四十四、Linux 线程——线程同步之死锁以及线程和信号
44.1 死锁
- 死锁:
- 两个线程试图同时占有两个资源,并按不同的次序锁定相应的共享资源
- 解决方式:
- 按相同的次序锁定相应的共享资源
- 使用函数 pthread_mutex_trylock(),它是函数 pthread_mutex_lock() 的非阻塞版本
44.2 线程和信号
44.2.1 介绍
- 进程中每个线程都有自己的信号屏蔽字和信号未决字
- 信号的处理方式是进程中所有线程共享的
- 进程中的信号是递送到单个线程的
- 定时器是进程资源,进程中所有的线程共享相同的定时器
- 子线程调用 alarm() 函数产生的 alarm 信号发送给主控线程
1 #include <signal.h> 2 int pthread_sigmask(int how, const sigset_t *restrict set, sigset_t *restrict oset);
- 函数功能:线程的信号屏蔽
- 返回值:成功返回0,出错,返回错误编号
44.2.2 例子1
子线程调用 alarm() 函数产生的 alarm 信号发送给主控线程
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <signal.h> 4 #include <pthread.h> 5 #include <unistd.h> 6 7 void sig_handler(int signo) 8 { 9 printf("pthread id in the sig_handler: %lx\n", pthread_self()); 10 if(signo == SIGALRM) { 11 printf("timeout...\n"); 12 } 13 alarm(2); 14 } 15 16 void *th_fn(void *arg) 17 { 18 if(signal(SIGALRM, sig_handler) == SIG_ERR){ 19 perror("signal sigalrm error"); 20 } 21 22 /** 在子线程中设置定时器 */ 23 alarm(2); 24 25 int i; 26 for(i = 1; i <= 555550; i++){ 27 printf("(%lx) i: %d\n", pthread_self(), i); 28 sleep(1); 29 } 30 return (void *)0; 31 } 32 33 int main(void) 34 { 35 int err; 36 pthread_t th; 37 pthread_attr_t attr; 38 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 39 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 40 41 if((err = pthread_create(&th, &attr, th_fn, (void *)0)) != 0) { 42 perror("pthread create error"); 43 } 44 45 while(1){ 46 printf("control thread(%lx) is running\n", pthread_self()); 47 sleep(10); 48 } 49 50 printf("control thread over\n"); 51 52 return 0; 53 }
编译运行结果如下:
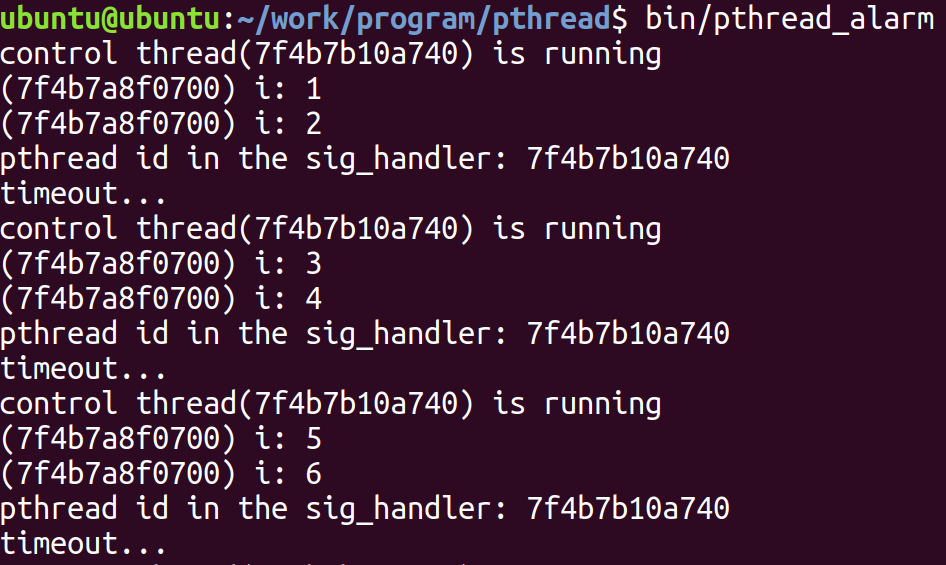
44.2.3 例子 2
线程信号屏蔽,线程发送信号给其他线程,达到一定条件后,另一线程终止另一个线程
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <signal.h> 4 #include <pthread.h> 5 #include <unistd.h> 6 7 void sig_handler(int signo) 8 { 9 printf("pthread id in the sig_handler: %lx\n", pthread_self()); 10 if(signo == SIGALRM) { 11 printf("timeout...\n"); 12 } 13 alarm(2); 14 } 15 16 void *th_fn(void *arg) 17 { 18 if(signal(SIGALRM, sig_handler) == SIG_ERR){ 19 perror("signal sigalrm error"); 20 } 21 22 /** 在子线程中设置定时器 */ 23 alarm(2); 24 25 int i; 26 for(i = 1; i <= 555550; i++){ 27 printf("(%lx) i: %d\n", pthread_self(), i); 28 sleep(1); 29 } 30 return (void *)0; 31 } 32 33 void *th_fn2(void *arg) 34 { 35 pthread_t th1 = (pthread_t)arg; 36 int i; 37 for(i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ 38 if(i == 5){ 39 /** 终止线程 1 的运行 */ 40 pthread_cancel(th1); 41 alarm(0); 42 } 43 printf("(%lx) i: %d\n", pthread_self(), i); 44 sleep(1); 45 } 46 return (void *)0; 47 } 48 49 int main(void) 50 { 51 int err; 52 pthread_t th, th2; 53 pthread_attr_t attr; 54 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 55 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 56 57 if((err = pthread_create(&th, &attr, th_fn, (void *)0)) != 0) { 58 perror("pthread create error"); 59 } 60 61 if((err = pthread_create(&th2, &attr, th_fn2, (void *)th)) != 0) { 62 perror("pthread create error"); 63 } 64 65 sigset_t set; 66 sigemptyset(&set); 67 sigaddset(&set, SIGALRM); 68 /** 对主控线程屏蔽 SIGALRM 信号 */ 69 pthread_sigmask(SIG_SETMASK, &set, NULL); 70 71 72 while(1){ 73 printf("control thread(%lx) is running\n", pthread_self()); 74 sleep(10); 75 } 76 77 printf("control thread over\n"); 78 79 return 0; 80 }
编译运行:




