SpringMVC的URL映射器注册篇之SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
写在前面
本文源码项目中用到的依赖有 spring-webmvc,javax.servlet-api,测试依赖有 junit 和 spring-test。
本文不对 web.xml 中的配置做过多阐述。更多参考文档:
本文不去细究 <property> 标签内的子标签是如何变成 setXXX 的参数对象的,但是会关心 setXXX 方法内做了什么。
主要的四类 “Handler”:
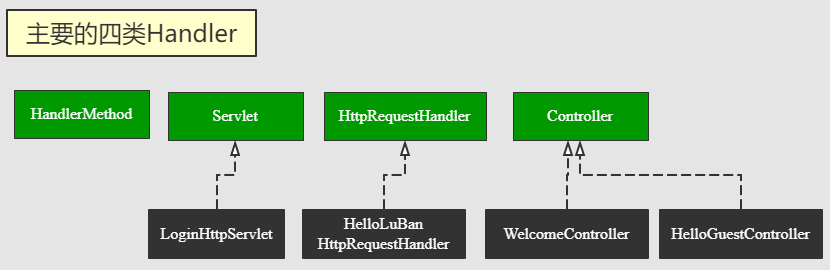
接下来我们准备把实现了 Controller 和 HttpRequestHandler 以及继承了 HttpServlet 的类加入到 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 中
注意:本文中没有实现 HandlerMethod 的映射,另外,这里的 Controller 指的是 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller,而不是我们常用的注解 @Controller。
映射配置
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 可以通过setMappings(Properties mappings) 和 setUrlMap(Map<String, ?> urlMap)来设置 url 和 “Handler” 的映射。
setMappings
方式一:使用 <props> 填入多个 <prop>
spring-mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="welcomeController" class="coderead.springframework.mvc.WelcomeController" />
<bean id="helloGuestController" class="coderead.springframework.mvc.HelloGuestController" />
<bean id="helloLuBanController" class="coderead.springframework.mvc.HelloLuBanHttpRequestHandler" />
<bean id="loginHttpServlet" class="coderead.springframework.mvc.LoginHttpServlet" />
<!-- Fixed problem : javax.servlet.ServletException: No adapter for handler [coderead.springframework.mvc.LoginHttpServlet@2f2f30df]-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleServletHandlerAdapter"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter" />
<bean id="simpleUrlHandlerMapping" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<!-- 方式一: props 中填入 prop 列表-->
<!-- key 是 url,属性值是 Bean 的 id。-->
<props>
<prop key="/welcome">welcomeController</prop>
<prop key="/hello">helloGuestController</prop>
<prop key="/hi">helloLuBanController</prop>
<prop key="/login">loginHttpServlet</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
方式二:使用 <value> 填入配置文件文本
<!-- 方式二: value 中填入配置文件内容 -->
<!-- 等号左边是URL模式,等号右边是 Bean 的 id。 -->
<property name="mappings">
<value>
/welcome=welcomeController
/hello=helloGuestController
/hi=helloLuBanController
/login=loginHttpServlet
</value>
</property>
用这段代码代替方式一中的 <property name="mappings"/>
方式三:<map> 填入 <entry> 键值对
<!-- 方式三: map -->
<!-- entry: key 保存 URL 模式,value 保存 Bean id。 -->
<property name="mappings">
<map>
<entry key="/welcome" value="welcomeController" />
<entry key="/hello" value="helloGuestController" />
<entry key="/hi" value="helloLuBanController" />
<entry key="/login" value="loginHttpServlet" />
</map>
</property>
用这段代码代替方式一中的 <property name="mappings"/>
方式四:使用 PropertiesFactoryBean 和 properties 文件
<!-- 方式四:properties 配置文件 -->
<property name="mappings">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean">
<property name="location" value="classpath:spring/url-mapping.properties"/>
</bean>
</property>
url-mapping.properties
/welcome=welcomeController
/hello=helloGuestController
/hi=helloLuBanController
/login=loginHttpServlet
setUrlMap
将 <property name="mappings"/> 替换为 <property name="urlMap"/> ,经过我的测试,上面的四种方式都依然奏效! 我的测试方法参考了 SpringMVC 测试 mockMVC 这篇博客,基于 MockMvc 进行了测试。
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 源码分析
填充 urlMap
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 只有 urlMap 成员变量
private final Map<String, Object> urlMap = new HashMap();
因此,setUrlMap 和 setMapping 无论调用那个,最终都会为 urlMap 增加键值对。
setUrlMap
// 其中 setUrlMap 比较简单,没什么好说的
public void setUrlMap(Map<String, ?> urlMap) {
this.urlMap.putAll(urlMap);
}
setMapping
public void setMappings(Properties mappings) {
// 顾名思义,把 mappings 中的键值对合并到 urlMap 中
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, this.urlMap);
}
org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap
public static <K, V> void mergePropertiesIntoMap(@Nullable Properties props, Map<K, V> map) {
String key;
Object value;
if (props != null) {
// 遍历 props 的键,并在循环体执行完毕后,将键值对存入 map
for(Enumeration en = props.propertyNames(); en.hasMoreElements(); map.put(key, value)) {
key = (String)en.nextElement();
value = props.get(key);
if (value == null) {
value = props.getProperty(key);
}
}
}
}
这个方法就是把 Properties 的 key=value 取出来,再放入目标 map 中。
填充 handlerMap
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 是 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 的父类,其中一个成员变量 Map<String, Object> handlerMap 存储 key 是 url patterns,value 就是 “Handler” 对象
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping#registerHandlers
protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.trace("No patterns in " + formatMappingName());
}
else {
urlMap.forEach((url, handler) -> {
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
});
// 这段 if 代码没有实质性作用,仅仅是为了打印一段日志,可以忽略
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
List<String> patterns = new ArrayList<>();
if (getRootHandler() != null) {
patterns.add("/");
}
if (getDefaultHandler() != null) {
patterns.add("/**");
}
patterns.addAll(getHandlerMap().keySet());
logger.debug("Patterns " + patterns + " in " + formatMappingName());
}
}
}
细节一:urlMap.forEach 是 Java8 Lambda 表达式的写法,等同于下面这段 foreach 代码。
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
Object handler = entry.getValue();
}
细节二:对 url 字符串的前置处理,确保 url 以 / 开头,并且开头和结尾没有空格符。
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping#registerHandler
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}
细节一:根据字符串类型的 handler,生成 Bean。
resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName);
细节二:obtainApplicationContext()
obtainApplicationContext() 是父类 ApplicationObjectSupport 的方法,该类实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口。
Spring容器会在上下文创建完成后,主动回调 void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) 方法,该方法会调用 protected void initApplicationContext()
public final void setApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !this.isContextRequired()) {
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
} else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
if (!this.requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + this.requiredContextClass().getName() + "]");
}
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
this.initApplicationContext(context);
} else if (this.applicationContext != context) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" + this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]");
}
}
细节三:SimpleUrlHandlerMapping#initApplicationContext() 何时触发?
ApplicationContext 实例创建完成,回调 ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) 之后。
获取源码
获取项目源码:
git clone https://gitee.com/kendoziyu/coderead-spring-mvc-parent.git
其中 url-handler-mapping 项目就是本文的示例代码。你可以运行项目进行访问,也可以直接运行测试。
mvn jetty:run
通过 jetty:run 命令直接启动项目,如果你使用的是 IDEA,那你可以参考这篇文章:使用maven-Jetty9-plugin插件运行第一个Servlet
mvn test
通过 mvn test 命令执行测试用例,测试请求是否可以正常返回。这个测试用例主要是方便你修改 spring-mvc.xml 后,检验基本功能是否正常。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号