ASP.NET Core C# 反射 & 表达式树 (第一篇)
前言
以前就写过几篇关于反射和表达式树的学习笔记, 但是写的很乱. 最近常用到反射和表达式树, 所以特别写一篇做一个整理吧.
反射在项目中会用到的地方, 一般不是因为要实现业务逻辑, 更多的是因为要更好的代码管理. 这个动机很重要.
这篇不会讲原理, 主要是整理出常用到的方式. 会从简单和常用到的慢慢讲到复杂的.
Get/Set Property Value
Typescript 可以很直接的动态读写属性值
class Person { name: string = 'default name'; } const person = new Person(); const propertyName = 'name'; console.log('default name', person[propertyName]); // 动态获取属性值 person[propertyName] = 'new name'; // 动态写入属性值 console.log('new name', person[propertyName]);
但是在 C# 是写不到这种语法的, 不包括 dynamic ExpandoObject
C# 要做到上面这种动态读写就需要反射
public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } = "Default Name"; } public class Program { public static void Main() { var person = new Person(); var type = person.GetType(); // step 1. 从 object 获取到 Type var property = type.GetProperty("Name")!; // step 2. 通过 Type + propertyName (string) 获取到 PropertyInfo var name = (string)property.GetValue(person, null)!; // step 3. 通过 PropertyInfo 的读方法, 获取对象属性值 Console.WriteLine(name); property.SetValue(person, "Derrick"); // step 3. 通过 PropertyInfo 的写方法, 写入对象属性值 Console.WriteLine(person.Name); } }
流程大概就是:
1. 先反射出对象类型
2. 再反射出属性操作器 (依据 string)
3. 通过操作器, 把 object + object 类型属性操作器 + 值, 搞在一起, 最后就修改掉了对象属性值.
如果只看这一个需求的话, 需要这么多步骤才能做到这点事情, 确实很烦. 但是如果站在一个类型语言要让它"动态"的话, 它的这个步骤就可以做到非常多事情了. 所以我们接着往下.
Invoke Method
调用方法和读写属性值差不多.
public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } = "Default Name"; public void ChangeName(string newName) { Name = newName; } } public class Program { public static void Main() { var person = new Person(); var type = person.GetType(); var method = type.GetMethod("ChangeName")!; // 从对象类型中, 通过方法名字(string), 获取到方法执行器 method.Invoke(person, new object[] { "new name" }); // 对象 + 方法执行器 + 参数 = 执行了方法 Console.WriteLine(person.Name); } }
找出方法执行器, 然后调用就可以了.
Optional Parameter
如果遇到 Optional Parameter 需要做一点点需改
public void ChangeName(string newName = "optional new name") { Name = newName; }
method.Invoke(person, new object[] { Type.Missing }); // 使用 Type.Missing 来表示没有传参数
注: Type.Missing 是一定要放的哦, 不放会直接报错的.
Return Value
public string GetName() { return Name; }
var name = (string)method.Invoke(person, Array.Empty<string>())!;
关键就是要强转, 不然返回都是 object 类型.
Async Task
public async Task DoSomethingAsync() { await Task.Delay(2000); }
await (Task)method.Invoke(person, Array.Empty<string>())!;
关键依然是强转就可以了.
Async Task<string>
public async Task<string> GetNameAsync() { await Task.Delay(2000); return Name; }
var name = await (Task<string>)method.Invoke(person, Array.Empty<string>())!;
也是强转就可以了.
如果不清楚返回的类型, 那么可以用 dynamic (而不是 Task<object> 哦)
var name = await (dynamic)method.Invoke(person, Array.Empty<string>())!; if (name is string) { Console.WriteLine("name is string"); }
Anonymous method / Delegate
匿名函数, 通常出现在一个方法作用域内.
public static async Task Main() {async Task<string> GetNameAsync(string value) { await Task.Delay(2000); return "test"; } }
直接装进 variable 调用
var @delegate = GetNameAsync; // 把函数装进变量中 var returnValue = await @delegate("value"); // 直接调用变量. 因为类型推导所以完全等价于 await GetNameAsync("value")
把 var 改成 Delegate 类型, 就需要换一个方式调用
Delegate @delegate = GetNameAsync; var returnValue = await (Task<string>)@delegate.Method.Invoke(@delegate.Target, new object[] { "value" })!;
因为没有类型推导, 所以需要很多强转.
另外, 需要用 delegate.Method 和 delegate.Target 来调用这个方法.
委托方法和对象是无关的, 所以 Invoke 的时候传入的是 Target 而不是 Object.
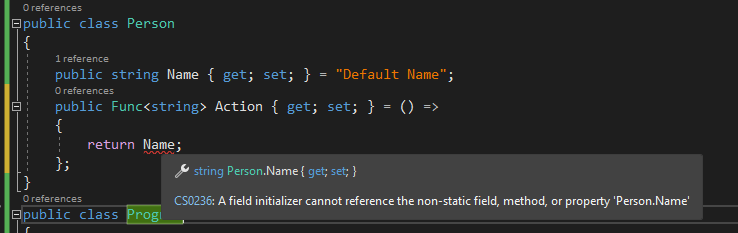
比如在类里面有一个委托, 它内部是调用不到 this 的哦.
我们可以通过 get property value 获取到这个委托, 然后通过 delegate.Method 来调用, 它的 target 依然是 delegate.Target 而不是 object.
Tips: DynamicInvoke 调用 (推荐)
var returnValue = await (Task<string>)@delegate.DynamicInvoke(new object[] { "value" })!;
这个更好用, 效果和上面一样(没有 100% 测试). 但语法更简单.
Extensions Method
扩展方法调用起来感觉好像是对象中的方法, 但其实并不是, 它是某个类的静态方法来的, 所以想要获取这个方法的时候一定要找对它的类型. 不可以用 object.GetType()
public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } = "default name"; } public static class PersonExtensions { public static string ReturnName(this Person person, string otherParameter) { return person.Name; } } public class Program { public static async Task Main() { var person = new Person(); // var returnName = person.ReturnName("otherParameter"); // 普通调用会以为 ReturnName under person var type = typeof(PersonExtensions); // 不可以通过 person.GetType() 哦, 因为方法并不在 Person class 内, 而是在 PersonExtensions class 内. var returnNameMethod = type.GetMethod("ReturnName")!; var name = returnNameMethod.Invoke(null, new object[] { person, "otherParameter" }); // 注意: 第一个参数是 null, 因为它是静态方法, 反而是把 object 用作第一个 parameter 传进去. Console.WriteLine(name); } }
Assembly & Class
上面讲了基本 get/set 和方法调用. 现在来看看 Assembly 和 Class 实例化的部分.
如果想通过一个 ClassName string, 来动态创建实例.
Get Assembly Type
通过 class 获取 Assembly, 比较常用在获取 library
typeof(Program).Assembly
获取当前运行着的 Assembly
Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
Create Instance
有了 Assembly 之后就可以用 string 找到 Class 了
var personType = typeof(Program).Assembly.GetType("Reflection.Person")!; // 一定要是 namespace + class name 哦 (也叫 class full name) var instance = (Person)Activator.CreateInstance(personType)!; // 通过 Activator.CreateInstance 来实例化对象, 然后又是强转 Console.WriteLine(instance.Name);
Constructor & Overload
即使有重载构造函数也不怕, 它挺聪明的
public class Person { public Person() { } public Person(int age) { } public Person(string name) { } public string Name { get; set; } = "default name"; }
传入参数, 它自己会配对成功哦.
var instance = (Person)Activator.CreateInstance(personType, new object[] { 1 })!;
Constructor + Dependency Injection
安装
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
Program.cs
public class SomeService { public string GetValue() => "new value"; } public class Person { public Person (SomeService someService, int age) // 注入 service { Name = someService.GetValue(); } public string Name { get; set; } = "default name"; } public class Program { public static void Main() { var services = new ServiceCollection(); services.AddSingleton<SomeService, SomeService>(); var serviceProvider = services.BuildServiceProvider(); var personType = typeof(Program).Assembly.GetType("Reflection.Person")!; var instance = (Person)ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(serviceProvider, personType, new object[] { 5 }); // 通过 ActivatorUtilities 可以传入 serviceProvider Console.WriteLine(instance.Name); } }
做法和之前差不多, 只是换了 ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance, 然后把 ServiceProvider 传进去就可以了, 虽然用了依赖注入, 但是依然可以传 parameters 哦.
Generic & Nullable
导入 Generic Type
public class Person1<T> {} public class Person2<T,U> { } var personType1 = typeof(Person1<>).MakeGenericType(typeof(int)); var personType2 = typeof(Person2<,>).MakeGenericType(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) });
关键就是 Person1<> 里面空的, Person2<,> 里面有一个逗号, 然后后面就是通过 MakeGenericType 去填充 generic type.
导出 Generic Type
var personType2 = typeof(Person2<,>).MakeGenericType(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) }); Type[] genericTypes = personType2.GetGenericArguments(); Console.WriteLine(string.Join(',', genericTypes.Select(t => t.Name))); // Int32,String
通过 GetGenericArguments 就可以获取所有的 generic types 了.
导出 Nullable
var type = typeof(int?); var same = Nullable.GetUnderlyingType(type) == typeof(int);
More about nullable
nullable 有时候会有点乱,我们理一理
var type1 = typeof(int?); var type2 = typeof(Nullable<int>); Console.WriteLine(type1 == type2); // True
上面两个写法完全等价。
把它换成 string 或者任何一个 class 会直接报错
var type1 = typeof(Person); var type2 = typeof(Person?); // The typeof operator cannot be used on a nullable reference type var type3 = typeof(string?); // string 也是 nullable 所以不可以
原因是 int? 会被 compile 成 Nullable<int>,Nullable 是一个 class 来的,而 string? compile 后依然是 string。

string? 和 string,Person 和 Person? 只有在 compile 阶段有区别,runtime 阶段是一样的。
而 int? 和 int 在 compile 和 runtime 都有区别。
这一点要特别留意,因为反射是发生在 runtime。
Attribute
C# attribute 和 Typescript 的 decorator 有点像, 但是它更偏向 metadata. 所以也只有反射能获取到它的值了.
public class SomethingAttribute : Attribute { public string Value { get; set; } = ""; } public class Person { [Something(Value = "default value")] public string Name { get; set; } = ""; } public class Program { public static void Main() { var personType = typeof(Person); var nameProperty = personType.GetProperty("Name")!; var something = (SomethingAttribute)nameProperty.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(SomethingAttribute))!; // var something = nameProperty.GetCustomAttribute<SomethingAttribute>()!; // 有时候需求没有太过动态的话, 可以用泛型. Console.WriteLine(something.Value); } }
小总结
可以看得出来, 整个反射的套路就那几招.
找到类型, 获取一些操作器, 然后传入 object, 返回 object, 然后强转.
反射就是撇开了静态类型, 让东西都变成 object, 然后靠你自己去使用它, 如果不习惯写动态语言的人, 就容易遇到 run time error.
下一篇, 我们主要来看看找类型这个环节.






【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· [.NET]调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· 一个费力不讨好的项目,让我损失了近一半的绩效!
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· 百万级群聊的设计实践
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战
· 永远不要相信用户的输入:从 SQL 注入攻防看输入验证的重要性
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
2018-11-02 Asp.net core 学习笔记 (library)