ASP.NET Core – Work with X509
前言
这篇主要是说如何用 ASP.NET Core 读写系统里的证书 Store 和创建一个证书, 还有使用证书做加密, 解密, 签名.
主要参考:
C#数字证书编程总结 (读写证书 Store)
Encryption and signing credentials (创建证书)
X.509 Store and Create
using var store = new X509Store(StoreName.My, StoreLocation.CurrentUser); // 也可以从 LocalMachine 拿 store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite); // 如果只是要读, 可以放 ReadOnly // 查找 // var certificates = store.Certificates.Find( // X509FindType.FindBySubjectName, // findValue: "jbreviews.com.my", // validOnly: false // validOnly 可以检查 expired 和 是否 under root 证书 (self sign 的通常不 under root) // ); // 遍历 foreach (var certificate in store.Certificates) { } // 制作 certificate using var algorithm = RSA.Create(keySizeInBits: 2048); var subject = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN=My signing certification"); var request = new CertificateRequest(subject, algorithm, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pkcs1); // X509KeyUsageFlags.DigitalSignature for 签名, X509KeyUsageFlags.KeyEncipherment for 加密 request.CertificateExtensions.Add(new X509KeyUsageExtension(X509KeyUsageFlags.DigitalSignature, critical: true)); var newCertificate = request.CreateSelfSigned( notBefore: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow, notAfter: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddYears(1) ); var rowData = newCertificate.Export(X509ContentType.Pfx, "password"); // 添加私钥的保护密码, 因为我们要 store 起来所以需要一个保护密码 newCertificate = X509CertificateLoader.LoadPkcs12(rowData, "password", X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable); // 添加新的 cert store.Add(newCertificate);
注意: 要写入 store 的 permission 需要是 admin 等级. 一般上在 production server 是做不到的.

参考: ASP.NET Core app within aspnet:3.1-nanoserver-1809 gets Access Denied on X509Store.Add()
解决方法是 manual import certificate, 设置 OpenFlags.ReadOnly 就好.
然后把做好的 certificate export 成 .pfx, 记得要配置 X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable 才可以 export 哦.
var certificateBytes = certificate.Export(X509ContentType.Pfx, password); System.IO.File.WriteAllBytes("Certificate.pfx", certificateBytes);
然后双击一直 next 就可以了.
疑难杂症 in Azure VM
在 production server (Azure VM) 有可能拿不到 CurrentUser 的 certificate. 参考: Can't Get Current User Certificate From X.509 Store
可能是因为 IIS User 的权限问题吧. 解决方法是用 LocalMachine
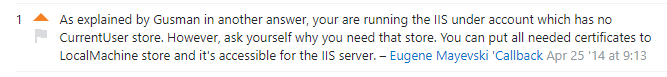
在创建 X509 时遇到 Error: The system cannot find the file specified
var certificate = X509CertificateLoader.LoadPkcs12(data: privateKeyBytes, password: null); // Error:The system cannot find the file specified
解决方法之一是 IIS set pool Load User Profile = true
但这个不是很好. 比较好的是这样创建
var certificate = X509CertificateLoader.LoadPkcs12( data: privateKeyBytes, password: null, keyStorageFlags: X509KeyStorageFlags.MachineKeySet | X509KeyStorageFlags.EphemeralKeySet );
原理看这里: What exactly happens when I set LoadUserProfile of IIS pool?
既然 Server store 和 IIS 经常会遇到权限问题, 那也可以改用 Azure KeyVault Certificate Service. 看这篇.
加密, 解密, 签名
参考: Encrypt / Decrypt in C# using Certificate
Public Key 加密, Private Key 解密 (注: 通常非对称加密, 只用来加密对称加密的密钥, 内容要短, 不然很慢的)
签名和验证签名则反过来 Private Key 签名, Public Key 验证. (注: 还需要 SHA256 消息摘要哦)
加密, 解密
using var algorithm = RSA.Create(keySizeInBits: 2048); var subject = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN=jbreviews"); var request = new CertificateRequest(subject, algorithm, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pss); request.CertificateExtensions.Add(new X509KeyUsageExtension(X509KeyUsageFlags.KeyEncipherment, critical: true)); var certificate = request.CreateSelfSigned( notBefore: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow, notAfter: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddDays(30) ); var password = "password"; using var privateKey = certificate.GetRSAPrivateKey()!; using var publicKey = certificate.GetRSAPublicKey()!; var encryption = publicKey.Encrypt(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(password), RSAEncryptionPadding.OaepSHA256); var decryption = privateKey.Decrypt(encryption, RSAEncryptionPadding.OaepSHA256); var valid = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(decryption) == password;
request.CertificateExtensions 加不加好像不太重要. 我试过不加也可以正常跑.
签名, 验证签名
using var algorithm = RSA.Create(keySizeInBits: 2048); var subject = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN=jbreviews"); var request = new CertificateRequest(subject, algorithm, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pss); request.CertificateExtensions.Add(new X509KeyUsageExtension(X509KeyUsageFlags.DigitalSignature, critical: true)); var certificate = request.CreateSelfSigned( notBefore: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow, notAfter: DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddDays(30) ); var message = "value"; using var sha256 = SHA256.Create(); var messageDigest = sha256.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(message)); using var privateKey = certificate.GetRSAPrivateKey()!; using var publicKey = certificate.GetRSAPublicKey()!; var signature = privateKey.SignHash(messageDigest, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pss); var valid = publicKey.VerifyHash(messageDigest, signature, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pss);
RSA Padding
关于 RSA padding 我没有 research 太多
有 3 种:
PKCS 1 是最开始的 (签名, 加密都可以用)
PSS 是后来用作签名的
OAEP 是后来用作加密的
OpenIddict Core 的 example 是 PKCS 1, 不知道我换掉 ok 不 ok 啦.
关于 PEM, CER, .pem, .cer, .crt .key, .pfx
参考:
网络安全 / crt、pem、pfx、cer、key 作用及区别
那些证书相关的玩意儿(SSL,X.509,PEM,DER,CRT,CER,KEY,CSR,P12等)
大家都是 X509.
一个 X509 包含证书信息, private key & public key
PEM 和 CER 是 format 格式.
Windows 通常是 CER 格式, Linux 是 PEM.
extension 则非常乱, 通常 Windows 用 .pfx, 里面包含了证书信息, public key 和 private key, 所以要 fully export 需要密码.
Linux 通常会分 2 个文件, 一个负责 public key 和证书信息 .crt, .cer, 另一个负责 private key extension 是 .key
以上全部都是可以相互 convert 的.




