Sping备忘三(涵盖Spring2.5)
bean的作用域
|
作用域 |
描述 |
|
singleton |
在每个Spring IoC容器中一个bean定义对应一个对象实例。 |
|
prototype |
一个bean定义对应多个对象实例。 |
|
request |
在一次HTTP请求中,一个bean定义对应一个实例;即每次HTTP请求将会有各自的bean实例, 它们依据某个bean定义创建而成。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。 |
|
session |
在一个HTTP Session中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。 |
|
global session |
在一个全局的HTTP Session中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。典型情况下,仅在使用portlet context的时候有效。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。 |
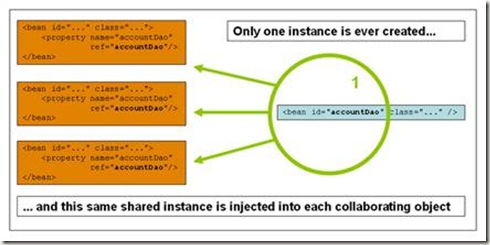
a) singleton(默认)
当一个bean的作用域为singleton, 那么Spring IoC容器中只会存在一个共享的bean实例,并且所有对bean的请求,只要id与该bean定义相匹配,则只会返回bean的同一实例。当把一个bean定义设置为singlton作用域时,Spring IoC容器只会创建该bean定义的唯一实例。这个单一实例会被存储到单例缓存(singleton cache)中,并且所有针对该bean的后续请求和引用都将返回被缓存的对象实例。
设置指定scope属性为sigleton:
|
<bean id="userDao" class="com.kay.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" scope="singleton"></bean> |
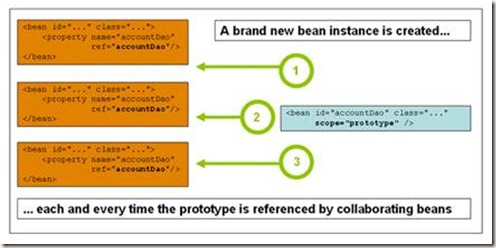
b) prototype
Prototype作用域的bean会导致在每次对该bean请求(将其注入到另一个bean中,或者以程序的方式调用容器的getBean()方法)时都会创建一个新的bean实例。根据经验,对有状态的bean应该使用prototype作用域,而对无状态的bean则应该使用singleton作用域。
设置指定的scope属性为prototype:
|
<bean id="userDao" class="com.kay.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" scope="prototype"></bean> |
c) 其他作用域(request session globalsession)
详情见spring 开发手册。
bean的延迟加载
ApplicationContex默认的行文就是在初始化的时候加载所有的Singleton Bean并实例化。如果在开发中不需要把一个Singleton的Bean在初始化的时候进行实例化操作,那么就需要在配置文件中利用lazy-init属性进行配置:
|
<bean id="userBean" class="com.kay.bean.UserBean" lazy-init="true"/> |
注意:如果一个非延迟加载的Singleton Bean依赖与一个延迟加载的Singleton Bean,那么在实例化非延迟加载的Singleton Bean的时候会将延迟加载的Singleton Bean进行实例化,也就是说延迟加载作用将失效。
Spring2.5中扫描ClassPath中的Bean
如果把Bean都在Spring的配置文件中进行配置,那么随着项目的进展,配置文件的体积会急速的增加,加重开发人员对配置文件维护的的负担。在Spring2.5中,Spring容器提供了利用Annotation注解的方法自动扫描ClassPath中Bean的功能,利用这个功能,可以极大的减轻配置文件的体积。
使用步骤:
1. 导入common-annotations.jar包(该包在Spring2.5完全包的lib/j2ee/中)
2. 修改Spring配置文件的schema如下:
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"> </beans> |
3. 在配置文件中加入如下配置:
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.kay"/> |
其中base-package属性指定要扫描的包,Spring容器会自动的扫描该包及其子包。
4. 在要受管理的Bean加上如下四种Annotation
1) @Service à业务逻辑Bean(例如Service)
2) @Controller à视图Bean(例如Struts的Action)
3) @Component à未分类Bean(例如切面Bean)
4) @Repository à实例化Bean(例如DAO)
在当前的Spring的版本中(2.5.6),未对上述四种Annotation做出处理上的区别,所以只要在要受管理的Bean上加上上述随意一个Annotation即可。
例如:
|
@Component public class UserBean { public void add() { System.out.println("Add method is runing~~~~~"); } } |
自动扫描的Bean的命名:
使用自动扫描后,Bean的Id在默认情况下为Bean的类名,但首字母小写,例如上面的UserBean,Bean的ID为userBean,当然可以指定自定义的ID:
|
@Component("user") public class UserBean { public void add() { System.out.println("Add method is runing~~~~~"); } } |
这样修改后Bean的ID变成了user。
自动扫描的Bean的作用域:
受Spring管理的Bean,默认的作用域为singleton,在开发中可以需要其他的作用域,Spring提供了@Scope Annotation进行配置:
|
@Scope("prototype") @Component("user") public class UserBean { public void add() { System.out.println("Add method is runing~~~~~"); } } |