因为我是在stm32上面做的加密操作,所以我只对stm32的方案做总结。
1.ATECC508的底层接口是i2c的,工程中跟i2c相关的操作放在文件hal_stm32l0_ateccx08_i2c.c中,文件应该放在cryptoauthlib\lib\hal\目录下。
2.Armel对这个库封装的比较深,分析下应用程序是如何调用底层的:
atecc508_init
atcab_init( gIfaceCfg ) //这个全局变量很重要,底层的驱动结构体就是绑定在这个全局变量上,后面调用底层驱动,就直接调用这个指针了。
_gDevice = newATCADevice( cfg );
cadev->mIface = (ATCAIface)newATCAIface(cfg);
atinit(caiface)
_atinit( caiface, &hal );
可以看看_atinit(ATCAIface caiface, ATCAHAL_t *hal)这个函数:
ATCA_STATUS _atinit(ATCAIface caiface, ATCAHAL_t *hal)
{
// get method mapping to HAL methods for this interface
hal_iface_init( caiface->mIfaceCFG, hal );
caiface->atinit = hal->halinit;
caiface->atpostinit = hal->halpostinit;
caiface->atsend = hal->halsend;
caiface->atreceive = hal->halreceive;
caiface->atwake = hal->halwake;
caiface->atsleep = hal->halsleep;
caiface->atidle = hal->halidle;
caiface->hal_data = hal->hal_data;
return ATCA_SUCCESS;
}
先看最开始的那个函数,我粗体标识的:
ATCA_STATUS hal_iface_init( ATCAIfaceCfg *cfg, ATCAHAL_t *hal ) { // Because C isn't a real object oriented language or dynamically typed, some switch in the overall system is unavoidable // The key here is to provide the flexibility to include just the types of interfaces you want/need without breaking the // object model. The former is needed so in an embedded, constrained memory environment, you don't have to pay the price // (in terms of memory) for interfaces you don't use in your application. ATCA_STATUS status = ATCA_COMM_FAIL; switch (cfg->iface_type) { case ATCA_I2C_IFACE: #ifdef ATCA_HAL_I2C hal->halinit = &hal_i2c_init; hal->halpostinit = &hal_i2c_post_init; hal->halreceive = &hal_i2c_receive; hal->halsend = &hal_i2c_send; hal->halsleep = &hal_i2c_sleep; hal->halwake = &hal_i2c_wake; hal->halidle = &hal_i2c_idle; hal->halrelease = &hal_i2c_release; hal->hal_data = NULL; status = ATCA_SUCCESS; #endif break; 。。。。。。。。。。。。
只截取了跟i2c相关的部分,清楚了函数的调用关系了吧。我们需要在hal_stm32l0_ateccx08_i2c.c里面实现这些函数:
ATCA_STATUS hal_i2c_send(ATCAIface iface, uint8_t *txdata, int txlength)
{
ATCAIfaceCfg *cfg = atgetifacecfg(iface);
txdata[0] = 0x03; //!< Word Address Value = Command
txlength++; //!< count Word Address byte towards txlength
uint32_t status = HAL_ERROR;
do{
status = HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, ECC508_IIC_ADDRESS, txdata, txlength, ECC508_TX_TIMEOUT);
if(status != HAL_OK)
{
I2C_Reset();
__HAL_I2C_CLEAR_FLAG(&hi2c1, I2C_FLAG_STOPF); /* Clear STOP Flag */
I2C_RESET_CR2(&hi2c1); /* Clear Configuration Register 2 */
hi2c1.State = HAL_I2C_STATE_READY;
hi2c1.Mode = HAL_I2C_MODE_NONE;
__HAL_UNLOCK(&hi2c1); /* Process Unlocked */
hal_i2c_wake(iface);
}
}while(status != HAL_OK);
return ATCA_SUCCESS;
}
ATCA_STATUS hal_i2c_receive( ATCAIface iface, uint8_t *rxdata, uint16_t *rxlength)
{
uint32_t status = HAL_ERROR;
do{
status = HAL_I2C_Master_Receive(&hi2c1, ECC508_IIC_ADDRESS,rxdata,*rxlength,ECC508_RX_TIMEOUT);
if(status != HAL_OK)
{
I2C_Reset();
__HAL_I2C_CLEAR_FLAG(&hi2c1, I2C_FLAG_STOPF); /* Clear STOP Flag */
I2C_RESET_CR2(&hi2c1); /* Clear Configuration Register 2 */
hi2c1.State = HAL_I2C_STATE_READY;
hi2c1.Mode = HAL_I2C_MODE_NONE;
__HAL_UNLOCK(&hi2c1); /* Process Unlocked */
hal_i2c_wake(iface);
}
}while(status != HAL_OK);
return ATCA_SUCCESS;
}
ATCA_STATUS hal_i2c_wake(ATCAIface iface) { I2C_As_Normal_Gpio(); SCL_H; SDA_L; HAL_Delay(1); /*86us*/ SDA_H; HAL_Delay(1); /*830us*/ // wait tWHI + tWLO which is configured based on device type and configuration structure I2C_As_I2c_Gpio(); return ATCA_SUCCESS; }
2.我遇到的问题:
1.延时函数,如上hal_i2c_wake里面有些延时函数,HAL_Delay()这个函数在ATECC508里面到处用到了,所以不同的芯片需要不同的实现,根本点就是要保证时间尽量准确。
2.遇到的最严重的问题还是stm32本身I2C的问题,设置的传输速率是400kbps,但是经常传着传着i2c就收不到数据了,这个在前面已经说过,没什么好说的。
我用普通io模拟了I2C,但是传输速率只能做到300kbps左右,再高上不去,虽然传输不存在问题,但是遇到了新的问题,看下面的函数,
ATCA_STATUS atcab_read_zone(uint8_t zone, uint8_t slot, uint8_t block, uint8_t offset, uint8_t *data, uint8_t len) { ATCA_STATUS status = ATCA_SUCCESS; ATCAPacket packet; uint16_t addr; uint16_t execution_time = 0; do { // Check the input parameters if (data == NULL) return ATCA_BAD_PARAM; if ( len != 4 && len != 32 ) return ATCA_BAD_PARAM; // The get address function checks the remaining variables if ( (status = atcab_get_addr(zone, slot, block, offset, &addr)) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; // If there are 32 bytes to write, then xor the bit into the mode if (len == ATCA_BLOCK_SIZE) zone = zone | ATCA_ZONE_READWRITE_32; // build a read command packet.param1 = zone; packet.param2 = addr; if ( (status = atRead( _gCommandObj, &packet )) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; execution_time = atGetExecTime( _gCommandObj, CMD_READMEM); if ( (status = atcab_wakeup()) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; // send the command if ( (status = atsend( _gIface, (uint8_t*)&packet, packet.txsize )) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; // delay the appropriate amount of time for command to execute atca_delay_ms(execution_time); // receive the response if ( (status = atreceive( _gIface, packet.data, &(packet.rxsize) )) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; // Check response size if (packet.rxsize < 4) { if (packet.rxsize > 0) status = ATCA_RX_FAIL; else status = ATCA_RX_NO_RESPONSE; break; } if ( (status = isATCAError(packet.data)) != ATCA_SUCCESS ) break; memcpy( data, &packet.data[1], len ); } while (0); _atcab_exit(); return status; }
看看函数中粗斜体,执行的顺序就是wake->send->delay->receive.
如果hal_delay函数不准,就会导致这个地方delay会不准,就要导致芯片已经休眠了,才去发送receive命令,当然收不到。
还有一点,如果传输的速率比较低,也会导致在send的时候花很多时间,即使delay是准时的,也会导致芯片已经休眠,才去发送receive。
因为不知道库里有多少个地方是这样处理的,所以还是尽量将函数时间弄准确,I2C的速率尽量高点。
3.关于是如何发现这些问题的,我用到了逻辑分析仪:
从下图可以看出,我send command之后,delay了0.7248s才去receive,这个时候芯片早已休眠。
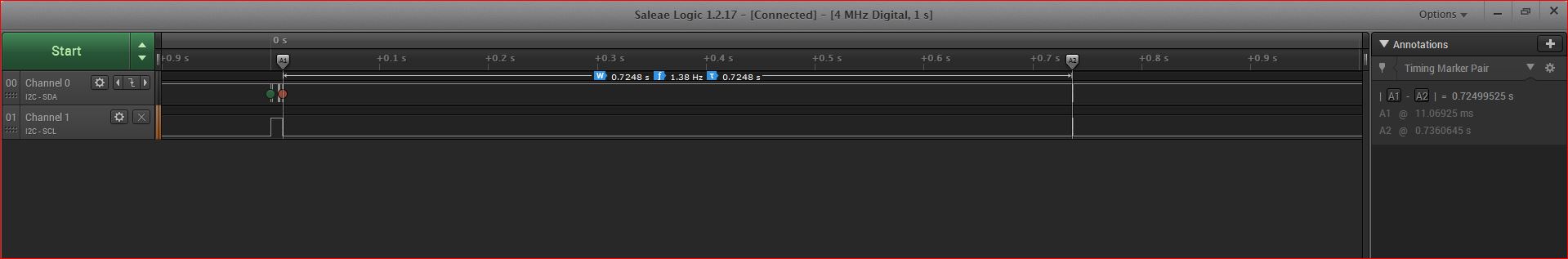
就是通过下图看出ATECC508芯片没有响应的。
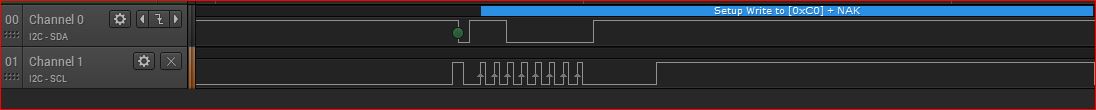
最后上一张完整通讯的截图:






