Wireshark for Ethical Hackers - 5
Networking of Sniffing Crash Theory Practice - Part 1
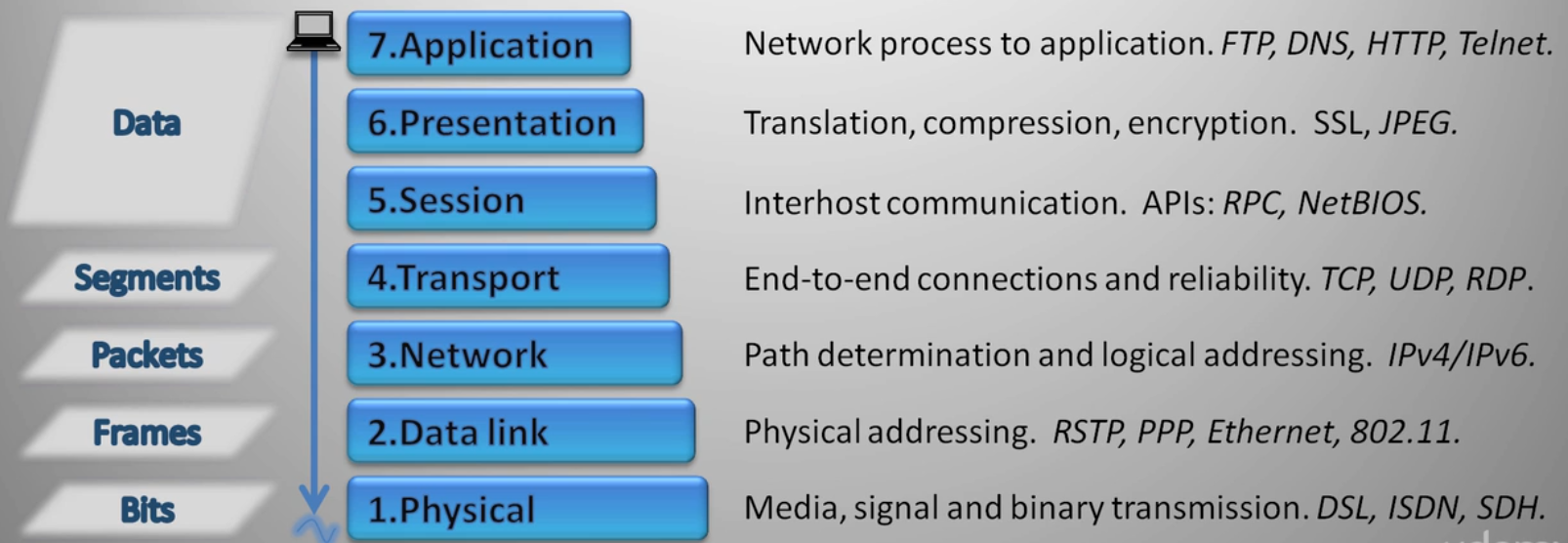
OSI Model
Secure vs. Insecure protocols
Insecure protocols: HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SNMP v1/2 etc.
Secure protocols: HTTPS (HTTP + SSL/TLS), SFTP, SSH, SNMP v3, IPSEC
Hubs, Switches, Routers
| Hub | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|
| L1 device | L2 device | L3 device |
| Central connection for your network equipment | Forwards packets from one network to another | |
| Just a multiport repeater | Uses the mac-address table | Uses the routing table |
| Shares its bandwidth with each port | Hosts always have access to the maximum amount of bandwidth |
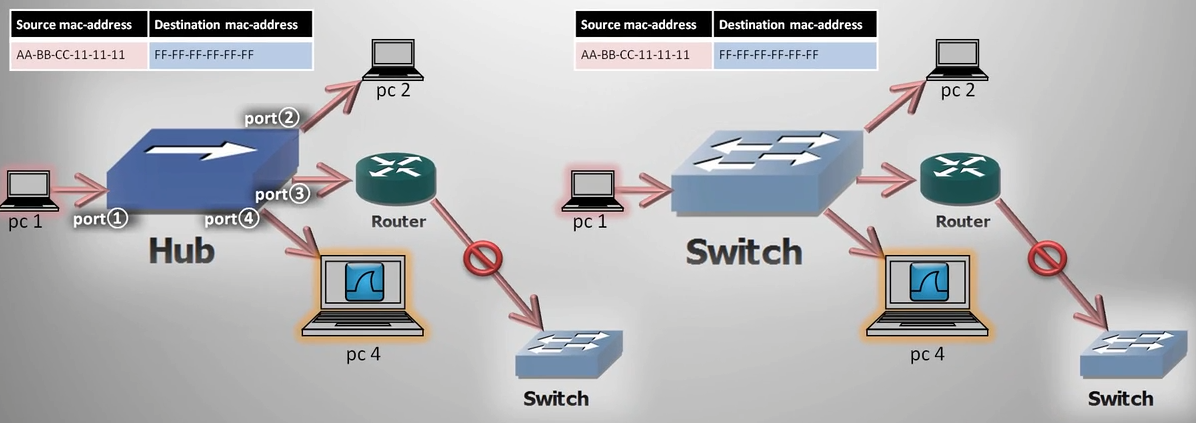
Collision & Broadcast domains
Collision domain
- The Collision domain is a set of LAN devices whose frames can collide with one another
- The Collision occurs if more than one device tries to send anything within a "Shared media" simultaneously
- Collision domains are separated by switches
- Every interface on a switch creates a separate collision domain
- Everything can be sniffed in the Collision domain (if your network card can operate in the promiscuous mode)

Broadcast domain
- The Broadcast domain consists of all devices that will receive a Layer 2 broadcast
- Broadcast domains are separated by routers
VLANs
- Used to separate Broadcast domains
- 802.1Q tags help to tell one VLAN from another
- untagged VLAN on a trunk port = "native VLAN"
Important
- Everything can be sniffed within a Collision domain by an attacker if its network card can operate in the promiscuous mode
- The traffic from some hosts within a Broadcast domain can be sniffed by an attacker if he performs different types of MITM-attacks within its Broadcast domain, but the attacker cannot sniff at the Broadcast domains which he does not have a direct access to.
- Switches (and Routers) separate Collision domains
- VLANs and Routers separate Broadcast domains
相信未来 - 该面对的绝不逃避,该执著的永不怨悔,该舍弃的不再留念,该珍惜的好好把握。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号