信号(第六章)
Unix/Linux支持31种不同的信号,每种信号在signal.h文件中都有定义。
#define SIGHUP 1
#define SIGINT 2
#define SIGQUIT 3
#define SIGILL 4
#define SIGTRAP 5
#define SIGABRT 6
#define SIGIOT 6
#define SIGBUS 7
#define SIGFPE 8
#define SIGKILL 9
#define SIGUSR1 10
#define SIGSEGV 11
#define SIGUSR2 12
#define SIGPIPE 13
#define SIGALRM 14
#define SIGTERM 15
#define SIGSTKFLT 16
#define SIGCHLD 17
#define SIGCONT 18
#define SIGSTOP 19
#define SIGTSTP 20
#dpfine STGTTTN 21
#define SIGTTOU 22
#define SIGURG 23
#define SIGXCPU 24
#define SIGXFSZ 25
#define SIGVTALRM 26
#define SIGPROF 27
#define SIGWINCH 28
#define SIGPOLL 29
#define SIGPWR 30
#define SIGSYS 31
问题与解决思路
为什么多个Ctrl+c只处理了一次?
这应该和信号处理的具体实现有关,其数据结构是位图,而不是链表或者数组
当一个信号产生时,对应的位就会翻转成1,信号处理后,该位翻转回0
也就是说,如果在信号处理期间,多次Ctrl+c,只是多次让该信号对应的位变成1,其效果和一次Ctrl+c的效果一样
实践内容
signal函数
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <signal.h>
3 void sig_catch(int signo){
4 printf("catch you : %d\n",signo);
5 return ;
6 }
7
8 int main(){
9 signal(SIGINT,sig_catch);
10 while(1);
11 return 0;
12 }
sigaction函数
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <signal.h>
3 void sig_catch(int signo){
4 if(signo == SIGINT){
5 printf("catch you SIGINT: %d\n",signo);
6 }else if(signo == SIGQUIT){
7 printf("catch you SIGQUIT: %d\n",signo);
8 }
9 return ;
10 }
11
12 int main(){
13 struct sigaction act,oldact;
14 act.sa_handler = sig_catch;
15 sigemptyset(&(act.sa_mask));
16 act.sa_flags = 0;
17 int ret = sigaction(SIGINT,&act,&oldact);
18 ret = sigaction(SIGQUIT,&act,&oldact);
19 signal(SIGINT,sig_catch);
20 while(1);
21 return 0;
22 }
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <string.h>
jmp_buf env;
int count = 0;
void handler(int sig, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *context)
{
printf("handler: sig=%d from PID=%d UID=%d count=%d\n",
sig, siginfo->si_pid, siginfo->si_uid, ++count);
if (count >= 4) // let it occur up to 4 times
longjmp(env, 1234);
}
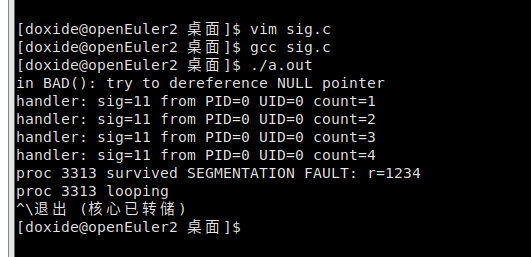
int BAD()
{
int *ip = 0;
printf("in BAD(): try to dereference NULL pointer\n");
*ip = 123; // dereference a NULL pointer
printf("should not see this line\n");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int r;
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act, 0, sizeof(act));
act.sa_sigaction = &handler;
act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &act, NULL);
if ((r = setjmp(env)) == 0)
BAD();
else
printf("proc %d survived SEGMENTATION FAULT: r=%d\n", getpid(), r);
printf("proc %d looping\n", getpid());
while (1)
;
}
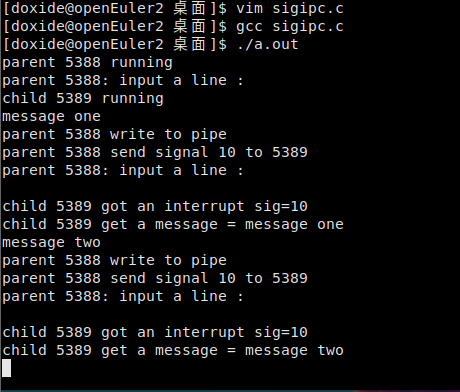
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <signal.h>
3 #include <fcntl.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6
7 #define LEN 64
8 int ppipe[2]; // pipe descriptors
9 int pid; // child pid
10 char line[LEN];
11
12 int parent()
13 {
14 printf("parent %d running\n", getpid());
15 close(ppipe[0]); // parent = pipe writer
16 while(1){
17 printf("parent %d: input a line : \n", getpid());
18 fgets(line, LEN, stdin);
19 line[strlen(line)-1] = 0; // kill \n at end
20 printf("parent %d write to pipe\n", getpid());
21 write(ppipe[1], line, LEN); // write to pipe
22 printf("parent %d send signal 10 to %d\n", getpid(), pid);
23 kill(pid, SIGUSR1); // send signal to child process
24 } }
25 void chandler(int sig)
26 {
27 printf("\nchild %d got an interrupt sig=%d\n", getpid(), sig);
28 read(ppipe[0], line, LEN); // read pipe
29 printf("child %d get a message = %s\n", getpid(), line);
30 }
31 int child()
32 {
33 char msg[LEN];
34 int parent = getppid();
35 printf("child %d running\n", getpid());
36 close(ppipe[1]); // child is pipe reader
37 signal(SIGUSR1, chandler); // install signal catcher
38 while(1);
39 }
40 int main()
41 {
42 pipe(ppipe); // create a pipe
43 pid = fork(); // fork a child process
44 if (pid) // parent
45 parent();
46 else
47 child();
48 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号