Git分支

分支的本质
指向commit object的可变指针
master分支并不特殊
Git 的默认分支就是 master。如果你刚接触Git,恐怕对分支不会有啥概念。这种情况下,你所作的commit会在master分支上自动移动。 在多次提交操作之后,master分支指向最后那个commit object。
Git 的 “master” 分支并特殊,跟其它分支没有区别。 之所以几乎每一个仓库都有 master 分支,是因为 git init 命令默认创建它,并且大多数人都懒得去改动它。
但很多时候听别人说master分支,往往有一种 这个分支是稳定、无bug的分支。而develop往往预示这新功能,不稳定的分支。这和分支策略有关,但本质上这两个分支没区别,分支的本质就是指向commit object的指针。
分支策略
master 分支:保留完全稳定的代码——有可能仅仅是已经发布或即将发布的代码。
develop 或 next 分支:用于后续开发或者测试稳定性——这些分支不必保持绝对稳定,但是一旦达到稳定状态,它们就可以被合并入 master 分支了
proposed (建议)或 proposedupdates(建议更新)分支:包含一些不成熟的内容而不能进入 next 或者 master 分支,稳定性上弱于next
描述分支常用图示有线性图、流水线图
线性图
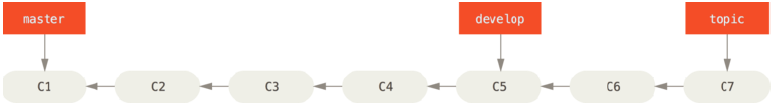
流水线图
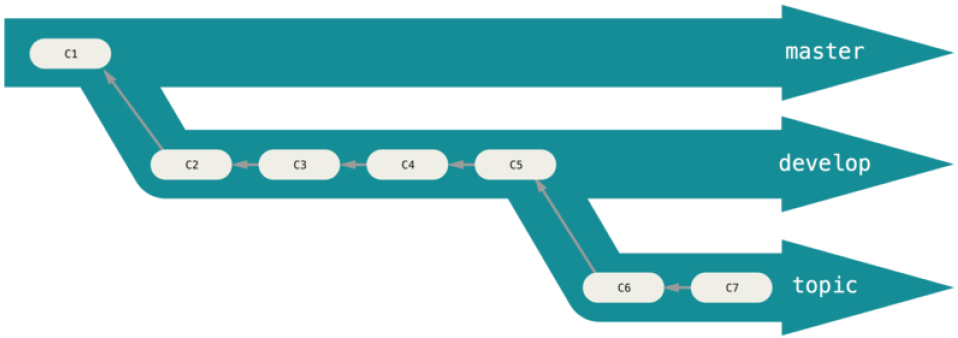
分支创建
使用git branch命令
演示
创建一个testing分支
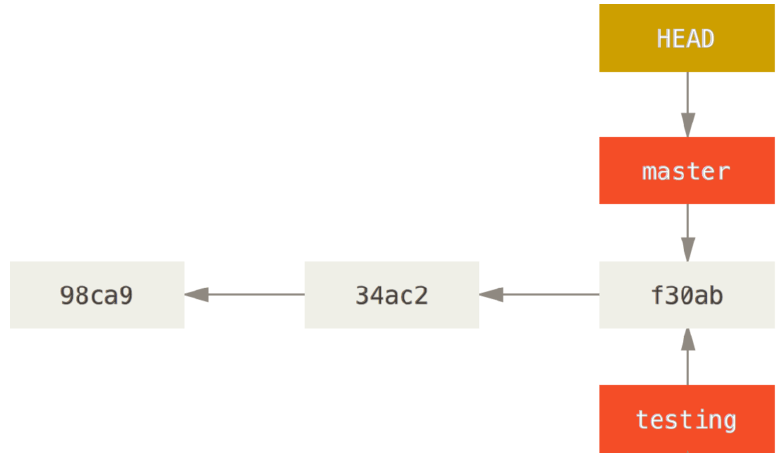
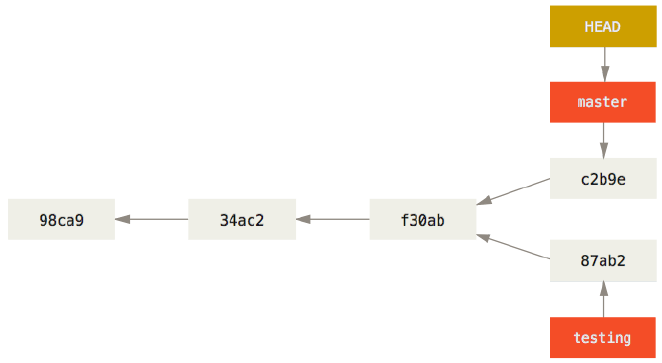
HEAD指针
可以将 HEAD 想象为当前分支的别名,他会告诉你当前所在分支

$ git log --oneline --decorate f30ab (HEAD, master, testing) add feature #32 - ability to add new 34ac2 fixed bug #1328 - stack overflow under certain conditions 98ca9 initial commit of my project
分支删除
git branch -d branch
切换分支
使用git checkout命令
演示
从master切换到testing
$ git checkout testing
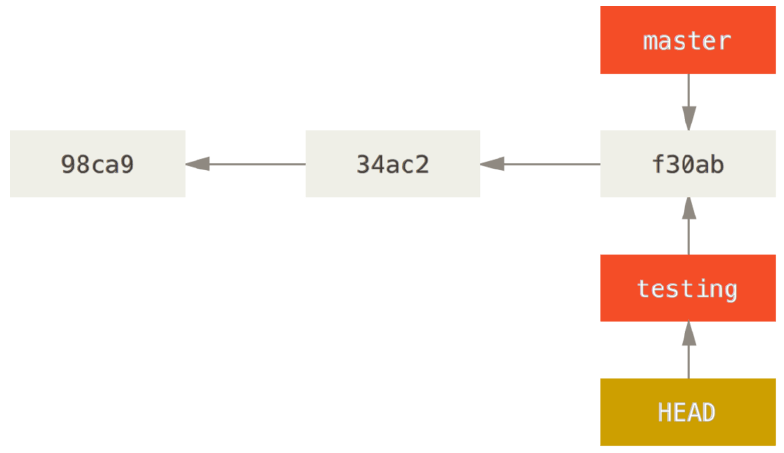
如果新建分支并同时切换到新分支上,使用-b参数。git checkout -b new_branch
查看分支历史
运行 git log --oneline --decorate --graph --all ,它会输出你的提交历史、各个分支的指向以及项目的分支分叉情况。
 View Code
View Code风险
当你切换分支的时候,Git 会重置你的工作目录,使其看起来像回到了你在那个分支上最后一次提交的样子。 Git 会自动添加、删除、修改文件以确保此时你的工作目录和这个分支最后一次提交时的样子一模一样。
分支合并
案例1

$ git checkout master $ git merge hotfix Updating f42c576..3a0874c Fast-forward index.html | 2 ++ 1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
首先切换到master分支,然后将hotfix分支合并到master上。如下图
合并前
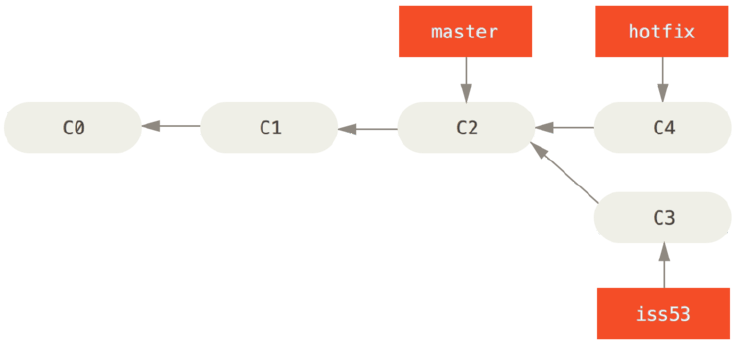
合并后

fast-forward:因为master在hotfix的上游,因此hotfix往master合并,Git只是简单讲分支指针下移。当你试图合并两个分支时,如果顺着一个分支走下去能够到达另一个分支,那么 Git 在合并两者的时候,只会简单的将指针向前推进(指针右移),因为这种情况下的合并操作没有需要解决的分歧——这就叫做 “快进(fast-forward)”。
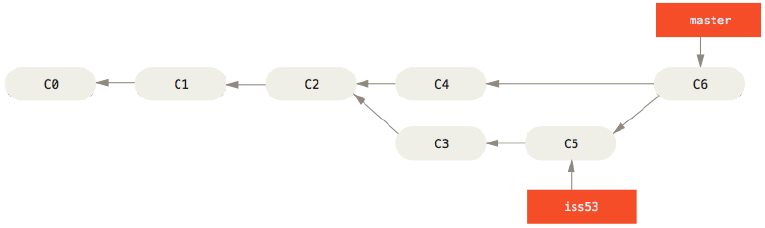
案例2
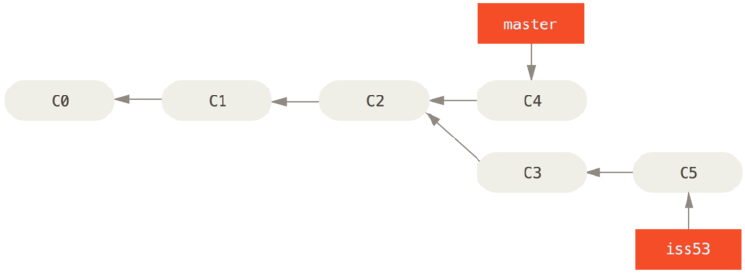
checkout切换到master分支,再将iss53分支合并到master

$ git checkout master Switched to branch 'master' $ git merge iss53 Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy. index.html | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
与举例1不同,master分支当前指针C4并不是iss53分支C5的直接祖先。也就是说C5没办法返回到C4,看箭头指向。
Git解决办法,每个分支末端+共同祖先(Git自己选最优共同祖先) 三个快照做合并,如下图
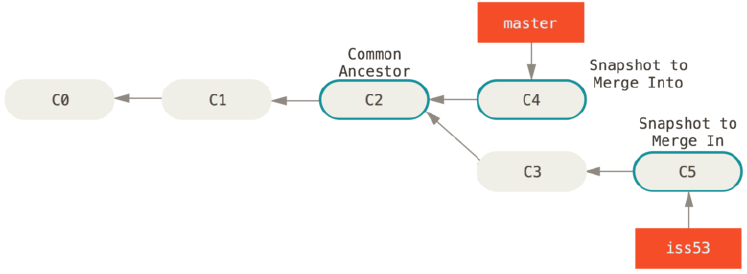
合并后效果
案例3
分支合并并非总是一帆风顺,当项目变大,文件增多后更是如此。如果你在两个不同的分支中,对同一个文件的同一个部分进行了不同的修改,Git 就没法合并它们。承接案例2,案例2在没合并之前,master分支其实就是hotfix分支,因为master是hotfix合并过来的,合并后又把hotfix分支删除了。案例2假设iss53与master没有冲突文件。案例3则假设master与iss53有冲突文件,现在将iss53合并到master。整个合并前后效果图和案例2是一样的,不过由于有冲突文件的存在,会稍显麻烦点。
git merge iss53时会报冲突文件

$ git merge iss53 Auto-merging index.html CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in index.html Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
git做了合并工作,但是没有创建一个新的merge commit,像上图C6。这是因为还有冲突文件没有解决,git没法判断该应用哪一个,判断工作是由人完成。git status查看有哪些unmerged文件。

$ git status On branch master You have unmerged paths. (fix conflicts and run "git commit") Unmerged paths: (use "git add <file>..." to mark resolution) both modified: index.html no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
git会在unmerged文件加入标准冲突解决标记

<<<<<<< HEAD:index.html <div id="footer">contact : email.support@github.com</div> ======= <div id="footer"> please contact us at support@github.com </div> >>>>>>> iss53:index.html
======上下两个版本你选一个,或者都不选自己在写一个。修改后git add加入到staging area,git便标记冲突以解决。
分支管理
git branch 命令不只是可以创建与删除分支(见上文)。 如果不加任何参数运行它,会得到当前所有分支的一个列表:

$ git branch iss53 * master testing
*表示HEAD指针指向的分支
查看每一个分支的最后一次提交,可以运行 git branch -v

$ git branch -v iss53 93b412c fix javascript issue * master 7a98805 Merge branch 'iss53' testing 782fd34 add scott to the author list in the readmes
--merged 列出已合并到当前分支的分支

$ git branch --merged
iss53
* master
在这个列表中分支名字前没有 * 号的分支通常可以使用 git branch -d 删除掉;你已经将它们的工作整合到了另一个分支,所以并不会失去任何东西。
--no-merged 列出尚未合并到当前分支的分支

$ git branch --no-merged
testing
testing分支包含了还未合并的工作,尝试使用 git branch -d 命令删除它时会失败

$ git branch -d testing error: The branch 'testing' is not fully merged. If you are sure you want to delete it, run 'git branch -D testing'.
如果真的想要删除分支并丢掉那些工作,如同帮助信息里所指出的,可以使用 -D 选项强制删除它。
远程分支
如何查看remote repository的branches,tags 等等信息?
git ls-remote [remote]
或者
git remote show [remote]
我们把这些返回的信息称为remote references。
Remote-tracking branches
比起简单粗暴的直接查看remote references,更常用的做法是remote-tracking branches
Remote-tracking branches are references to the state of remote branches.
Remote-tracking branches是你不能移动的本地引用(local references),当你做任何网络通信操作时,它们会自动移动。Remote-tracking branches就像是书签,他提醒你上次连接到远程仓库时所处分支的状态。
Remote-tracking branches以 (remote)/(branch) 形式命名
git clone [remote]发生了什么?
git自动将remote命名为origin
git 拉取(pulls down)remote上的全部数据
git创建一个指向remote的master分支,并在本地命名为origin/master
git创建一个本地master分支,和origin/master指向一个地方
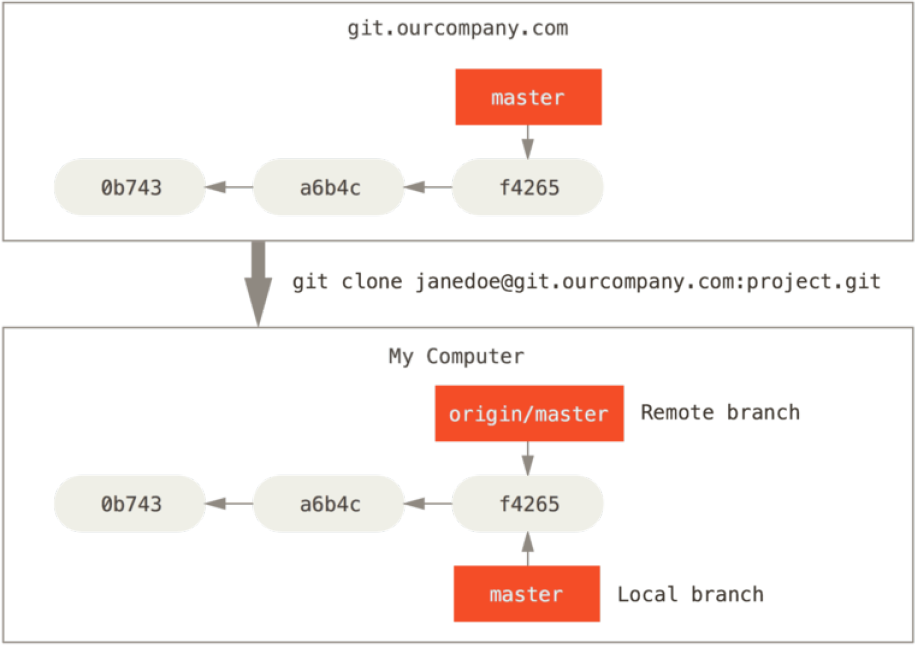
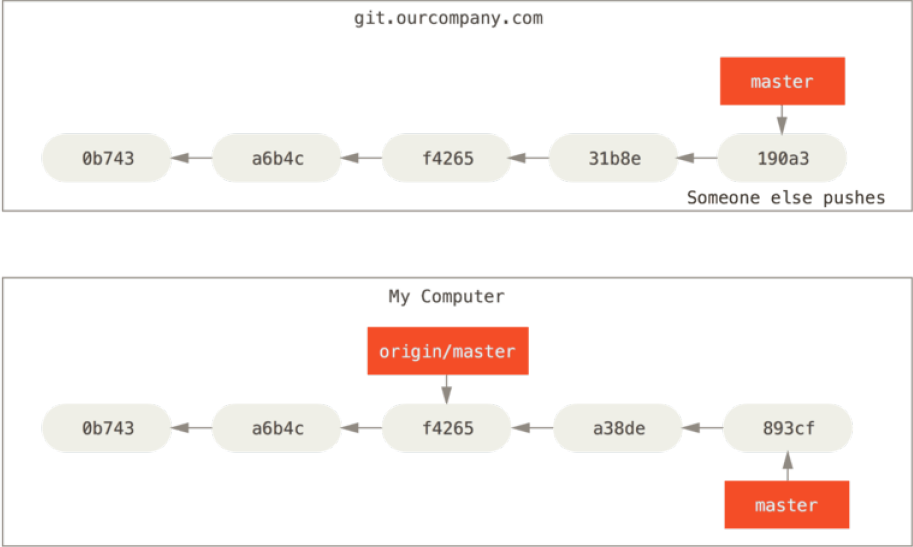
如果后续你在本地做了提交,master将会移动。而origin/master的移动这由不得我们。如果其他人推送提交到 git.ourcompany.com 并更新了它的 master 分支,只要你与origin有网络通信,origin/master就会自动移动。进攻一段时间以后会像下图一样
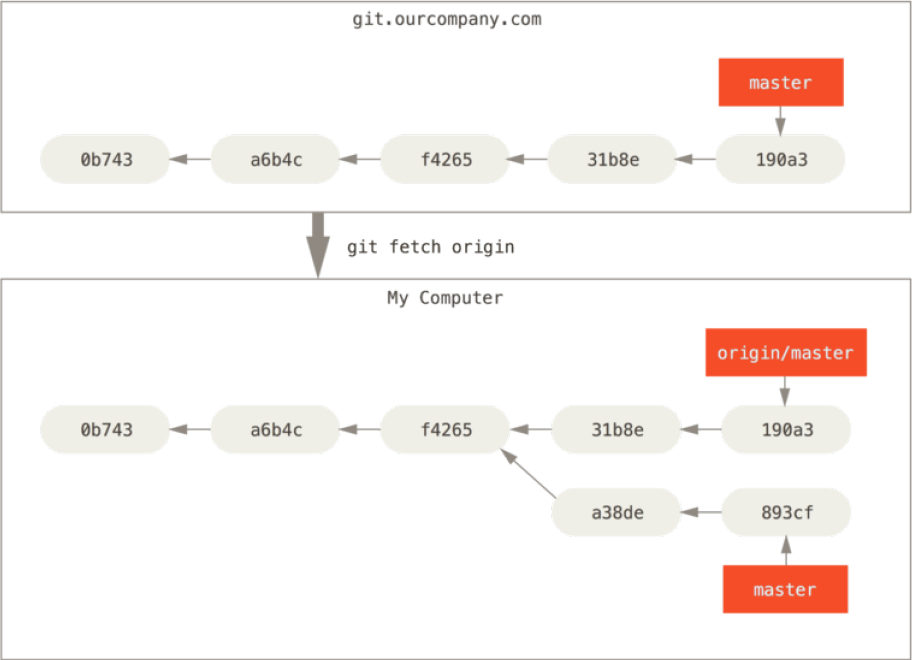
git fetch origin同步remote repository
origin并不特殊
“origin” 同 “master” 一样,在 Git 中并没有任何特别的含义一样。
“master” 是当你运行 git init 时默认的起始分支名字,原因仅仅是它的广泛使用。
“origin” 是当你运行 git clone 时默认的远程仓库名字。 如果你运行 git clone -o booyah,那么你默认的远程分支名字将会是 booyah/master。





