十一、文件和目录——文件操作函数(续)
11.3 truncate 和 ftruncate 函数 --- 文件截短函数
11.3.1 函数介绍
改变文件大小的函数
相关函数 open
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 int truncate(const char * path, off_t length); 3 int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
- 函数说明
- 在文件尾端处截去一些数据以缩短文件
- 将一个文件的长度截短为 0 是一个特例,用 O_TRUNC 标志可以做到这一点
- 如果该文件以前的长度大于 length,则超过 length 以外的数据就不再能存取。如果以前的长度短于 length,则其后果与系统有关
- truncate()会将参数 path 指定的文件大小改为参数 length 指定的大小。如果原来的文件大小比参数 length 大,则超过的部分会被删去。
- ftruncate()会将参数 fd 指定的文件大小改为参数 length 指定的大小。参数 fd 为已打开的文件描述词,而且必须是以写入模式打开的文件。如果原来的文件大小比参数 length 大,则超过的部分会被删去。
- 参数:
- @ length:文件截短后的长度
- 返回值
- 执行成功则返回0,失败返回 -1 ,错误原因存于 errno。
- 错误代码
- EACCESS 参数path所指定的文件无法存取。
- EBADF 参数fd文件描述词为无效的或该文件已关闭。(ftruncate)
- EROFS 欲写入的文件存在于只读文件系统内
- EFAULT 参数path指针超出可存取内存空间
- EINVAL 参数path包含不合法字符
- ENAMETOOLONG 参数path太长
- ENOTDIR 参数path路径并非一目录
- EINVAL 参数fd 为一socket 并非文件,或是该文件并非以写入模式打开。(ftruncate)
- EISDIR 参数path 指向一目录
- ETXTBUSY 参数path所指的文件为共享程序,而且正被执行中
- ELOOP 参数path’有过多符号连接问题
- EIO I/O 存取错误。
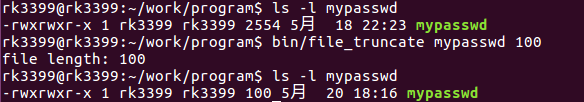
11.3.2 例子
file_truncate.c
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 #include <fcntl.h> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <errno.h> 6 7 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 8 { 9 if(argc < 3) 10 { 11 fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s file length\n", argv[0]); 12 exit(1); 13 } 14 15 //判断文件是否有写的权限 16 if(access(argv[1], W_OK) < 0) { 17 perror("write permission error"); 18 exit(1); 19 } 20 21 //将文件截短为传入的长度 22 if(truncate(argv[1], atoi(argv[2])) < 0) { 23 perror("truncate error"); 24 exit(1); 25 } 26 27 //查看文件长度 28 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); 29 if(fd < 0) { 30 perror("open error"); 31 exit(1); 32 } 33 34 long len = lseek(fd, 0L, SEEK_END); 35 printf("file length: %ld\n", len); 36 close(fd); 37 38 return 0; 39 }
编译运行: