spring源码解析---spring-core(一)
使用版本spring4.2.2或者4.1.1
基本
本部分从最基本的Spring开始。配置文件:
<?
xml
version
=
"
1.0
"
encoding
=
"
UTF-8
"
?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
">
<
bean
class
=
"
base.SimpleBean
"
></
bean
>
</
beans
>
###原作者没有写beans的命名空间及约束 导致xml验证失败,这里加上了
###bean部分就是类的引用地址
启动代码:
public
static
void
main(
String
[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
context
=
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
(
"
config.xml
"
);
SimpleBean
bean
=
context
.
getBean(
SimpleBean
.
class);
bean
.
send();
context
.
close();
}
SimpleBean:
public
class
SimpleBean
{
public
void
send
() {
System
.
out
.
println(
"
I am send method from SimpleBean!
"
);
}
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
整个继承体系如下:

ResourceLoader代表了
加载资源的一种方式,正是策略模式的实现
。
构造器源码:
public
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String
[] configLocations,
boolean
refresh,
ApplicationContext
parent) {
//
null
super
(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
//
默认true
if
(refresh) {
refresh();
}
}



ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
context
=
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
(
"
config.xml
"
); 调用只会是上述两个方法其中一个,这里明显是
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation)
后面实际调用的都是本类的这个方法,如下图:

其实ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类里面的构造器(包括无参的共有9个在这个版本)。
构造器


。。。。。。此处省略几个向上的父类,一直到底抽象类
AbstractApplicationContext
首先看父类构造器,沿着继承体系一直向上调用,直到AbstractApplicationContext:


public
AbstractApplicationContext(
ApplicationContext
parent) {
this
();
setParent(parent);
}
public
AbstractApplicationContext() {
this
.
resourcePatternResolver
=
getResourcePatternResolver();
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver支持Ant风格的路径解析。下面简单概述下ant风格路径.

设置配置文件路径
即
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.
setConfigLocations:
public
void
setConfigLocations(
String
.
..
locations) {
if
(locations
!=
null
) {
Assert
.
noNullElements(locations,
"
Config locations must not be null
"
);
this
.
configLocations
=
new
String
[locations
.
length];
for
(
int
i
=
0
; i
<
locations
.
length; i
++
) {
this
.
configLocations[i]
=
resolvePath(locations[i])
.
trim();
}
}
else
{
this
.
configLocations
=
null
;
}
}
resolvePath:
protected
String
resolvePath(
String
path) {
return
getEnvironment()
.
resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}
此方法的目的在于将占位符(placeholder)解析成实际的地址。比如可以这么写:
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:config.xml");
那么classpath:就是需要被解析的。

getEnvironment方法来自于ConfigurableApplicationContext接口,源码很简单,如果为空就调用createEnvironment创建一个。AbstractApplicationContext.createEnvironment:
protected
ConfigurableEnvironment
createEnvironment() {
return
new
StandardEnvironment
();//看下面的继承关系可以知道
StandardEnvironment是
ConfigurableEnvironment的实现类
}

Environment接口
继承体系:

Environmen接口**代表了当前应用所处的环境。**从此接口的方法可以看出,其主要和profile、Property相关。
Profile
Spring Profile特性是从3.1开始的,其主要是为了解决这样一种问题: 线上环境和测试环境使用不同的配置或是数据库或是其它。有了Profile便可以在 不同环境之间无缝切换。**Spring容器管理的所有bean都是和一个profile绑定在一起的。**使用了Profile的配置文件示例:

在启动代码中可以用如下代码设置活跃(当前使用的)Profile:
context
.
getEnvironment()
.
setActiveProfiles(
"
dev
"
);
当然使用的方式还有很多(比如注解),参考:
spring3.1 profile 配置不同的环境
(打开失败)
Property
这里的Property指的是程序运行时的一些参数,引用注释:
properties files, JVM system properties, system environment variables, JNDI, servlet context parameters, ad-hoc Properties objects,Maps, and so on.
Environment实现类 AbstractEnvironment 构造器
private
final
MutablePropertySources
propertySources
=
new
MutablePropertySources
(
this
.
logger);
public
AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(
this
.
propertySources);
}

PropertySources接口
继承体系:
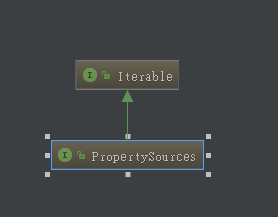

此接口实际上是PropertySource的容器,默认的MutablePropertySources实现内部含有一个CopyOnWriteArrayList作为存储载体。
StandardEnvironment.customizePropertySources:
/*
* System environment property source name: {@value}
*/
public
static
final
String
SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
=
"
systemEnvironment
"
;
/*
* JVM system properties property source name: {@value}
*/
public
static
final
String
SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
=
"
systemProperties
"
;
@Override
protected
void
customizePropertySources(
MutablePropertySources
propertySources) {
propertySources
.
addLast(
new
MapPropertySource
(
SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources
.
addLast(
new
SystemEnvironmentPropertySource
(
SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
PropertySource接口
PropertySource接口代表了键值对的Property来源。继承体系:

AbstractEnvironment.getSystemProperties:(此方法在
org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment里面
)

@Override
public
Map<
String
,
Object
> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return (
Map)
System
.getProperties();
}
catch (
AccessControlException ex) {
return (
Map)
new
ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected
String
getSystemAttribute(
String
attributeName) {
try {
return
System
.getProperty(attributeName);
}
catch (
AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger
.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger
.info(format(
"
Caught AccessControlException when accessing system
"
+
"
property [%s]; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: %s
",
attributeName, ex
.getMessage()));
}
return
null;
}
}
};
}
}
这里的实现很有意思,如果安全管理器阻止获取全部的系统属性,那么会尝试获取单个属性的可能性,如果还不行就抛异常了。
getSystemEnvironment方法也是一个套路,不过最终调用的是System.getenv,可以获取jvm和OS的一些版本信息。
路径Placeholder处理
AbstractEnvironment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders:
@Override
public
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(
String text) throws
IllegalArgumentException {
//
text即配置文件路径,比如classpath:config.xml
return
this
.propertyResolver
.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
propertyResolver是一个PropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象:
private
final
ConfigurablePropertyResolver
propertyResolver
=
new
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
(
this
.
propertySources);
PropertyResolver接口
PropertyResolver继承体系(排除Environment分支):
路径Placeholder处理
AbstractEnvironment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders:
@Override
public
String
resolveRequiredPlaceholders(
String
text) throws
IllegalArgumentException
{
//
text即配置文件路径,比如classpath:config.xml
return
this
.
propertyResolver
.
resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
propertyResolver是一个PropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象:
private
final
ConfigurablePropertyResolver
propertyResolver
=
new
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
(
this
.
propertySources);
PropertyResolver接口
PropertyResolver继承体系(排除Environment分支):

此接口正是用来解析PropertyResource。
解析
AbstractPropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders:



@Override
public
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(
String text) throws
IllegalArgumentException {
if (
this
.strictHelper
==
null) {
this
.strictHelper
= createPlaceholderHelper(
false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text,
this
.strictHelper);
}
private
PropertyPlaceholderHelper
createPlaceholderHelper(
boolean
ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
//
三个参数分别是${, }, :
return
new
PropertyPlaceholderHelper
(
this
.
placeholderPrefix,
this
.
placeholderSuffix,
this
.
valueSeparator, ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders);
}
doResolvePlaceholders:
private
String
doResolvePlaceholders(
String
text,
PropertyPlaceholderHelper
helper) {
//
PlaceholderResolver接口依然是策略模式的体现
return
helper
.
replacePlaceholders(text,
new
PropertyPlaceholderHelper
.
PlaceholderResolver
() {
@Override
public
String
resolvePlaceholder
(
String
placeholderName
) {
return
getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);
}
});
}
其实代码执行到这里的时候还没有进行xml配置文件的解析,那么这里的解析placeHolder是什么意思呢,原因在于可以这么写:
System
.
setProperty(
"
spring
"
,
"
classpath
"
);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
context
=
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
(
"
${spring}:config.xml
"
);
SimpleBean
bean
=
context
.
getBean(
SimpleBean
.
class);
这样就可以正确解析。placeholder的替换其实就是字符串操作,这里只说一下正确的属性是怎么来的。实现的关键在于PropertySourcesPropertyResolver.getProperty:
@Override
protected
String getPropertyAsRawString(
String key) {
return getProperty(key,
String
.class,
false);
}
protected
<
T
>
T getProperty(
String key,
Class<
T
> targetValueType,
boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (
this
.propertySources
!=
null) {
for (
PropertySource<?> propertySource
:
this
.propertySources) {
Object value
= propertySource
.getProperty(key);
return value;
}
}
return
null;
}
很明显了,就是从System.getProperty和System.getenv获取,但是由于环境变量是无法自定义的,所以其实此处只能通过System.setProperty指定。
注意,classpath:XXX这种写法的classpath前缀到目前为止还没有被处理。
refresh

super(parent)和this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);说完 下面说是refresh这个方法
Spring bean解析就在此方法,所以单独提出来。
AbstractApplicationContext.refresh:

作者版本:
@Override
public
void
refresh() throws
BeansException
,
IllegalStateException
{
synchronized
(
this
.
startupShutdownMonitor) {
//
Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh
();
//
Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
beanFactory
=
obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//
Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try
{
//
Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//
Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//
Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//
Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
//
Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//
Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
//
Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
//
Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//
Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch
(
BeansException
ex) {
//
Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
//
Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
//
Propagate exception to caller.
throw
ex;
}
finally
{
//
Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
//
might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
prepareRefresh
protected
void prepareRefresh() {
this
.startupDate
=
System
.currentTimeMillis();
this
.closed
.set(
false);
this
.active
.set(
true);
//
Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
//
空实现
initPropertySources();
//
Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable
//
see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment()
.validateRequiredProperties();
//
Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
//
to be published once the multicaster is available...
this
.earlyApplicationEvents
=
new
LinkedHashSet<
ApplicationEvent
>();
}
属性校验
AbstractEnvironment.validateRequiredProperties:
@Override
public
void
validateRequiredProperties() throws
MissingRequiredPropertiesException
{
this
.
propertyResolver
.
validateRequiredProperties();
}
AbstractPropertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties:
@Override
public
void
validateRequiredProperties() {
MissingRequiredPropertiesException
ex
=
new
MissingRequiredPropertiesException
();
for
(
String
key
:
this
.
requiredProperties) {
if
(
this
.
getProperty(key)
==
null
) {
ex
.
addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
if
(
!
ex
.
getMissingRequiredProperties()
.
isEmpty()) {
throw
ex;
}
}

requiredProperties是通过setRequiredProperties方法设置的,保存在一个set里面,默认是空的,也就是不需要校验任何属性。
BeanFactory创建
在refresh的这个方法里面
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.
obtainFreshBeanFactory
();//下面会讲到这个
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
由obtainFreshBeanFactory调用AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory:(见下图)


(这部分与作者源码一致)
BeanFactory接口
此接口实际上就是Bean容器,其继承体系:

BeanFactory定制
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.customizeBeanFactory方法用于给子类提供一个自由配置的机会,默认实现:
protected
void
customizeBeanFactory(
DefaultListableBeanFactory
beanFactory) {
if
(
this
.
allowBeanDefinitionOverriding
!=
null
) {
//
默认false,不允许覆盖
beanFactory
.
setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(
this
.
allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if
(
this
.
allowCircularReferences
!=
null
) {
//
默认false,不允许循环引用
beanFactory
.
setAllowCircularReferences(
this
.
allowCircularReferences);
}
}
Bean加载
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions,这个便是核心的bean加载了:
@Override
protected
void
loadBeanDefinitions
(
DefaultListableBeanFactory
beanFactory) {
//
Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
beanDefinitionReader
=
new
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
(beanFactory);
//
Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
//
resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader
.
setEnvironment(
this
.
getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader
.
setResourceLoader(
this
);
beanDefinitionReader
.
setEntityResolver(
new
ResourceEntityResolver
(
this
));//
为Bean读取器设置SAX xml解析器,
下面会说到这个
//
Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
//
then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
//
默认空实现
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
EntityResolver
此处只说明用到的部分继承体系:


EntityResolver
接口在org.xml.sax中定义。
DelegatingEntityResolver
用于schema和dtd的解析。
BeanDefinitionReader
继承体系:


路径解析(Ant)
protected
void
loadBeanDefinitions(
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
reader) {
Resource
[] configResources
=
getConfigResources();
if
(configResources
!=
null
) {
reader
.
loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String
[] configLocations
=
getConfigLocations();
//
here
if
(configLocations
!=
null
) {
reader
.
loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions:


下面作者这个肯定是不对的,因为调用了方法一样但参数列表不一样,实际是重载的
loadBeanDefinitions方法
,上图两个是4.1.1的方法内容,与作者的版本不同。故贴出来。
4.1.1版本与这个稍微有些不同
@Override
public
int loadBeanDefinitions(
String
.
.. locations) throws
BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert
.notNull(locations,
"
Location array must not be null
");
int counter
=
0;
for (
String location
: locations) {
counter
+= loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return counter;
}

之后调用:
//第二个参数为空
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = this.getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
} else {
int loadCount;
if (!(resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver)) {
Resource resource =
resourceLoader.getResource
(location);
loadCount = this.loadBeanDefinitions((Resource)resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
} else {
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver)resourceLoader).
getResources
(location);
loadCount = this.loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Resource[] var6 = resources;
int var7 = resources.length;
for(int var8 = 0; var8 < var7; ++var8) {
Resource resource = var6[var8];
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
} catch (IOException var10) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", var10);
}
}
}
}
getResources(作者写成
getResource,一字之差缪之千里
),
在AbstractApplicationContext.
getResources
:
@Override
public
Resource
[] getResources(
String
locationPattern) throws
IOException
{
//
构造器中初始化,PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver对象
return
this
.
resourcePatternResolver
.
getResources(locationPattern);
}



进入第二个方法,因为第一个是掉本类的方法。
public
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern)
throws
IOException {
//如果是ResourcePatternResolver
return this
.resourceLoader
instanceof
ResourcePatternResolver ? ((ResourcePatternResolver)
this
.resourceLoader).getResources(locationPattern) :
super
.getResources(locationPattern)
;
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver是ResourceLoader继承体系的一部分。
public
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern)
throws
IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern
,
"Location pattern must not be null"
)
;
if
(locationPattern.startsWith(
"classpath*:"
)) {
//
matcher是一个AntPathMatcher对象
return this
.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(
"classpath*:"
.length())) ?
this
.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) :
this
.findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(
"classpath*:"
.length()))
;
}
else
{
int
prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(
":"
) +
1
;
return this
.getPathMatcher().
isPattern
(locationPattern.substring(
prefixEnd
)) ?
this
.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) :
new
Resource[]
{
this
.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)}
;
}
}
isPattern:

注:本来以为是数字 ,后面才发现ASCII代表的数字:详情可查
https://baike.baidu.com/item/ASCII/309296?fr=aladdin
也经过测试发现是根据十进制的ASCII码参与运算的。


也就是可以这么写:
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
(
"
con*.xml
"
);
更多的例子

具体怎么解析ant风格的就不写了。
配置文件加载
入口方法在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader:

//
加载
Resource
[] resources
=
((
ResourcePatternResolver
) resourceLoader)
.
getResources(location);
//
解析
int
loadCount
=
loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
最终逐个调用XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法:

Resource是代表一种资源的接口,其类图:
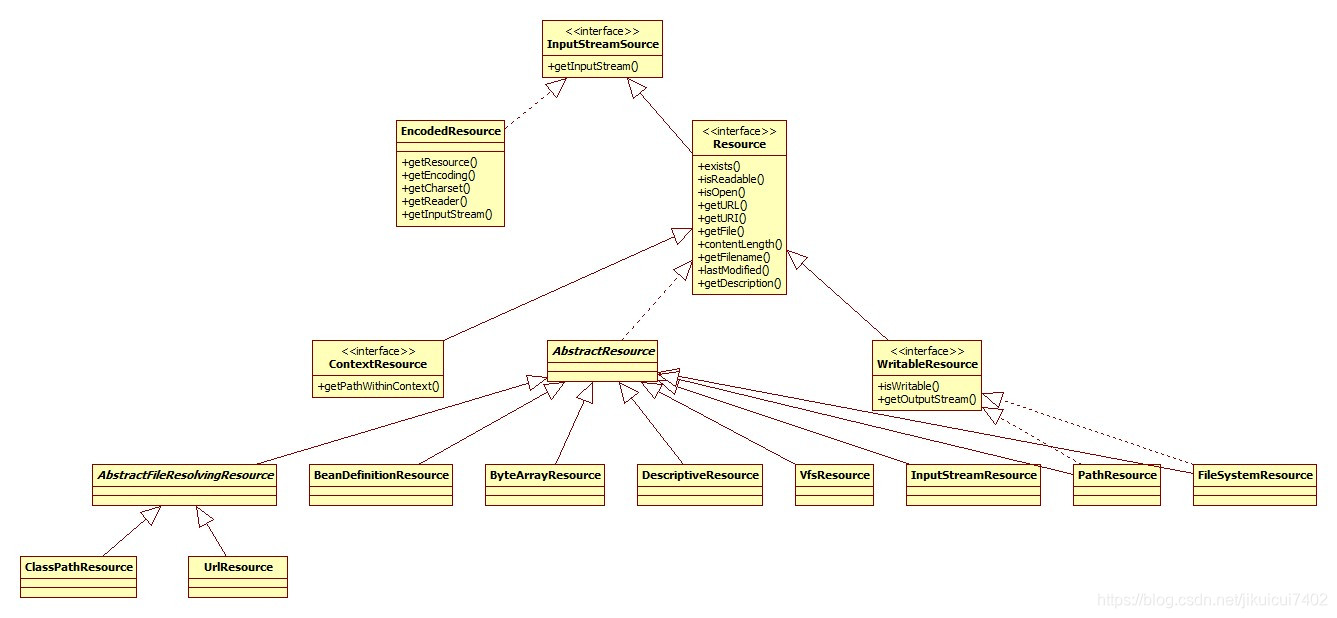
EncodedResource扮演的其实是一个装饰器的模式,为InputStreamSource添加了字符编码(虽然默认为null)。这样为我们自定义xml配置文件的编码方式提供了机会。
之后关键的源码只有两三行:(这个是4.1.1版本中的源码,关键部分为标红的地方)
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = (Set)this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!((Set)currentResources).add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
} else {
int var5;
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()
;
try {
InputSource inputSource =
new
InputSource(inputStream)
;
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
var5 =
this
.doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource
,
encodedResource.getResource())
;
} finally {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException var15) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), var15);
} finally {
((Set)currentResources).remove(encodedResource);
if (((Set)currentResources).isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
return var5;
}
}
 其实也差不多。
其实也差不多。
InputSource是org.xml.sax的类。
doLoadBeanDefinitions:
protected
int
doLoadBeanDefinitions(
InputSource
inputSource,
Resource
resource) {
Document
doc
=
doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);//下面先讲讲这部分 $
doLoadDocument
$ 加载document
return
registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);//在说说这部分$
registerBeanDefinitions
$ 主要是注册bean
}
(4.1.1版本有些不同,主要在抛出异常方面)
(
$
doLoadDocument
$
)doLoadDocument:
protected
Document
doLoadDocument(
InputSource
inputSource,
Resource
resource) {
return
this
.
documentLoader
.
loadDocument
(inputSource,
getEntityResolver
(),
this
.
errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
//loadDocument方法实际调用的是DefaultDocumentLoader里面的loadDocument方法 #DefaultDocumentLoader.loadDocument
}

实际这个documentLoader就是
DefaultDocumentLoader
.
此类是DocumentLoader接口的唯一实现。
getEntityResolver
方法返回ResourceEntityResolver,上面说过了。errorHandler是一个SimpleSaxErrorHandler对象。


校验模型
其实就是确定xml文件使用xsd方式还是dtd方式来校验,忘了的话左转度娘。Spring会通过读取xml文件的方式判断应该采用哪种。
NamespaceAware
默认false,因为默认配置了校验为true。(其实这个
默认校验
为true我还没找到)

DefaultDocumentLoader.loadDocument:
@Override
public
Document
loadDocument(
InputSource
inputSource,
EntityResolver
entityResolver,
ErrorHandler
errorHandler,
int
validationMode,
boolean
namespaceAware) {
//
这里就是老套路了,可以看出,Spring还是使用了dom的方式解析,即一次全部load到内存
DocumentBuilderFactory
factory
=
createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
DocumentBuilder
builder
=
createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return
builder
.
parse(inputSource);
}
createDocumentBuilderFactory比较有意思:

如上图所示,4.1.1版本的是这样,我跟确信下面的版本更成熟,因为很多地方是常量控制,4.1.1都是写死的常量。
protected
DocumentBuilderFactory
createDocumentBuilderFactory(
int
validationMode,
boolean
namespaceAware{
DocumentBuilderFactory
factory
=
DocumentBuilderFactory
.
newInstance();
factory
.
setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware);
if
(validationMode
!=
XmlValidationModeDetector
.
VALIDATION_NONE
) {
//
此方法设为true仅对dtd有效,xsd(schema)无效
factory
.
setValidating(
true
);
if
(validationMode
==
XmlValidationModeDetector
.
VALIDATION_XSD
) {
//
Enforce namespace aware for XSD...
//
开启xsd(schema)支持
factory
.
setNamespaceAware(
true
);
//
这个也是Java支持Schema的套路,可以问度娘
factory
.
setAttribute(
SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE
,
XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE
);
}
}
return
factory;
}
Bean解析(这部分放在 spring源码解析---spring-core(二))


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号