转换为八进制为:",oct(dec))print("转换为十六进制为:",hex(dec))# 输入数字:2# 十进制数为: 2# 转换为二进制为: 0b10# 转换为八进制为: 0o2# 转换为十六进制为: 0x2 |
10. 斐波那契数列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | #斐波那契数列指的是这样一个数列0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13;特别指出:第0项是0,第1项是第一个1.#从第三项开始,每一项都等于前两项之和。#获取用户输入数据nterms = int(input("你需要几项?"))#第一和第二项n1 = 0n2 = 1count = 2#判断输入的值是否合法if nterms <= 0: print("请输入一个正整数。")elif nterms == 1: print("斐波那契数列:") print(n1)else: print("斐波那契数列:") print(n1, ",", n2 ,end = ",") while count < nterms: nth = n1 + n2 print(n1+n2, end=",") #更新值 n1 = n2 n2 = nth count +=1 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | 你需要几项?0请输入一个正整数。你需要几项?1斐波那契数列:0你需要几项?2斐波那契数列:0 , 1,你需要几项?3斐波那契数列:0 , 1,1,你需要几项?8斐波那契数列:0 , 1,1,2,3,5,8,13, |
11. 文件I/O
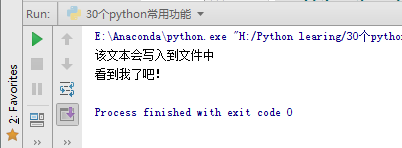
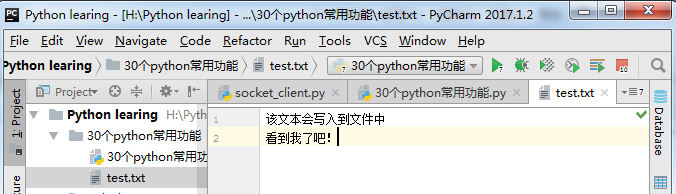
1 2 3 4 5 6 | with open("test.txt", "wt") as out_file: out_file.write("该文本会写入到文件中\n看到我了吧!")#Read a filewith open("test.txt", "rt") as in_file: text = in_file.read()print(text) |
12. 获取最大值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | N = int(input('输入需要对比大小数字的个数:'))print("请输入需要对比的数字:")num = []for i in range(1, N+1): temp = int(input('输入第%d个数字:' %i)) num.append(temp)print('您输入的数字为:',num)print('最大值为:',max(num))N = int(input('输入需要对比数字的个数:\n'))num = [int(input('请输入第%d 个对比数字:\n' %i)) for i in range(1, N+1)]print('您输入的数字为:', num)print('最大值为:',max(num))# 输入需要对比大小数字的个数:2# 请输入需要对比的数字:# 输入第1个数字:12# 输入第2个数字:23# 您输入的数字为: [12, 23]# 最大值为: 23<br># 输入需要对比数字的个数:# 4# 请输入第1 个对比数字:# 1# 请输入第2 个对比数字:# 2# 请输入第3 个对比数字:# 3# 请输入第4 个对比数字:# 4# 您输入的数字为: [1, 2, 3, 4]# 最大值为: 4 |
13. 判断闰年
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | year = int(input("输入一个年份:"))if (year % 4) ==0: if (year % 100) ==0: if (year % 400) ==0: print("{0}是闰年".format(year)) #整百年能被400整除的是闰年 else: print("{0}不是闰年".format(year)) else: print("{0}是闰年".format(year))else: print("{0}不是闰年".format(year))year = int(input("请输入一个年份:"))if (year % 4 ) == 0 and (year %100 ) !=0 or (year % 400) ==0: print("{0}是闰年.format(year)")else: print("{0}不是闰年".format(year))import calendaryear = int(input("请输入年份:"))check_year = calendar.isleap(year)if check_year == True: print("%d是闰年"% year)else: print("%d是平年"% year)# 输入一个年份:1990# 1990不是闰年# 请输入一个年份:1001# 1001不是闰年# 请输入年份:2014# 2014是平年 |
14. 判断奇偶数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | num = int(input("输入一个数字:"))if (num % 2) == 0: print("{0}是偶数".format(num))else: print("{0}是奇数".format(num))while True: try: num = int(input('输入一个整数:')) except ValueError: print("输入的不是整数!") continue if num % 2 ==0: print('偶数') else: print('奇数') break# 输入一个数字:0# 0是偶数# 输入一个整数:1# 奇数 |
15. 计算平方根
1 2 3 4 5 6 | num = float(input('请输入一个数字:'))num_sqrt = num ** 0.5print('%0.2f的平方根为%0.2f'%(num,num_sqrt))# 请输入一个数字:9# 9.00的平方根为3.0 |
16. 随机生成验证码的两种方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | import random #导入随机函数list1 = [] #新建列表for i in range(65,91): list1.append(chr(i)) #通过for循环遍历assii追加到空列表中for j in range(97,123): list1.append(chr(j))for k in range(48,58): list1.append(chr(k))ma = random.sample(list1,6)print(ma) #获取到的为列表ma = ''.join(ma) #将列表转化为字符串print(ma)import randomi = 1a = random.randint(0,100)b = int(input('请输入0-100中的一个数字\n然后查看是否与电脑一样:'))while a !=b: if a > b: print('你第%d输入的数字小于电脑随机数字'%i) b = int(input('请再次输入数字:')) else: print('你第%d输入的数字大于电脑随机数字'%i) b = int(input('请再次输入数字:')) i+=1else: print('恭喜你,你第%d次输入的数字与电脑的随机数字%d一样'%(i,b)) # 请输入0-100中的一个数字# 然后查看是否与电脑一样:1# 你第1输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:4# 你第2输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:6# 你第3输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:90# 你第4输入的数字大于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:12# 你第5输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:16# 你第6输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:24# 你第7输入的数字小于电脑随机数字# 请再次输入数字:56# 恭喜你,你第8次输入的数字与电脑的随机数字56一样 |
17. 合并去重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | list1 = [2,3,8,4,9,5,6]list2 = [5,6,10,17,11,2]list3 = list1 + list2print(list3) #不去重只进行两个列表的组合print(set(list3)) #去重,类型为set需要转换成list# [2, 3, 8, 4, 9, 5, 6, 5, 6, 10, 17, 11, 2]# {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 17} |
18. 打印每个名字
1 2 3 4 5 6 | L = ["James", "Meng", "Xin"]for i in range(len(L)): print("Hello,%s"%L[i])# Hello,James# Hello,Meng# Hello,Xin |
19. 替换列表中所有的3为3a
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | num = ["harden", "lampard", 3,34,45,56,76,87,78,45,3,3,3,87686,98,76]print(num.count(3))print(num.index(3))for i in range(num.count(3)): #获取3出现的次数 ele_index = num.index(3) #获取首次3出现的坐标 num[ele_index] = "3a" #修改3为3 print(num)# 4# 2# ['harden', 'lampard', '3a', 34, 45, 56, 76, 87, 78, 45, 3, 3, 3, 87686, 98, 76]# ['harden', 'lampard', '3a', 34, 45, 56, 76, 87, 78, 45, '3a', 3, 3, 87686, 98, 76]# ['harden', 'lampard', '3a', 34, 45, 56, 76, 87, 78, 45, '3a', '3a', 3, 87686, 98, 76]# ['harden', 'lampard', '3a', 34, 45, 56, 76, 87, 78, 45, '3a', '3a', '3a', 87686, 98, 76] |
20. 打印9*9乘法表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | for i in range(1, 10): for j in range(1, i+1): # print('{}x{}={}\t'.format(j,i,i*j),end='') print('%d x %d =%d \t'%(i,j,i*j),end='') print()1 x 1 =12 x 1 =2 2 x 2 =43 x 1 =3 3 x 2 =6 3 x 3 =94 x 1 =4 4 x 2 =8 4 x 3 =12 4 x 4 =165 x 1 =5 5 x 2 =10 5 x 3 =15 5 x 4 =20 5 x 5 =256 x 1 =6 6 x 2 =12 6 x 3 =18 6 x 4 =24 6 x 5 =30 6 x 6 =367 x 1 =7 7 x 2 =14 7 x 3 =21 7 x 4 =28 7 x 5 =35 7 x 6 =42 7 x 7 =498 x 1 =8 8 x 2 =16 8 x 3 =24 8 x 4 =32 8 x 5 =40 8 x 6 =48 8 x 7 =56 8 x 8 =649 x 1 =9 9 x 2 =18 9 x 3 =27 9 x 4 =36 9 x 5 =45 9 x 6 =54 9 x 7 =63 9 x 8 =72 9 x 9 =81 |
21.把原字典的键值对颠倒并生产新的字典
dict1 = {"A": "a", "B": "b", "C": "c"}
dict2 = {y:x for x,y in dict1.items()}
print(dict2)
# {'a': 'A', 'b': 'B', 'c': 'C'}
22. 合并去重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | list1 = [2,3,8,4,9,5,6]list2 = [5,6,10,17,11,2]list3 = list1 + list2print(list3) #不去重只进行两个列表的组合print(set(list3)) #去重,类型为set需要转换成list# [2, 3, 8, 4, 9, 5, 6, 5, 6, 10, 17, 11, 2]# {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 17} |
23. 输出某个路径及其子目录下所有以.html为后缀的文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import osdef print_dir(filepath): for i in os.listdir(filepath): path = os.path.join(filepath, i) if os.path.isdir(path): print_dir(path) if path.endswith(".html"): print(path)filepath = "E:\Anaconda"print_dir(filepath)E:\Anaconda\Lib\idlelib\help.htmlE:\Anaconda\Lib\site-packages\alabaster\about.htmlE:\Anaconda\Lib\site-packages\alabaster\donate.htmlE:\Anaconda\Lib\site-packages\alabaster\layout.htmlE:\Anaconda\Lib\site-packages\alabaster\navigation.html |
24. 输出某个路径及其子目录下的所有文件路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | import osdef show_dir(filepath): for i in os.listdir(filepath): path = (os.path.join(filepath, i)) #isdir()判断是否是目录 print(path) #如果是目录,使用递归方法filepath = "C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer"show_dir(filepath)C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\D3DCompiler_47.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\DiagnosticsHub.DataWarehouse.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\DiagnosticsHub.ScriptedSandboxPlugin.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\DiagnosticsHub_is.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\DiagnosticsTap.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\en-USC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\ExtExport.exeC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\F12.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\F12Resources.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\F12Tools.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\ie9props.propdescC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iediagcmd.exeC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iedvtool.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\ieinstal.exeC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\ielowutil.exeC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\ieproxy.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEShims.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iessetup.cebC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iessetup.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exeC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\imagesC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\jsdbgui.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\jsdebuggeride.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\JSProfilerCore.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\jsprofilerui.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\logC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\MemoryAnalyzer.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\msdbg2.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\networkinspection.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\pdm.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\pdmproxy100.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\perfcore.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\perf_nt.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\PluginsC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\SIGNUPC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\sqmapi.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\Timeline.cpu.xmlC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\Timeline.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\Timeline_is.dllC:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\zh-CN |
25. 输出某个路径下的所有文件和文件夹的路径
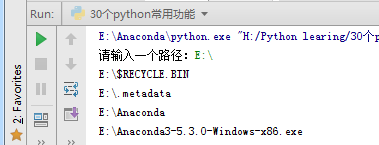
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | import osdef print_dir(): filepath = input("请输入一个路径:") if filepath == "": print("请输入正确的路径") else: for i in os.listdir(filepath): #获取目录中的文件及其子目录列表 print(os.path.join(filepath,i)) #把路径组合起来print(print_dir()) |
26. 把一个list中所有的字符串变成小写:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | L = ['Hello', 'World', 'SONY', 'SHARP', 'GEA']for s in L: s.lower() print(s.lower())helloworldsonysharpgea |
27. 列出当前目录下的所有文件和目录名
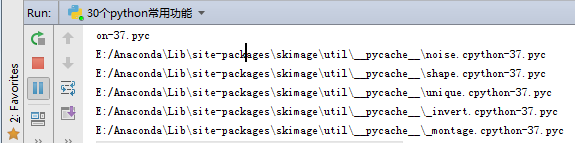
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | import osdef show_dir(filepath): for i in os.listdir(filepath): path = (os.path.join(filepath, i)) print(path) if os.path.isdir(path): # isdir()判断是否是目录 show_dir(path) # 如果是目录,使用递归方法filepath = "E:/"print(show_dir(filepath)) |
28.计算阶乘n!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | def fac(): num = int(input("请输入一个数字:")) factorial = 1#查看数字是负数,0或正数 if num < 0: print("抱歉,负数没有阶乘!!!") elif num == 0: print("0的阶乘为1") else: for i in range(1, num + 1): factorial = factorial * i print("%d 的阶乘为 %d" %(num, factorial))def factorial(n): result = n for i in range(1, n): result *=i return result# def fact(n):# if n==1:# return 1# return n * fact(n-1)print(fac()) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | 请输入一个数字:-1抱歉,负数没有阶乘!!!None请输入一个数字:00的阶乘为1None请输入一个数字:33 的阶乘为 6None |
29. 计算a*a +b*b +c*c +..........
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | #求平方和def calc(numbers): sum = 0 for n in numbers: sum = sum + n*n return sumprint(calc(numbers=[1,2,3] ))#14 |
30. 计算x的n 次方
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | def power(x,n): s = 1 while n >0 : n = n-1 s = s*x return sprint(power(2,3))# 8 |
31. 冒泡排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | list = [56,12,1,8,354,10,100,34,56,7,23,456,234,-58] #需要排序的列表def sortport(): #定义排序函数 for i in range(len(list)-1): #判断i在len(list)-1列表中 for j in range(len(list)-1-i): #判断j在len(list)-1-i列表中 if list[j] > list[j+1]: #判断list[j]的值和list[j+1]的值大小 list[j],list[j+1] = list[j+1],list[j] #进行排序 return list #返回最终排好序的列表,按从小到大顺序排列print(sortport())# [-58, 1, 7, 8, 10, 12, 23, 34, 56, 56, 100, 234, 354, 456]<br>print(len(list)) #len(list)为计算list中值的个数,为14 |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律