Go语言——值方法 & 指针方法
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func main() { 28 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 29 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 30 31 _, ok2 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 32 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 33 }
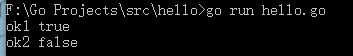
自定义类型SortableStrings实现了接口sort.Interface中3个开放函数。自定义接口Sortable,除了包含sort.Interface的3个函数外,增加的Sort没有被SortableStrings实现。所以SortableStrings只实现了一个接口,即sort.Interface
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 33 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 34 35 _, ok2 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 36 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 37 }

对自定义类型SortableStrings增加方法Sort,其实现是调用sort.Sort函数,该函数接受一个类型为sort.Interface的参数值,并利用这个值的Len,Less,Swap方法进行排序。
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 33 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 34 35 _, ok2 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 36 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 37 }
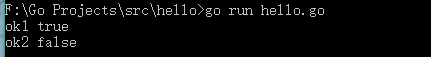
接口Sortable中有4个函数需要实现,虽然SortableStrings实现了4个函数,但是Sort版的实现,接收器是指针类型。SortableStrings{}是值类型,不能访问基本类型SortableStrings接收器是指针的方法(即Sort),相当于SortableStrings{}只实现了Len、Less、Swap 3个函数,少实现一个函数,所以不是Sortable类型
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 33 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 34 35 _, ok2 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 36 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 37 }
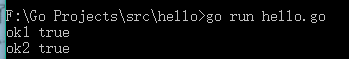
&SortableStrings{}是SortableStrings{}的指针类型,可以访问到基本类型SortableStrings中的4个函数。所以是Sortable的一个实现
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 _, ok1 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 33 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 34 35 _, ok2 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 36 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 37 }

&SortableStrings{}是SortableStrings{}的指针类型。指针类型可以访问基本类型中接收器为值(或者指针)的类型。
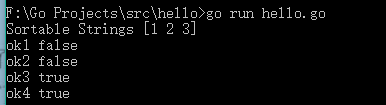
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 ss := SortableStrings{"2", "3", "1"} 33 ss.Sort() 34 fmt.Println("Sortable Strings", ss) 35 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 36 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 37 38 _, ok2 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 39 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 40 41 _, ok3 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 42 fmt.Println("ok3", ok3) 43 44 _, ok4 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 45 fmt.Println("ok4", ok4) 46 }

1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self *SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self *SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self *SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 ss := SortableStrings{"2", "3", "1"} 33 ss.Sort() 34 fmt.Println("Sortable Strings", ss) 35 _, ok1 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 36 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 37 38 _, ok2 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 39 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 40 41 _, ok3 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 42 fmt.Println("ok3", ok3) 43 44 _, ok4 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 45 fmt.Println("ok4", ok4) 46 }
上面关于“XX可以访问OO”的描述中,“访问“一词用的不准确。值变量可以访问接收器是指针类型的方法,指针变量也可以访问接收器是值类型的方法
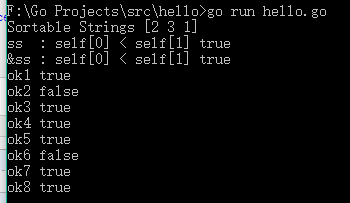
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "sort" 6 ) 7 8 type SortableStrings [3]string 9 10 type Sortable interface { 11 sort.Interface 12 Sort() 13 } 14 15 func (self SortableStrings) Len() int { 16 return len(self) 17 } 18 19 func (self SortableStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { 20 return self[i] < self[j] 21 } 22 23 func (self SortableStrings) Swap(i, j int) { 24 self[i], self[j] = self[j], self[i] 25 } 26 27 func (self *SortableStrings) Sort() { 28 sort.Sort(self) 29 } 30 31 func main() { 32 ss := SortableStrings{"2", "3", "1"} 33 ss.Sort() //值变量可以访问接收器是值类型的方法 34 fmt.Println("Sortable Strings", ss) 35 36 fmt.Println("ss : self[0] < self[1]", ss.Less(0, 1)) 37 fmt.Println("&ss : self[0] < self[1]", (&ss).Less(0, 1)) //指针变量可以访问接收器是值类型的方法 38 39 _, ok1 := interface{}(ss).(sort.Interface) 40 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) 41 42 _, ok2 := interface{}(ss).(Sortable) 43 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) 44 45 _, ok3 := interface{}(&ss).(sort.Interface) 46 fmt.Println("ok3", ok3) 47 48 _, ok4 := interface{}(&ss).(Sortable) 49 fmt.Println("ok4", ok4) 50 51 _, ok5 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 52 fmt.Println("ok5", ok5) 53 54 _, ok6 := interface{}(SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 55 fmt.Println("ok6", ok6) 56 57 _, ok7 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(sort.Interface) 58 fmt.Println("ok7", ok7) 59 60 _, ok8 := interface{}(&SortableStrings{}).(Sortable) 61 fmt.Println("ok8", ok8) 62 }
所以上面”访问“一词用的不准确。值变量可以访问接收器是值类型的方法 还是 指针变量可以访问接收器是值类型的方法,都是编译器帮我们做了部分转换工作。
http://play.golang.org/p/KG8-Qb7gqM
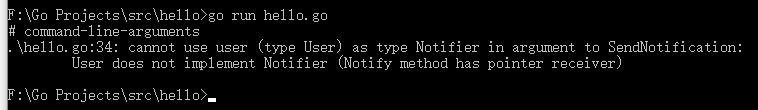
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "log" 5 ) 6 7 type User struct { 8 Name string 9 Email string 10 } 11 12 func (u *User) Notify() error { 13 log.Printf("User: Sending User Email To %s<%s>\n", 14 u.Name, 15 u.Email) 16 17 return nil 18 } 19 20 type Notifier interface { 21 Notify() error 22 } 23 24 func SendNotification(notify Notifier) error { 25 return notify.Notify() 26 } 27 28 func main() { 29 user := User{ 30 Name: "AriesDevil", 31 Email: "ariesdevil@xxoo.com", 32 } 33 34 SendNotification(user) 35 }
“值类型(或 指针类型)是否是该接口类型的实现呢?”
User的值类型变量不是 接口 Notifer的实现。也就是
1 _, ok1 := interface{}(user).(Notifier) 2 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) //false 3 4 _, ok2 := interface{}(&user).(Notifier) 5 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) //true 6 SendNotification(user)
上文报错,是因为user不是Notifier的实现,也就不能赋值给 SendNotification(notify Notifier)的notify.调用函数,参数就涉及到传值,只有相同类型或者其实现才可能相互赋值。如果不是调用函数,某一类型的值或者指针直接调用自己的方法(接收器是值或者指针)都是可以的
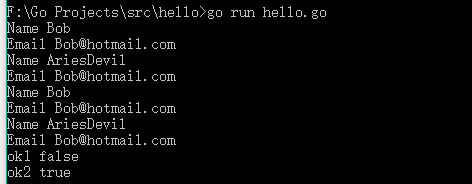
1 package main 2 3 import ( 4 "fmt" 5 "log" 6 ) 7 8 type User struct { 9 Name string 10 Email string 11 } 12 13 func (u *User) Notify() error { 14 log.Printf("User: Sending User Email To %s<%s>\n", 15 u.Name, 16 u.Email) 17 18 return nil 19 } 20 21 func (u User) NameString() { 22 u.Name = "Bob" 23 fmt.Println("Name", u.Name) 24 } 25 26 func (u *User) EmailString() { 27 u.Email = "Bob@hotmail.com" 28 fmt.Println("Email", u.Email) 29 } 30 31 type Notifier interface { 32 Notify() error 33 NameString() 34 EmailString() 35 } 36 37 func SendNotification(notify Notifier) error { 38 return notify.Notify() 39 } 40 41 func main() { 42 user := User{ 43 Name: "AriesDevil", 44 Email: "ariesdevil@xxoo.com", 45 } 46 47 user.NameString() 48 user.EmailString() 49 fmt.Println("Name", user.Name) 50 fmt.Println("Email", user.Email) 51 52 (&user).NameString() 53 (&user).EmailString() 54 fmt.Println("Name", (&user).Name) 55 fmt.Println("Email", (&user).Email) 56 57 _, ok1 := interface{}(user).(Notifier) 58 fmt.Println("ok1", ok1) //false 59 60 _, ok2 := interface{}(&user).(Notifier) 61 fmt.Println("ok2", ok2) //true 62 63 //SendNotification(user) 64 65 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号