MySQL数据库技术实战
MySQL数据库技术实战
一,安装mysql
很早之前就知道mysql提供了一套数据库样本(github地址),用于测试你的应用程序和数据库服务器。
今天分享下使用过程并将他发布到了码云,以便于同学们下载使用。
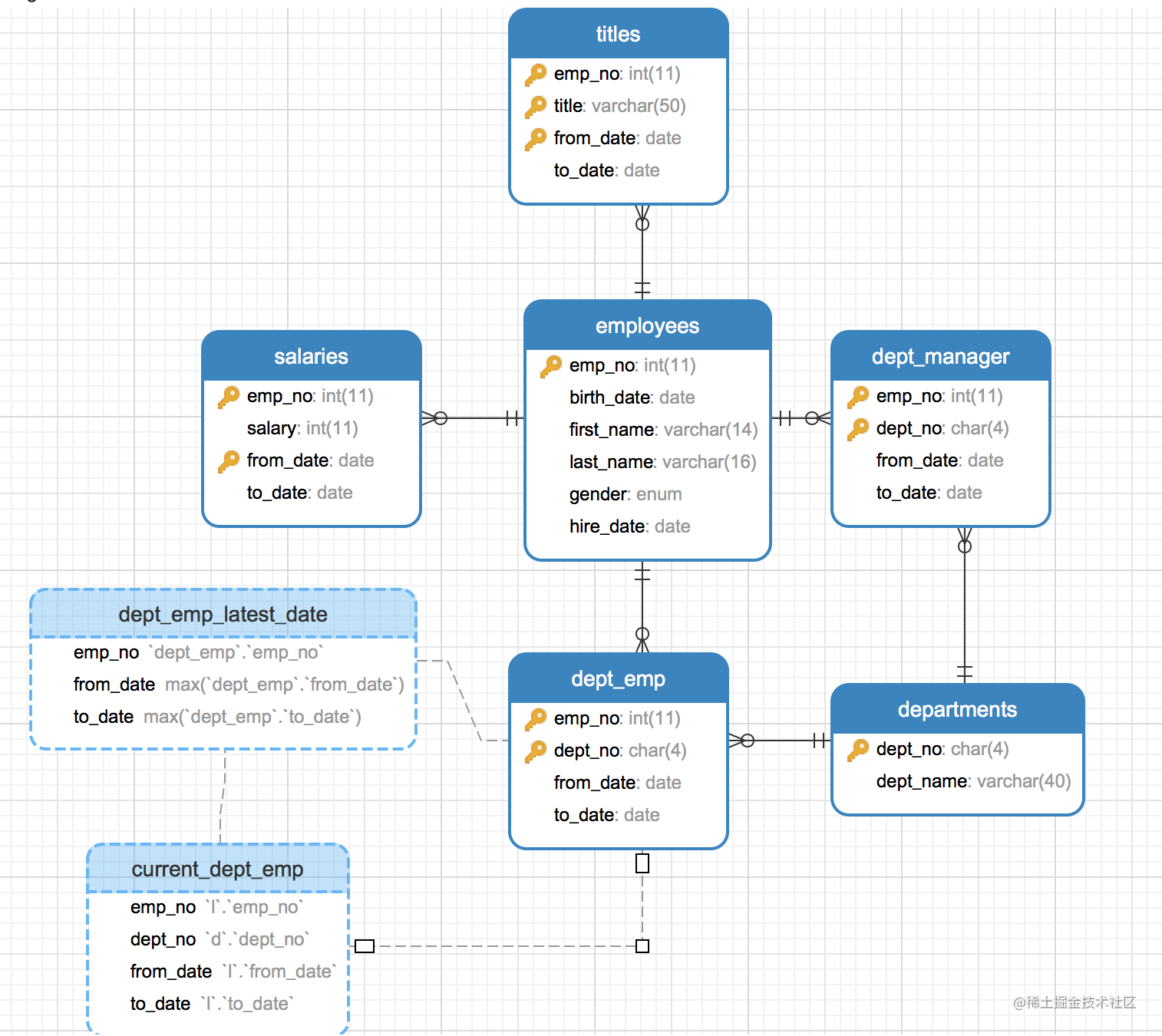
1. 要求
MySQL数据库服务器(5.0以上)
2. 安装使用
1.1
git clone https://gitee.com/JianQiangDeShiTouDian/mysql-demo-data.git
1.2
cd 下载好的仓库目录下
3. 使用说明
3.1.
mysql -u root -p < employees.sql

3.2
mysql -uroot -p < test_employees_md5.sql
或者 mysql -uroot -p < test_employees_sha.sql (校验是否安装成功)
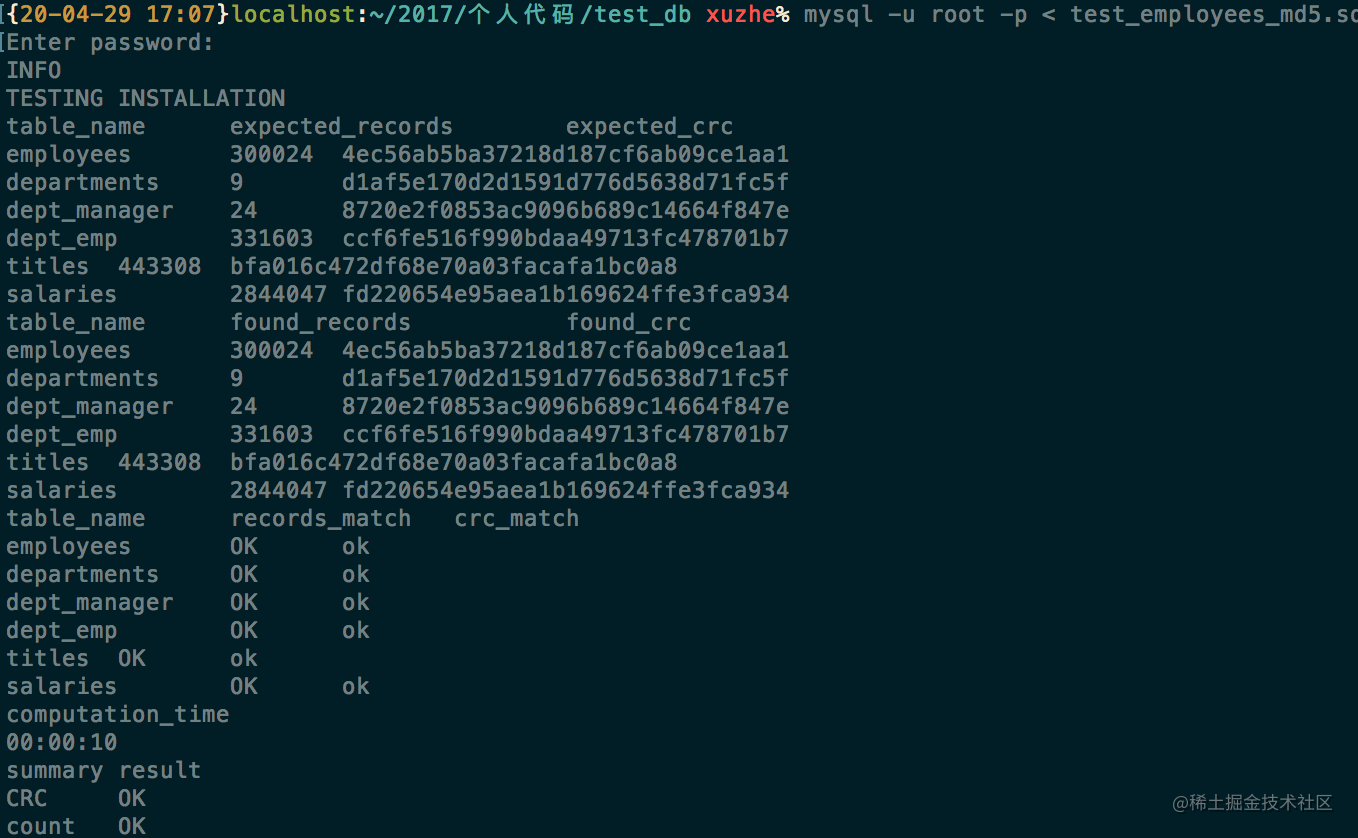
然后就可以愉快的使用数据进行sql优化了。
二,mysql的介绍
1. 设计mysql数据表
- 字符编码
- 表的创建
- 多表的设计规划
2. mysql基本操作
- 数据的增删改查
- 单一条件与多条件查询
- 数据筛选时的常用运算符
3.mysql高级查询
- 多表关联查询
- 子查询与联合查询
- 分组查询
4.mysql基本函数
-
mysql中的运算函数
-
sql使用的综合实战
-
熟悉掌握mysql的增删改查
-
掌握mysql中常用的运算符
-
掌握mysql中聚合函数的使用
5.mysql的应用环境
内部
- 移动APP
- web网站
- 客户端应用
外部
- 竞品网站
- 竞品app
- 三方公开信息
- 交换数据
6. 数据库的分类
关系型数据库
- mysql
- oracle
- sql server
非关系型数据库(nosql)
- redis
- mongodb
- memcached
关系型数据库的优点
- 关系型数据库是表和表,表和字段,数据和数据之间是存在着关系的
- 由于关系的存在,进行数据的增删改查非常方便
- 拥有事务的操作,保证书的完整性和一致性
关系型数据库的缺点
- 也正因为数据和数据之间是有关系的,这种关系的维护需要大量的算法,大量的算法就会降低系统的效果,同时降低性能
- 因为性能的降低使的关系型数据库面对海量的数据增删改查,数据维护的等场景显得比较无力
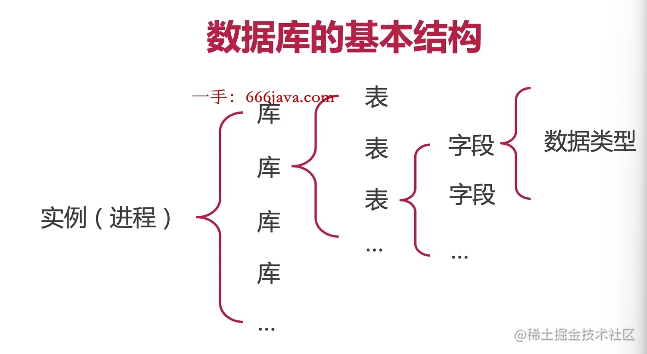
7. 数据库的基本结构
8. 设计mysql数据库
- 字符编码:

三,mysql基本操作
- 多表设计规范
- 标的创建
- 案例:多表创建
1. 数据库创建的两种方法
- 第一种,使用Navicat工具进行创建
- 第二种,使用sql语句进行创建
2. sql语句创建数据库的语法
- 创建数据库:CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS 数据库名字 DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
3. 表的创建
- 第一种,使用Navicat工具进行创建
- 第二种,使用sql语句进行创建
4. SQL语句创建表的语法
- 创建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS 'user'('user_id' INI UNSIGNED
AUTO_INCREMENT,'user_name' VARCHAR(100)NOT NULL,'birthday'DATE,
PRIMARY KEY('user_id'))ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET =utf8;



5.字段名
'birthday’DATE,字段名叫birthday日期类型
PRIMARY KEY(‘user_id’) 唯一主键user_id
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET =utf8; 存储引擎为InnoDB 默认字符编码是utf8
6. 代表. 多表创建
6.1. 学校表(表名school)
- id 数字 不能为空 自增 主键
- school_name 不能为空 字符串
- school_address 可以为空 字符串
6.2. 年级表(表名grade)
- id 数字 不能为空 自增 主键
- school_id 不能为空 数字
- grade_name 年级名称 不能为空 字符串
6.3.班级表(表名class)
- id 数字 不能为空 自增 主键
- grade_id 不能为空 数字
- class_name 班级名称 不能空 字符串
6.4. 学生表(表名student)
- class_id 班级id 不能为空 数字
- student_name 学生名称 不能为空 字符串
- student_birthday 学生生日 日期类型
- sex 性别 整数 不能为空
6.5. 课程表(表名course)
- id 数字 不能为空 自增 主键
- grade_id 年级id 不能为空 数字
- course_name 课程名称 不能为空 字符串
- full_mark 满分分数 数字类型
- passing_score 及格分数 数字类型
6.6.成绩表(表名score)
- id 数字 不能为空 自增 主键
- student_id 学生id 不能为空 数字
- course_id 课程id 整数 不能为空
- score 分数 可以为空 数字
7. 插入数据
7.1. SQL语句插入数据语法
新增一行数据
INSERT INTO 表名(字段名1,字段名2,...字段名N)
VALUES (值1,值1,...值N);
新增多行数据
INSERT INTO 表名(字段名1,字段名2,...字段名N)
VALUES
(值1,值1,...值N),
(值1,值1,...值N),
(值1,值1,...值N);
INSERT INTO USER ( user_name, birthday )
VALUES
( 'xiaoqiang', '2022-09-01' )
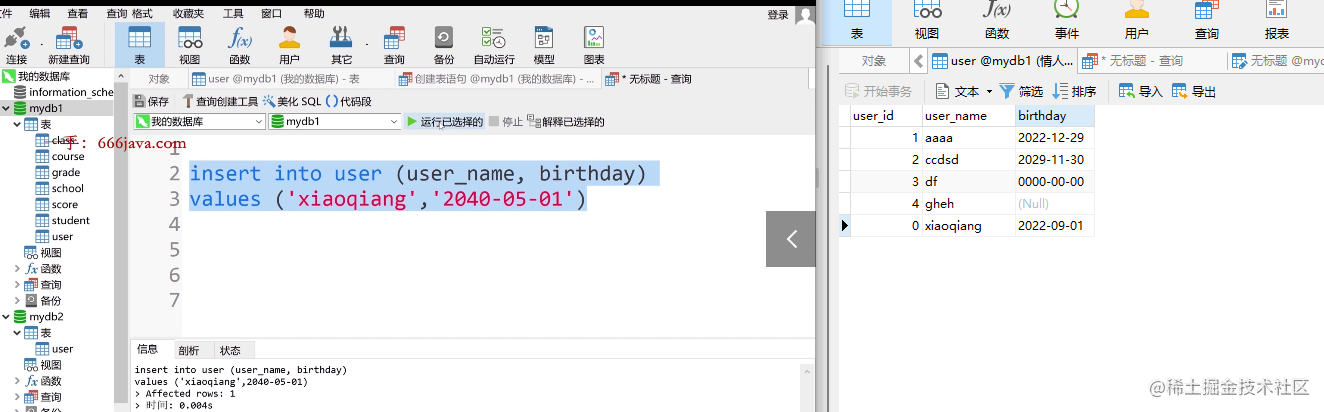
7.2.
INSERT into user(user_name,birthday)
VALUES
('小强','1987-01-01'),
('韩咩咩','1960-08-04'),
('建国','1955-06-07'),
('卫国','1930-08-09'),
('狗子个','1925-12-25');

8. 更新数据
8.1. 更新表中全部数据
UPDATE 表名 SET 列1=新值1,列2=新值
8.2. 按条件更新数据
UPDATE 表名 SET 列1=新值1,列2=新值2 WHERE 过滤条件
8.1.1. 点击对应的表,右键设计表可添加sex
输入
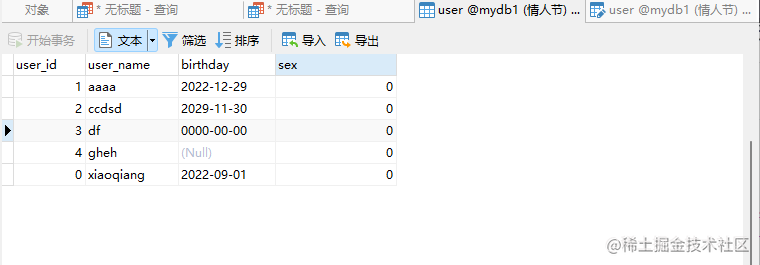
UPDATE user set sex=0;
刷新表格sex一列可变为0
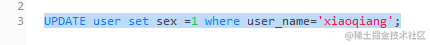
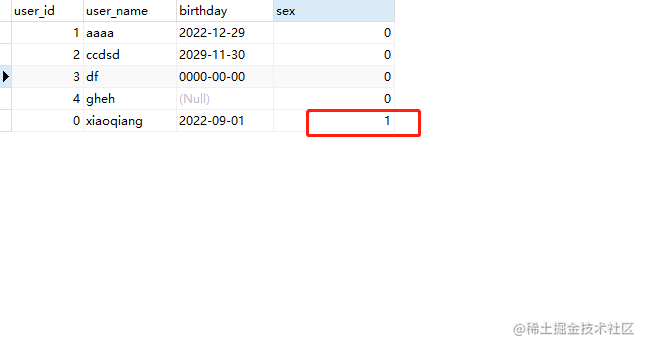
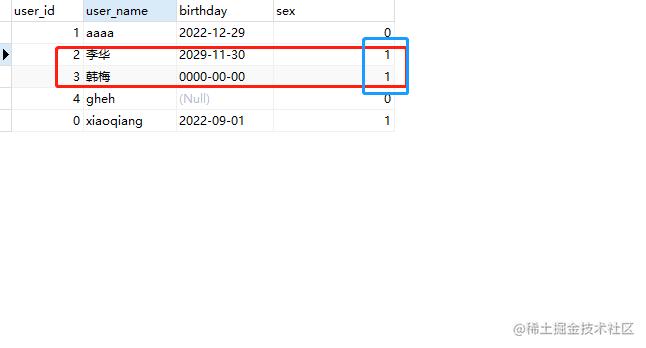
8.1.2. 如果修改xiaoqiang的sex参数可输入:
UPDATE user set sex =1 where user_name='xiaoqiang';
8.1.3. 同时修改两个人(中文名需要加上’')的sex参数可输入
UPDATE user set sex =1 where user_name='韩梅'or user_name ='李华';

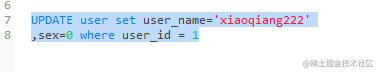
8.1.4. 修改表格里的名字和sex参数,可输入(要加where条件):
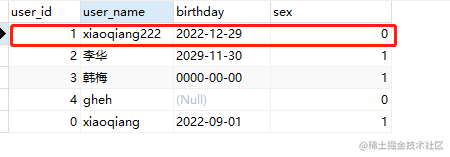
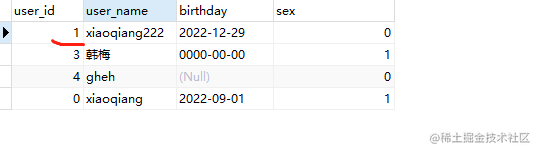
UPDATE user set user_name='xiaoqiang222'
,sex=0 where user_id = 1
9. 数据删除
9.1. 删除表中全部数据
delete from 表名;`
9.2. 按条件删除表中部分数据
delete from 表名 where 字段名=字段值;
9.3. 清空表中数据
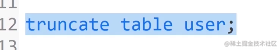
truncate table 表名;
9.4. 删除表
drop table [if exists] 表名;
演练
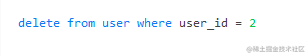
①:删除表格中其中一行可输入:
delete from user where user_id = 2
②:删除表格所有可输入(这个方法删除数据,会有轨迹存在):
delete from user -- where user_id = 2

③:删除表格所有可输入(这个方法是真的删除数据,不会有任何的轨迹):
truncate table user
④清空表
这个方法删除数据,会有轨迹存在
⑤截断表(这个方法是真的删除数据,不会有任何的轨迹)
⑥删除表(以下两种方法都可以删除)
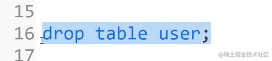
10. 数据基本查询
(1). 查询表中全部字段
select * from 表名
select 字段1,字段2... from 表名
①:查询全部可以输入:
select * from user;
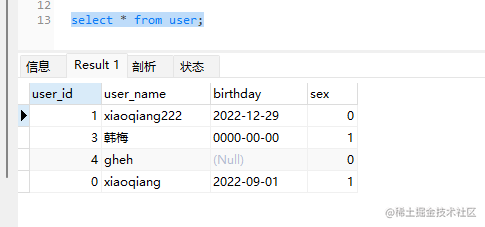
②:查取出来的结果,sex参数可以修改的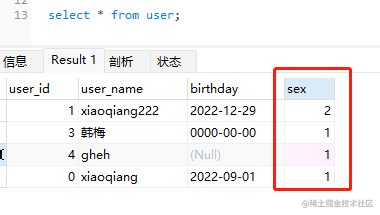
(2). 查询表中指定的字段
①:要什么给什么可输入:
select user_name,birthday from user;
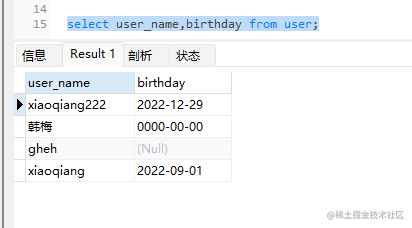
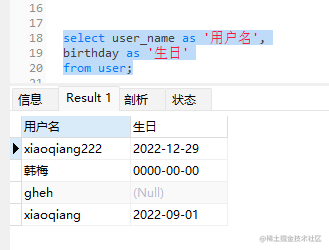
②:将表格中的字母改为中文可输入(如果不输入as,只是结果改为中文,表里并没有改为中文):
select user_name as '用户名',
birthday as '生日'
from user;
11. 条件查询
(1). 单条件查询
select * from 表名 where 字段名=字段值
(2). 模糊条件查询
- 前模糊
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "%关键字"
- 后模糊
- 前后模糊
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "%关键字%"
- 中间模糊
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "关键字%关键字"
- 哪里模糊就哪里模糊
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "关键字%关键字%关键字"
- 查询出姓李,并且名字只有两个的同学
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "李_"
- 查询出姓李,并且名字只有三个的同学
select * from 表名 where 字段名 like "李__"
注意:%代表一个或者多个,_代表一个下划线。
_是一个下划线,__是两个下划线,李后边是两个下划线
演练
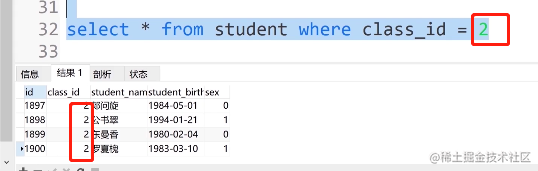
①. 查找2班所有的人可输入:
select * from student where class_id = 2
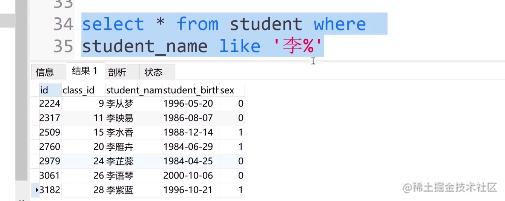
②. 查找姓李的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '李%'
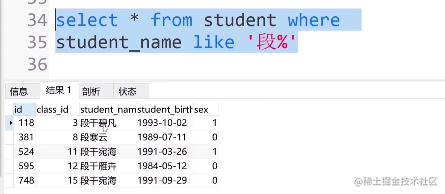
③. 查找姓段的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '段%'
④. 查找名字后面带有冬字的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '%冬'
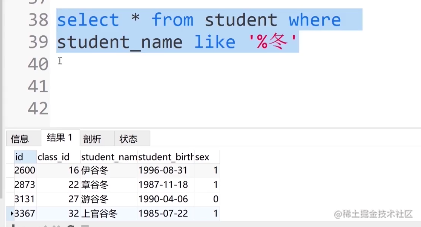
⑤. 查找名字中间带有冬字的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '%冬%'
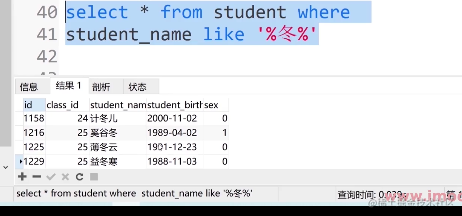
⑥. 查找名字里面带有薄,云字的人可输入:
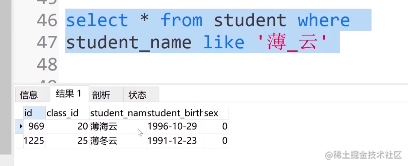
select * from student where student_name like '薄%云'

⑦. 查找名字里面有薄_云字的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '薄_云'
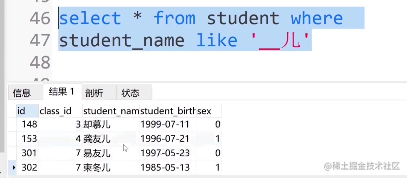
⑧. 查找名字里面有__儿字的人可输入:
select * from student where student_name like '__儿'
12. 数据筛选查询
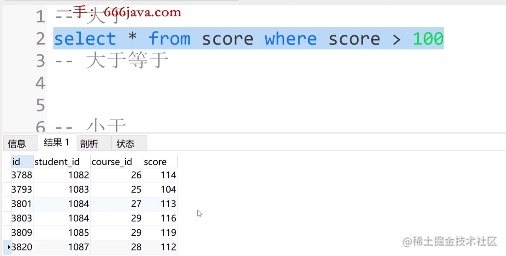
①. 大于
select * from score where score > 100
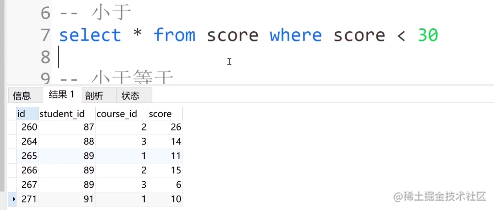
②. 小于
select * from score where score < 30
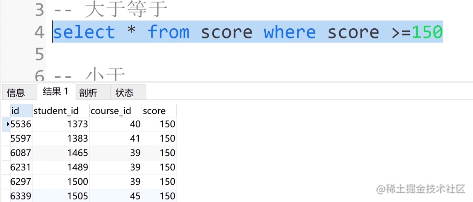
③. 大于等于
select * from score where score >= 150
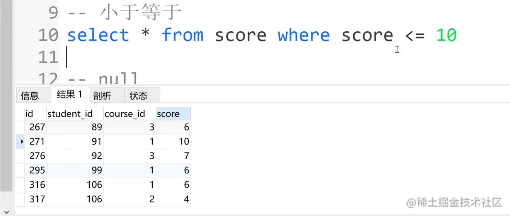
④. 小于等于
select * from score where score <= 10
⑤. null
select * from school where school_address is null
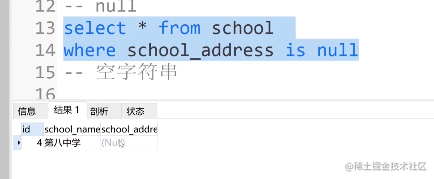
⑥. 空字符串
select * from school where school_address =""
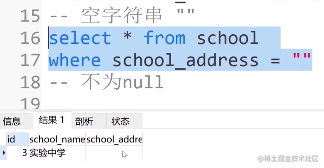
⑦. 不等于
select * from school where school_address !=""
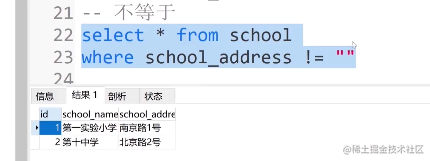
⑧. 不为null
select * from school where school_address is not null

⑨包含in
select * from score where score in (30,40,50)
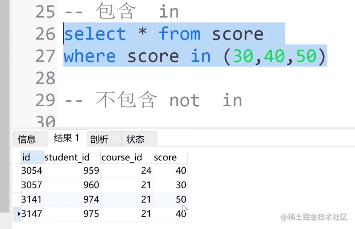
⑩不包含not in
select * from score where score not in (30,40,50)
⑪两者之间between and
select * from score where score between 90 and 100
⑫返回指定条数 limit
select * from score where score between 90 and 100 limut 3
⑬只显示从第三行开始,数到后五
select * from student limit 3,5

13. 多条件查询
① 与 and
select * from student where class sex =1 and sex = 1
select * from student where class sex =1 and sex = 1 and studen_name like "%香"
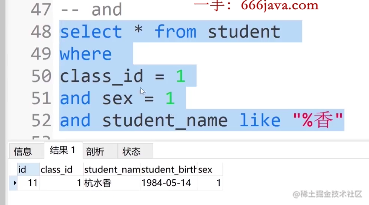
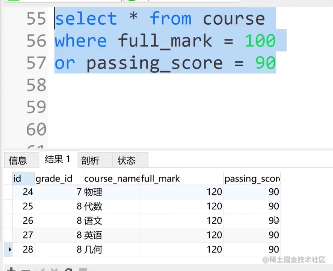
② 或 or
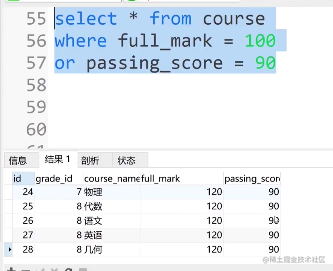
select * from course where full_mark = 100 or passing_score = 90
select * from course where full_mark = 100 or passing_score = 90 or grade_id = 10
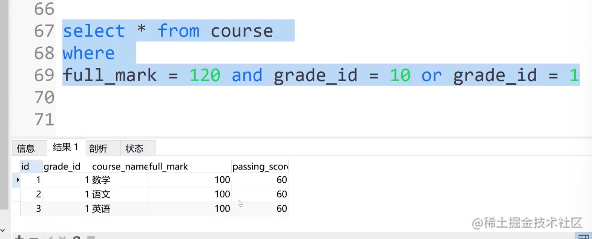
③如果and和or一起使用会怎样?
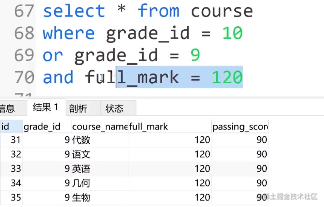
select * from course where full_mark = 120 and grade_id = 10 or grade_id =1
四,高级查询
1.关联查询的分类与定义
1.1演练
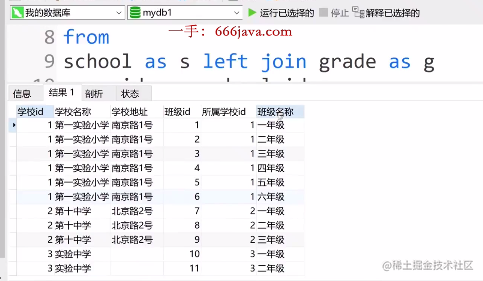
- 左关联查询实战
select s.id '学校id',
s.school_name '学校名称',
s.school_address '学校地址',
g.id '班级id'
g.school_id '所属学校id'
g.grade_name '班级名称'
from
school left join grade
on school.id = grade.school_id
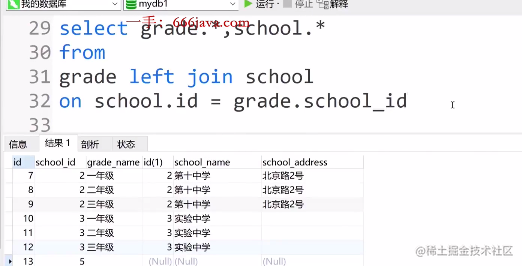
- 右关联查询实战
select school.*,grade.*
from
school left join grade
on school.id = grade.school_id
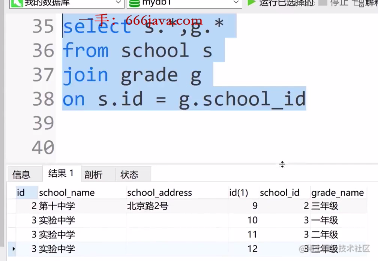
- 全关联查询实战
select s.*,g.*
from school s
join grade g
on s.id = g.school_id
- 子查询实战(括号内就叫做子查询)
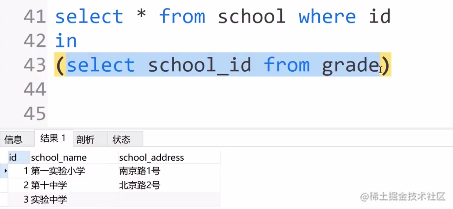
①要查寻有年纪的学校
select * from school where id
in
(select school_id from grade)
②查询出六年级,全体的数学分数
select * from score where score_id =
(select * from course where
grade_id
in
(select * from grade where ``grade_name='六年级')
and course_name ='数学')
- 联合查询
基本格式
select 字段名 from 表名 where 筛选条件
union
select 字段名 from 表名 where 筛选条件

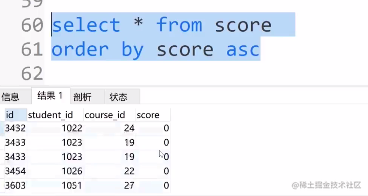
- 结果排序
select * from score
order by score asc
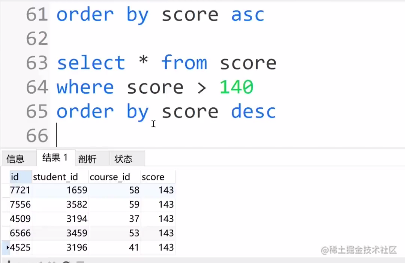
select * from score
where score > 140
order by score desc
- 分组查询与筛选

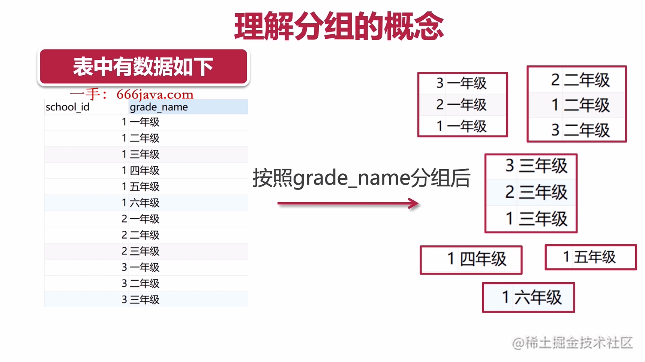
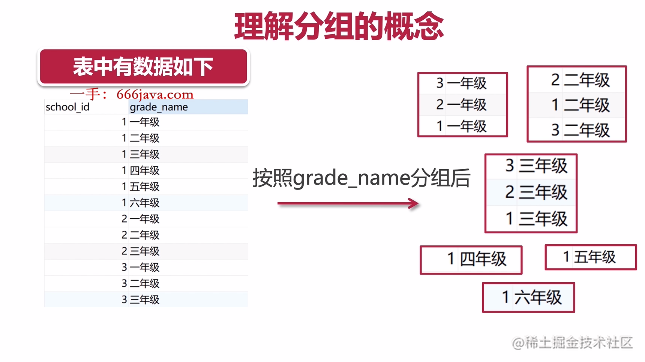
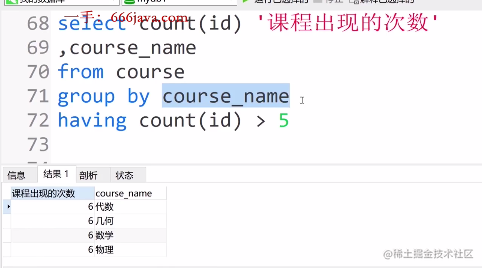
请查询出现过5次以上的课程
select count(id) '课程出现的次数'
,course_name
from course
group by course_name
having count(id) > 5
五,聚合函数
- 最大值
- 最小值
- 平均值
- 求和
演练一
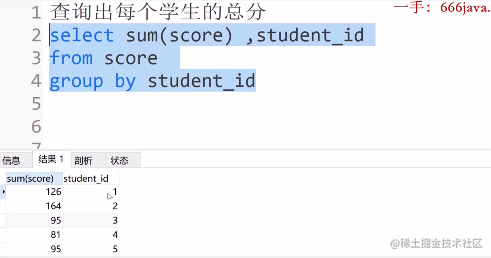
①查询出每个学生的总分
select sum(score)
from score
group by student_id
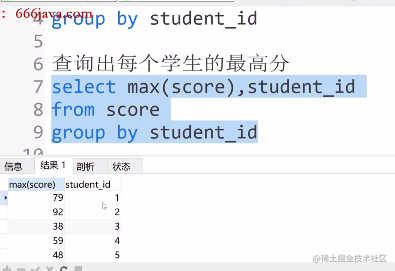
②查询出每个学生的最高分
select max(score),student_id
from score
group by student_id
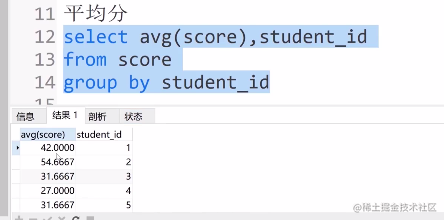
③平均分
select avg(score),student_id
from score
group by student_id
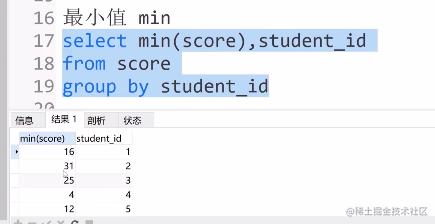
④最小值 min
select min(score),student_id
from score
group by student_id
演练二
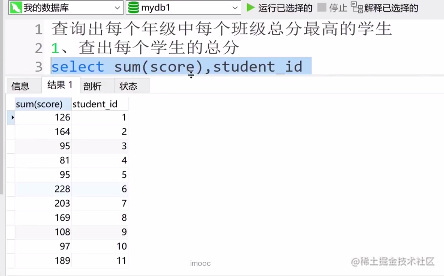
查询出每个年级中每个班级总分最高的学生
①查出每个学生的总分
select sum(score),student_id
from score
group by student_id
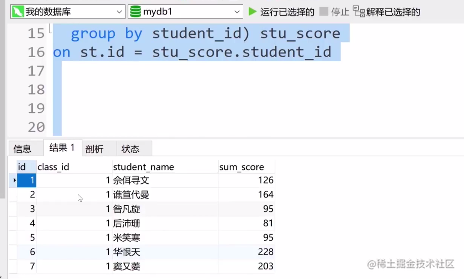
②查询出每个学生所在班级
select st.id,st.class_id,student_name,
stu_score.sum_score
from student st
left join
(select sum(score)sum_score,student_id
from score
group by student_id) stu_score
on st.id = stu_score.student_id
③根据我们现有的结果查询到学生所属班级
select
c.id,c.class_name,c.grade_id,
sn.student_name,sn.sum_score
from class c
left join
(select sum(score)sum_score,student_id
from score
group by student_id) stu_score
on st.id = stu_score.student_id
) sn
on c.id = sn.class_id
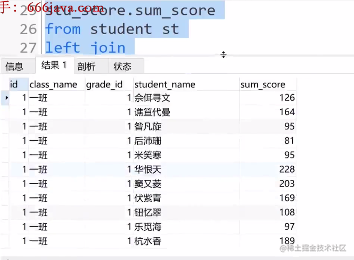
④根据现有结果查询出所在年级
select
g.grade_name,cc.class_name,cc.student_name,
cc.sum_score
from grade g
left join
(select c.id,c.class_name,c.grade_id,
sn.student_name,sn.sum_score
from class c
left join
(select sum(score)sum_score,student_id
from score
group by student_id) stu_score
on st.id = stu_score.student_id
) sn
on c.id = sn.class_id
) cc
on g.id = cc.class_id
六,总结
- 字符编码(utf-8)
- 三范式与反范式设计
- 数据写入语句
- 数据更新语句
- 条件查询
- 模糊查询
- 多条件查询
- 各种比较运算符
- 左关联查询
- 右关联查询
- 全关联查询
- 分组查询的概念与应用
- 聚合函数

 被折叠的 条评论 为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论 为什么被折叠? 
 点击重新获取
点击重新获取

 扫码支付
扫码支付
抵扣说明:
1.余额是钱包充值的虚拟货币,按照1:1的比例进行支付金额的抵扣。
2.余额无法直接购买下载,可以购买VIP、C币套餐、付费专栏及课程。
 余额充值
余额充值

