DS博客作业02--栈和队列
|这个作业属于哪个班级|数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 |学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 陈佳桐 |
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结(0-5分)
1.1 栈
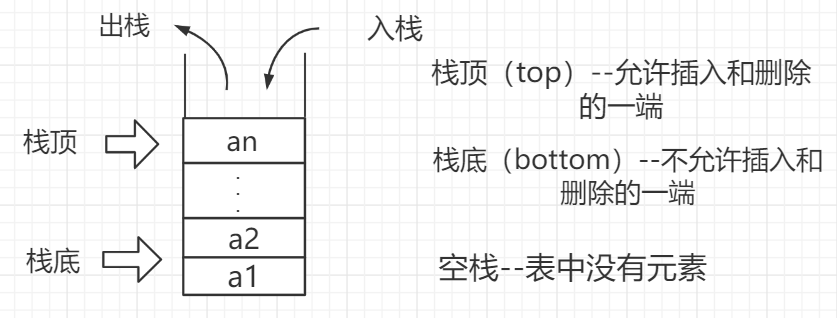
画一个栈的图形,介绍如下内容。
栈--又被称为后进先出的线性表(LIFO表,Last In First Out)
1.1.1顺序栈的结构、操作函数

声明顺序栈的类型SqStack
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;
}Stack;
typedef Stack *SqStack;
操作函数
(1)初始化栈initStack(&s)
void InitStack(&s)
{
s=new Stack;
s->top=-1;
}
(2)销毁栈ClearStack(&s)
void DestroyStack(SqStack &s)
{
delete s;
}
(3)判断栈是否为空StackEmpty(s)
bool StackEmpty(s)
{
return(s->top==-1)
}
(4)进栈Push(&s,e)
bool Push (SqStack &s,ElemtType e)
{
if(s->top==MaxSize-1) //顺序栈务必考虑栈满
return false;
s->top++; //栈顶指针增1
s->Data[s->top]=e;
return true;
}
(5)出栈Pop(&s,&e)
bool Pop(SqStack &s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top==-1) //栈为空,栈下益出
return false';
e=s->Data[s->top];//取栈顶指针元素
s->top--; //栈顶指针减一
return true;
}
(6)取栈顶元素GetTop(s)
//在栈不为空的条件下,将栈顶元素赋给e
bool GetTop(SqStack *s,ElemType &e)
{
if (s->top==-1) //栈为空的情况
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
(7)建立栈CreateStack
Stack CreateStack(int MaxSize)
{
Stack s=(Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
s->Data=(ElementType *)malloc (MaxSize*sizeof(ElementType));
s->top=0;
s->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return s;
}
链栈的结构、操作函数
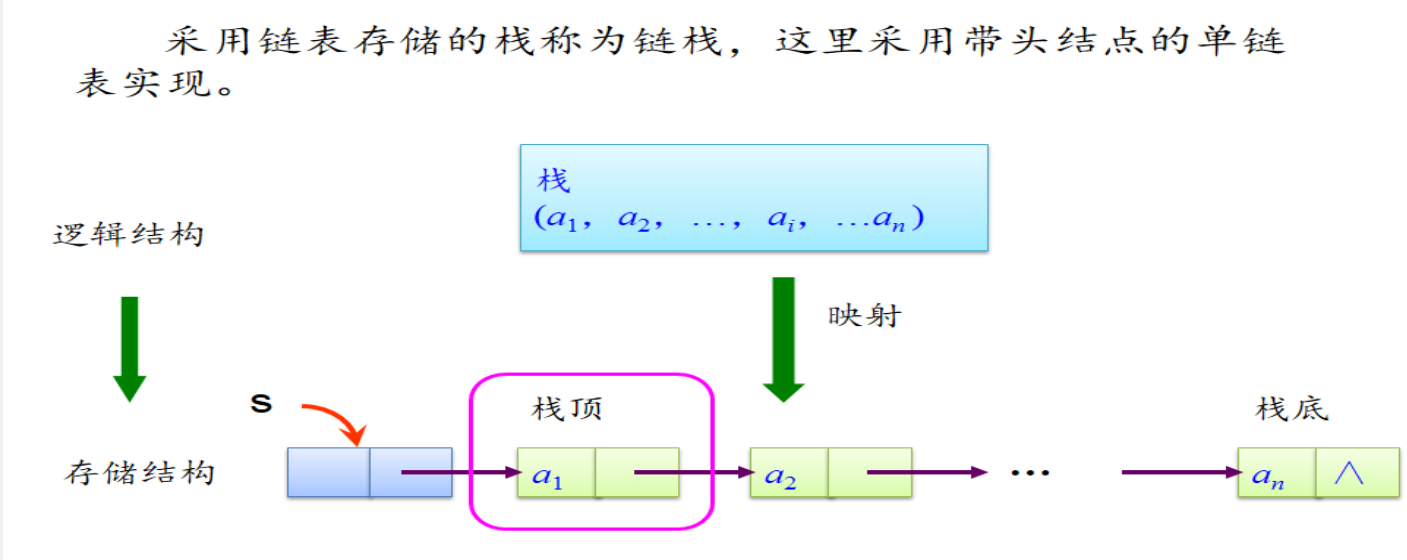
链栈的四要素

链栈中的数据节点的类型LiStack定义
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Linknode
{
ElemType data;
struct Linknode *next;
}LinkNode, *LiStack;
链栈的基本运算算法
(1)初始化栈initStack(&s)
void InitStack(LiStack &s)
{
s=new LiNode;
s->next=NULL;
}
(2)销毁栈ClearStack(&s)
void DestroyStack(LiStack &s)
{
LiStack node;
whilw(s!=NULL)
{
node=s;
s=s->next;
delete node;
}
}
(3)判断栈是否为空StackEmpty(s)
bool StackEmpty(LiStack s)
{
return (s->next==NULL);
}
(4)进栈Push(&s,e)
//该运算新建一个节点,用于存放元素e,将其插入到头节点之后作为新的首结点
void Push (LiStack &s)
{
LiStack p;
p=new LiNode;
p->data=e;
p->next=s->next;
s->next=p;
}
(5)出栈Pop(&s,&e)
//在栈不为空的条件下,将头节点后继数据节点的数据域赋给e
bool pop(LiStack &s,ElemType &e)
{
LiStack p;
if(s->next==NULL) //栈空的情况
return false;
p=s->next; //p指向开始节点
e=p->data;
s->next=p->next; //删除*p节点
delete p;
return true;
}
(6)取栈顶元素GetTop(s,e)
//在栈不为空的条件下,将头节点后继数据节点的数据域赋给e
bool GetTop(LiStack s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->next==NULL) //栈空的情况
return false;
e=s->next->data;
return true;
}
1.2 栈的应用
栈作为一种存放临时数据的容器。如果后存入的元素先处理,则采用栈。
表达式
1.2.1中缀表达式
(1)算术表达式中,运算符位于两个操作数中间的表达式称为中缀表达式,例如1+2*3。
(2)中缀表达式的运算一般遵循“先乘除,后加减,从左到右计算,先括号内,后括号外”的规则。
(3)中缀表达式依赖运算符优先级,还需处理括号。
1.2.2后缀表达式
(1)后缀表达式又称为逆波兰表达式,即为在算术表达式中运算符在操作数的后面,如1+2*3的后缀表达式为1 2 3 * +。
(2)后缀表达式在书写过程中已经考虑了运算符的优先级,没有括号,只有操作数和运算符,而且放在前面的运算符越优先执行。
1.2.3前缀表达式
如果运算符在操作数的前面,称为前缀表达式,如1+2*3的前缀表达式为+ 1 * 2 3。
1.2.4将算术表达式转换成后缀表达式
将一个中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式时,需要从左到有扫描算术表达式,将遇到的操作数直接存放到后缀表达式中,将遇到的每一个运算符或者左括号都暂时保存到运算符栈,而且先执行的运算符先出栈。
1.2.5后缀表达式求值
后缀表达式求值过程是从左到右扫描后缀表达式postexp,若读取到的是一个操作数,将它进操作数栈,若读取的是一个运算符op,从操作数栈中连续出栈两个操作数,当整个后缀表达式扫描结束时,操作数栈中的栈顶元素就是表达式的计算结果。
1.3 队列
画一个队列的图形,介绍如下内容。
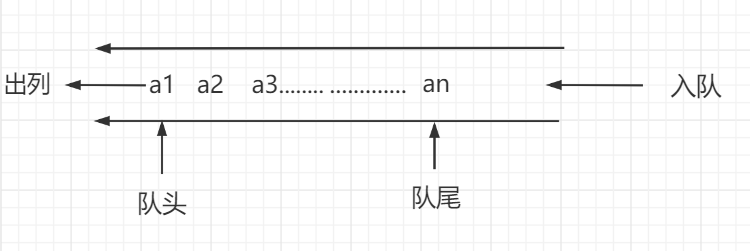

顺序队列的结构、操作函数
顺序队结构
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front,rear; //队首和队尾指针
}Queue;
typedef Queue *SqQueue;
操作函数
1. 初始化队列
void InitQueue(SqQueue &q)
{
q=new Queue;
q->front=q->rear=-1;
}
2.销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue &q)
{
delete q;
}
3.判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue q)
{
return (q->front==q->rear);
}
4.进队列
bool enQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType e)
{
if(q->rear+1==MaxSize)
return false; //从队满上溢出
q->rear=q->rear+1;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
5.出队列
bool deQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType &e)
{
if(q->front==q->rear)
return false; //从队空上溢出
q->front=q->front+1;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
环形队列的结构、操作函数
环形队列 结构体
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front,rear;
} Queue;
typedef Queue *SqQueue;
操作函数
进环形队列
bool enQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType e)
{
if((q->rear+1)%MaxSize==0) //队满溢出
return false;
q->rear=(q->rear+1)%MaxSize;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
bool deQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType &e)
{
if(q->front==q->rear)
return false;
q->front=(q->front+1)%MaxSize;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
链队列的结构、操作函数
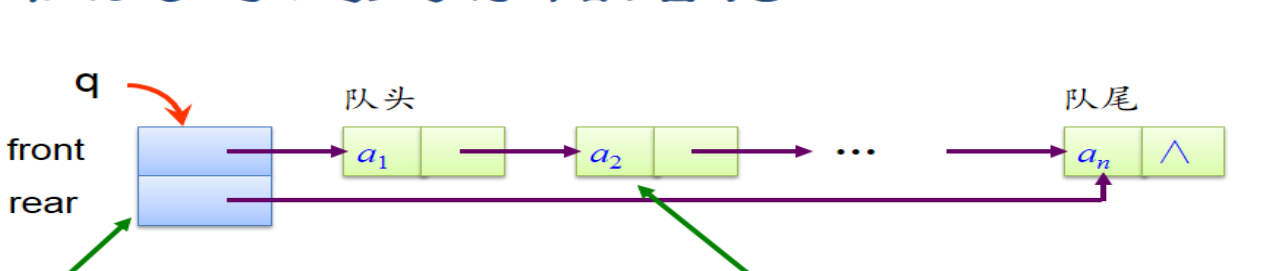
结构
typedf struct qnode
{
ElemType data;
struct qnode *next;
} QNode;
typedef struct Queue *LiQueue;
LiQueue front,rear;
入队
Q.rear->next=node;
Q.rear=node;
出队
node =Q.font->next;
Q.font->next=node->next;
delete node;
队列应用--配对舞伴

int QueueLen(SqQueue Q)
{
int len = 0;
int i = Q->front;
int j = Q->rear;
while(i != j)
{
i = (i+1)%MAXQSIZE;
len++;
}
return len;
}//队列长度
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person e)
{
if((Q->rear+1)%MAXQSIZE == Q->front)
return ERROR;
Q->rear = (Q->rear+1)%MAXQSIZE;
Q->data[((Q->rear))] = e;
return OK;
}//加入队列
int QueueEmpty(SqQueue &Q)
{
return (Q->front == Q->rear);
}//队列是否为空
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person &e)
{
if(QueueEmpty(Q))
return -1;
Q->front = (Q->front+1)%MAXQSIZE;
e = Q->data[Q->front];
return OK;
}
//出队列
void DancePartner(Person dancer[], int num)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < num; ++i)
{
if(dancer[i].sex == 'F')
EnQueue(Fdancers,dancer[i]); //女生入队
else
EnQueue(Mdancers,dancer[i]); //男生入队
}
Person e;
while((!QueueEmpty(Fdancers)) && (!QueueEmpty(Mdancers)))
{
DeQueue(Fdancers,e);
cout<<e.name<<" ";
DeQueue(Mdancers,e);
cout<<e.name<<endl;
}
} //配对舞伴
2.PTA实验作业
2.1 符号配对
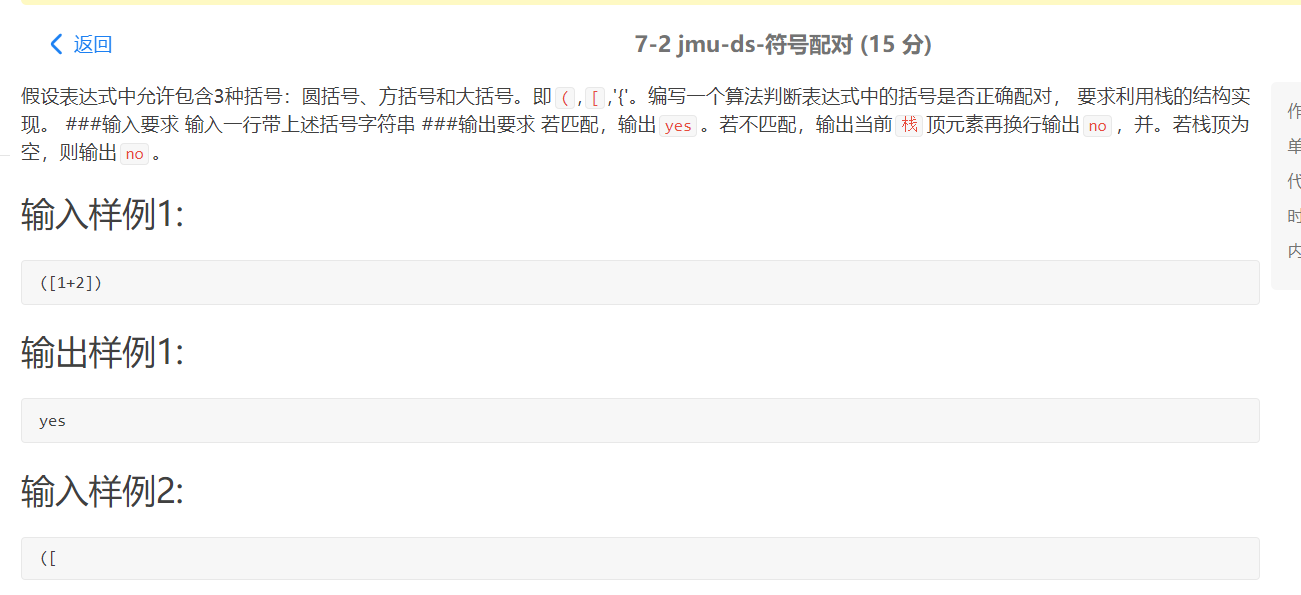
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
解题思路
1.对于左符号直接进行入栈操作
2.读入右符号,判断情况:
/用>来代替;
/用<来代替;
如果栈空,则缺少对应的左括号。
如果栈顶元素不匹配,缺少与栈顶元素对应的右括号
读入结束,如果栈空,则完全匹配,如果有剩余,则缺少右括号。
#include<stdio.h>
#define maxsize 1003
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct node *stack;
struct node
{
char ch[maxsize];
int top;
};
stack creat()
{
stack s;
s=(stack)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
s->top=-1;
return s;
}
void push(stack s,char cht)
{
s->top++;
s->ch[s->top]=cht;
}
int main()
{
int i,k=0,j;
static char ch1[1000],ch2[1000],ch[10000];
struct node *s1=NULL;
s1=creat();
ch1['(']=')';
ch1['{']='}';
ch1['[']=']';
ch1['<']='>';
for(i=0;;i++)
{
gets(ch);
if(ch[0]=='.'&&ch[1]=='\0') break;
for(j=0;ch[j]!='\0';j++)
{
if(ch[j]=='('||ch[j]==')'||ch[j]=='['||ch[j]==']'||ch[j]=='{'||ch[j]=='}')
{
ch2[k++]=ch[j];
}
else if(ch[j]=='/'&&ch[j+1]=='*')
{
ch2[k++]='<';
j++;
}
else if(ch[j]=='*'&&ch[j+1]=='/')
{
ch2[k++]='>';
j++;
}
}
}
int flag=1;
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{
if(ch2[i]=='('||ch2[i]=='['||ch2[i]=='{'||ch2[i]=='<')
{
push(s1,ch2[i]);
}
else if(ch2[i]==')'||ch2[i]==']'||ch2[i]=='}'||ch2[i]=='>')
{
if(s1->top!=-1&&ch1[s1->ch[s1->top]]==ch2[i])
{
s1->top--;
}
else
{
printf("NO\n");
if(s1->top==-1)
{
if(ch2[i]==')') printf("?-)");
else if(ch2[i]=='}') printf("?-}");
else if(ch2[i]==']') printf("?-]");
else if(ch2[i]=='>') printf("?-*/");
}
else if(ch1[s1->ch[s1->top]]!=ch2[i])
{
if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='(') printf("(-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='[') printf("[-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='{') printf("{-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='<') printf("/*-?");
}
flag=0;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag==1&&s1->top==-1) printf("YES");
else if(flag==1&&s1->top!=-1)
{
printf("NO\n");
if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='(') printf("(-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='[') printf("[-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='{') printf("{-?");
else if(s1->ch[s1->top]=='<') printf("/*-?");
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#define maxsize 1003
#include<stdlib.h>
创建队列
定义ch1[1000], ch2[1000]存放符号, ch[10000]判断符号的匹配
int flag=1
for j from 0 to ch[j]!='\0'
if ch[j]== 除/* */ 以外的符号
then
ch2[k++]=ch [j]
j++
else if ch[j]=='/' && ch [j+1]=='*'
ch2[k++]='<'
j++
else if ch[j]=='*' && ch [j+1]=='/'
ch2[k++]='>'
j++
end for
for i from 0 to k
if ch2[i] 为 左符号
then
直接放入 栈中
else if ch2[i]为右符号
then
if 栈中存在符号,且ch2中符号与栈符号对应
then
出栈
else
输出NO
判断缺少的符号
输出 ?-缺失符号
flag =0
break
end for
if flag==1 且栈空
then
输出 yes
else if 栈不为空
then
输出NO
判断栈中剩余符号,
输出?-缺失符号
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
使用malloc函数进行空间的动态申请
判断字符为左符号,右符号,对其进行相应的入出栈操作
使用替换的方式使判断更简单
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
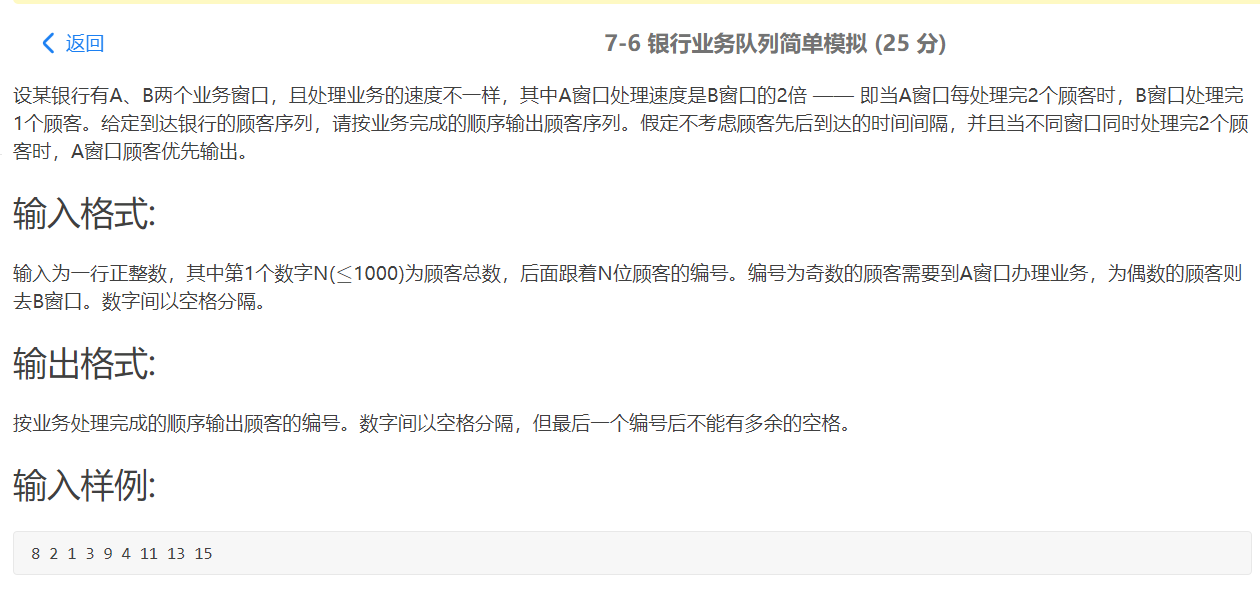
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
解题思路
偶数顾客一次两个,奇数顾客一次输出一个。
那么则创建两个队列,一个存放A窗口的客户,另一个存放B窗口的客户,并分别统计两个窗口的人数。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
定义数组a[]存放顾客数字
定义队列qa //存放奇数
定义队列qb //存放偶数
输入 N
for i from 0 to N-1
输入 a[i]
do if (a[i]为奇数)
进入qa
else
进入qb
end for
int x,y 存放队列头
if(qa队列长度大于qb队列长度的两倍)
while(qa队列或qb队列不为空队列情况)
if(qa不为空队列)
then
x = qa.front();
输出x
出队
if(qa长度不为0)
then
输出 " "
if(qa长度不为0)
then
输出 " "
if(qb不为空队列)
then
y = qb.front();
输出y
出队
输出" "
else //qa队列长度不大于qb队列长度两倍时
while (qa队列或qb队列不为空队列情况)
if(qa不为空队列)
then
x = qa.front();
输出x
出队
输出" "
x = qa.front();
输出x
出队
输出" "
if(qb不为空队列)
then
y = qb.front();
输出y
出队
if(qb长度不为0)
输出 " "
return 0;
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
c++库函数
出队列函数pop(),
判断队列是否为空队列函数empty()
使用队列头部进行判断
3.阅读代码----无法吃午餐的学生数量
来自于leetcode--队列
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-students-unable-to-eat-lunch/
3.1 题目及解题代码
题目如下

解题代码
逛了一圈,发现大佬们的解法各不相同,这里选择了几种方法比较阅读
int countStudents(int* students, int studentsSize, int* sandwiches, int sandwichesSize){
int arr[2];
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));
for (int i=0; i<studentsSize; ++i) {
++arr[students[i]];
}
for (int i=0; i<sandwichesSize; ++i) {
if (arr[sandwiches[i]] == 0) break;
--arr[sandwiches[i]];
}
return arr[0] + arr[1];
}
作者:dong-feng-32
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-students-unable-to-eat-lunch/solution/c-zhi-xu-yao-pan-ding-xi-huan-zhan-ding-iffdu/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAX 102
struct Queue
{
int a[MAX];
int front;
int rear;
};
//队列的基本操作
void Init_Queue(struct Queue *q)
{
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
int Queue_Length(struct Queue *q)
{
return (q->rear-q->front+MAX)%MAX;
}
int Is_Empty(struct Queue *q)
{
if(q->front == q->rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int Is_Full(struct Queue *q)
{
if(q->front == (q->rear+1)%MAX)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int En_Queue(struct Queue *q,int x)
{
if(Is_Full(q))
return 0;
q->a[q->rear] = x;
q->rear = (q->rear+1)%MAX;
return 1;
}
int De_Queue(struct Queue *q)
{
if(Is_Empty(q))
return 0;
q->front = (q->front+1)%MAX;
return 1;
}
//将队头元素移至队尾
int De_Queue1(struct Queue *q)
{
if(Is_Empty(q))
return 0;
q->a[q->rear] = (q->a[q->front]);
q->rear = (q->rear+1)%MAX;
q->front = (q->front+1)%MAX;
return 1;
}
//循环结束条件的判断
int judge(struct Queue *q,int *sandwiches,int j){
int n,i;
int count=0;
n = Queue_Length(q);
int n1 = q->front;
for(i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(q->a[n1] != sandwiches[j]){
count++;
n1 = (n1+1)%MAX;
}
}
if(count == n)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int countStudents(int* students, int studentsSize, int* sandwiches, int sandwichesSize){
int i,j=0;
struct Queue *q = (struct Queue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Queue ));
Init_Queue(q);
for(i = 0;i < studentsSize;i++){
En_Queue(q,students[i]);
}
作者:fzst
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-students-unable-to-eat-lunch/solution/cyu-yan-shi-xian-4ms59mb-by-fzst-en7d/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
第一版作者的解题思路很简单:若喜欢栈顶的甜点的学生存在,那么不管他们在队伍的哪个位置,必定会遍历到他。否则,一定无法继续拿掉栈顶甜点。
直接遍历,通过循环结构实现,不喜欢圆形和不喜欢方形三明治的被统计出。
这种解法的时间复杂度为o(n),相当简单。
void *memset(void *s, int ch, size_t n);
函数解释:将s中当前位置后面的n个字节 (typedef unsigned int size_t )用 ch 替换并返回 s 。
memset:作用是在一段内存块中填充某个给定的值,它是对较大的结构体或数组进行清零操作的一种最快方法 [1] 。
memset()函数原型是extern void *memset(void *buffer, int c, int count) buffer:为指针或是数组,c:是赋给buffer的值,count:是buffer的长度.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号