C++提高编程 3 STL常用容器 -map/multiset容器
3.9 map/multimap容器
3.9.1 map基本概念
简介:
1、map中所有元素都是pair
2、pair中第一个元素为key(键值),起到索引作用,第二个元素为value(实值)
3、所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序
本质:map/multimap属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现
优点:可以根据key值快速查到value值
区别:1、map不允许容器中有重复的key值元素;2、multimap允许容器中有重复发key值元素
3.9.2 map构造与赋值
对map容器进行构造和赋值操作
函数原型:
构造:
map<T1,T2>mp; //map默认构造函数;
map(const map &mp) //拷贝构造函数
赋值:
map& operator=(const map &mp); //重载等号操作符
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<map> //map容器 构造与赋值 void printMap(map<int, int>&m) { for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << "key值为:" << it->first << " " << "value为:" << (*it).second << endl; } cout << endl; } void test1() { map<int, int> m; m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //(1,10)1为键值,起到索引作用,10为插入元素 m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40)); printMap(m); //拷贝构造 map<int, int>m2(m); printMap(m2); //赋值 map<int, int>m3; m3 = m2; printMap(m3); } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
打印结果:
key值为:1 value为:10
key值为:2 value为:20
key值为:3 value为:30
key值为:4 value为:40
key值为:1 value为:10
key值为:2 value为:20
key值为:3 value为:30
key值为:4 value为:40
key值为:1 value为:10
key值为:2 value为:20
key值为:3 value为:30
key值为:4 value为:40
3.9.3 map大小和交换
统计map容器大小以及交换map容器
函数原型:
size(); //返回容器中元素(统计大小)
empty(); //判断是否为空
swap(); //交换容器
#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; //map容器 大小和交换 void test1() { map<int, int>m; m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); if (m.empty()) { cout << "m为空" << endl; } else { cout << "m不为空" << endl; cout << "m的大小为:" << m.size() << endl; } } void printMap(map<int, int>& m) { for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " " << "value = " << (*it).second << endl; } cout << endl; } //交换 void test2() { map<int, int>m1; m1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); m1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); map<int, int>m2; m2.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 100)); m2.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 200)); m2.insert(pair<int, int>(6, 300)); cout << "交换前:" << endl; printMap(m1); printMap(m2); cout << "交换后:" << endl; m1.swap(m2); printMap(m1); printMap(m2); } int main() { //test1(); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; }
3.9.4 map插入和删除
map容器进行插入数据和删除数据

#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; //map容器 大小和交换 void printMap(map<int, int>& m) { for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " " << "value = " << (*it).second << endl; } cout << endl; } void test1() { map<int, int>m; //插入 //第一种(推荐使用) m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //第二种(更推荐使用) m.insert(make_pair(2, 20)); //第三种(不推荐使用) m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30)); //第四种(不推荐使用) []不建议插入,因为若输错一个没有的键值,它会默认赋值0给键值对应的value。用途 可以利用key访问到value; m[4] = 40; //cout << m[5] << endl; //key = 5 value = 0 printMap(m); // key = 1 value = 10 // key = 2 value = 20 // key = 3 value = 30 // key = 4 value = 40 //删除 m.erase(m.begin()); printMap(m); // key = 2 value = 20 // key = 3 value = 30 // key = 4 value = 40 //按照key删除 m.erase(3); printMap(m); // key = 2 value = 20 // key = 4 value = 40 //清空 m.erase(m.begin(), m.end()); //两行换行符 m.clear(); //两行换行符 printMap(m); // // // // } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
3.9.5 map查找和统计

#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; //map容器 查找和统计void test1() { map<int, int>m; //查找 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 40)); map<int, int>::iterator pos = m.find(3); //查找key对应的元素 if (pos != m.end()) { cout << "查找到了该元素 key = " << (*pos).first << " " << "value = " << pos->second << endl; } else { cout << "未查找到该元素" << endl; } //统计 int num = m.count(3); //查找map里有几个key为3的元素 //count统计而言,结果要么为1,要么为0;因为map不允许插入重复的key值的元素。multimap的count统计可能大于1 cout << "num = " << num << endl; //num = 1 } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
3.9.6 map容器排序

#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; //map容器 排序 class myCompare { public: bool operator()(int v1,int v2) const { //降序 return v1 > v2; } }; void test1() { map<int, int>m; //查找 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); m.insert(make_pair(4, 40)); m.insert(make_pair(5, 50)); for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " " << "value = " << (*it).second << endl; /* key = 1 value = 10 key = 2 value = 20 key = 3 value = 30 key = 4 value = 40 key = 5 value = 50 */ } } void test2() { map<int, int, myCompare>m; //查找 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20)); m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30)); m.insert(make_pair(4, 40)); m.insert(make_pair(5, 50)); for (map<int, int, myCompare>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " " << "value = " << (*it).second << endl; } /* key = 5 value = 50 key = 4 value = 40 key = 3 value = 30 key = 2 value = 20 key = 1 value = 10 */ } int main() { //test1(); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; }
总结:
1、利用仿函数可以指定map容器的排序规则
2、对于自定义数据类型,map必须要指定排序规则,同set容器
3.10 案例-员工分组

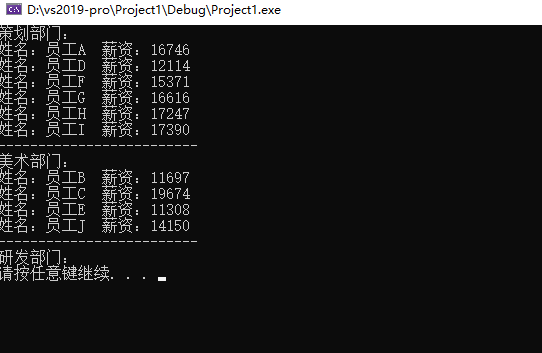
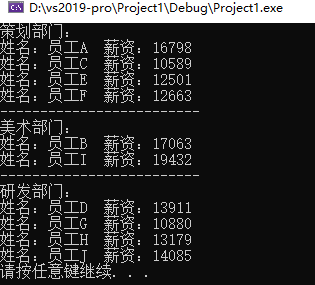
#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; #include<string> #include<vector> #include<ctime> #define CEHUA 0 #define MEISHU 1 #define YANFA 2 class Worker { public: string m_Name; int m_Salary; }; void createWorker(vector<Worker>& v) { string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ"; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Worker worker; worker.m_Name = "员工"; worker.m_Name += nameSeed[i]; worker.m_Salary = rand() % 10000 + 10000; //10000 ~ 19999 //将员工放入到容器中 v.push_back(worker); } } //员工分组 void setGroup(vector<Worker>& v, multimap<int, Worker>& m) { for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { //产生随机部门编号 int deptID = rand() % 3; //0 1 2 //将员工插入分组中 //key部门编号,value具体员工 m.insert(make_pair(deptID, *it)); //it是迭代器,*it是具体的人 } } void showWorkerByGroup(multimap<int, Worker>& m) {/* //自己想的 // 0 A B C 1 D E 2 F G... cout << "策划部门:" << endl; multimap<int, Worker>::iterator pos = m.find(CEHUA); for (; pos != m.find(MEISHU); pos++) { cout<<"姓名:"<<pos->second.m_Name<<" "<<"薪资:"<<pos->second.m_Salary<<endl; } cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "美术部门:" << endl; pos = m.find(MEISHU); for (; pos != m.find(YANFA); pos++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " " << "薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "研发部门:" << endl; pos = m.find(YANFA); for (; pos != m.end(); pos++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " " << "薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } */ //老师的 // 0 A B C 1 D E 2 F G... cout << "策划部门:" << endl; multimap<int, Worker>::iterator pos = m.find(CEHUA); int count = m.count(CEHUA); //统计具体人数 int index = 0; for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " " << "薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "美术部门:" << endl; pos = m.find(MEISHU); count = m.count(MEISHU); //统计具体人数 index = 0; for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " " << "薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "研发部门:" << endl; pos = m.find(YANFA); count = m.count(YANFA); //统计具体人数 index = 0; for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " " << "薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } } int main() { srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //1、创建员工 vector<Worker>vWorker; createWorker(vWorker); //2、员工分组 multimap<int, Worker>mWorker; setGroup(vWorker, mWorker); //3、分组显示员工 showWorkerByGroup(mWorker); system("pause"); return 0; }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构