类加载器深入理解和双亲委托模型的案例分析
类加载器深入理解和双亲委托模型的案例分析
- 我们知道类必须通过类加载器加载后,我们程序才可以使用。接下来我们就对类加载器进行分析,Java虚拟机的类加载器是如何加载类的。首先我们可以从ClassLoader的源码分析入手。
ClassLoader 的源码分析
ClassLoader 的javadoc文档
- javadoc文档是最权威的官方讲解,可以对ClassLoader有一个比较全面且正确的一个认知。下面是javadoc内容。
A class loader is an object that is responsible for loading classes. The class ClassLoader is an abstract class. Given the binary name of a class, a class loader should attempt to locate or generate data that constitutes a definition for the class. A typical strategy is to transform the name into a file name and then read a "class file" of that name from a file system.
翻译: 一个加载器就是一个对象负责加载类。ClassLoader 是抽象类,给定了一个二进制名字(可以简单的理解为一个字符串类似: "java.lang.String",就代码一个String类的二进制名称),ClassLoader应该尝试定位或者生成构成类定义的相应的数据。(定位说明类的相关数据已经存在例如String这个类,我们程序员已经编写好的类等,生成对应的是没有类的相关数据,需要classLoader进行生成,因为java一些类需要运行期动态生成出来的,例如动态代理,在运行期之前是不存在的),一种典型的策略就是将一个二进制的名字转换成一个文件名字。然后从文件系统中去读取这个文件中所包含的字节的class文件,我们就是从磁盘上去读取class字节码文件。这个是比较典型的,还可以从其他地方读取网络中,数据库等。
Every Class object contains a reference to the ClassLoader that defined it.
翻译:每个class对象都会包含定义这个class的ClassLoader的引用。因为class类都会有一个getClassLoader这个方法。换句话说class会含有加载该class对象的ClassLoader对象。
Class objects for array classes are not created by class loaders, but are created automatically as required by the Java runtime. The class loader for an array class, as returned by Class.getClassLoader() is the same as the class loader for its element type; if the element type is a primitive type, then the array class has no class loader.
翻译: 对于数组类的class对象,并不是有ClassLoader进行创建的,而是由java运行时按需要进行自动创建的。对于数组类的getclassloader()返回的数组类的类装入器与其元素类型的类装入器相同;如果元素类型是基本类型,则数组类没有类装入器。
代码案例如下所示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String 是rt.jar 是根类加载器负责加载的(后面会将各个加载器的加载范围) 通过getClassLoader可知 根类加载器返回为Null
String[] strings = new String[2];
System.out.println(strings.getClass().getClassLoader());
// Mytest08是程序员自己编写的 系统类加载器进行加载 返回为: 系统类加载器
Mytest08[] mytest08s = new Mytest08[2];
System.out.println(mytest08s.getClass().getClassLoader());
// int由于int是基本类型 所以返回为null
int[] ints = new int[2];
System.out.println(ints.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
Applications implement subclasses of ClassLoader in order to extend the manner in which the Java virtual machine dynamically loads classes.
Class loaders may typically be used by security managers to indicate security domains.
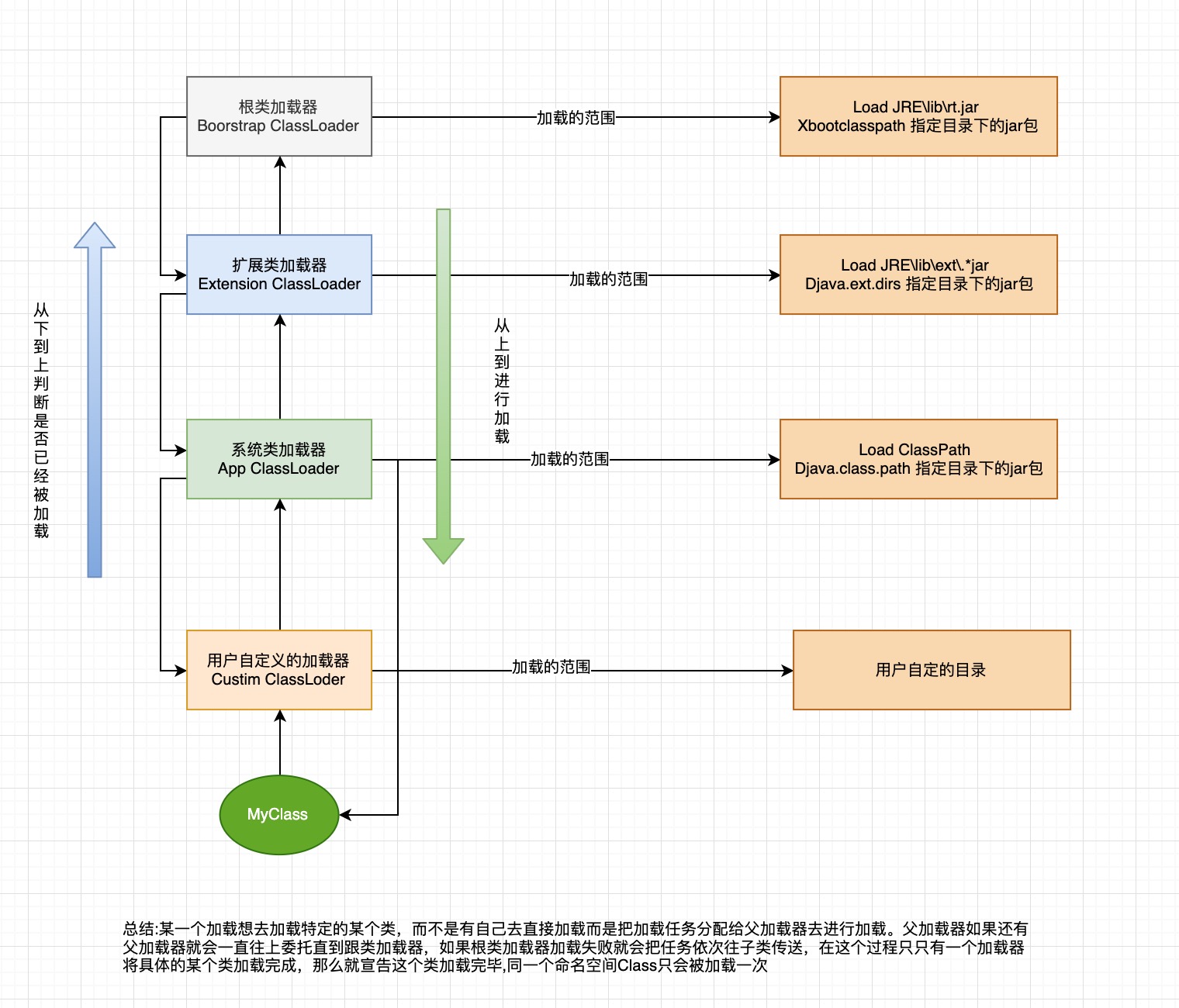
The ClassLoader class uses a delegation model to search for classes and resources. Each instance of ClassLoader has an associated parent class loader. When requested to find a class or resource, a ClassLoader instance will delegate the search for the class or resource to its parent class loader before attempting to find the class or resource itself. The virtual machine's built-in class loader, called the "bootstrap class loader", does not itself have a parent but may serve as the parent of a ClassLoader instance.
翻译:ClassLoader类使用委托模型来搜索类和资源。类装入器的每个实例都有一个关联的父类装入器。当请求查找类或资源时,类加载器实例将把对类或资源的搜索委托给其父类加载器,然后再尝试查找类或资源本身。虚拟机的内置类装入器称为“启动类加载器”,它本身没有父类加载器,但可以作为类加载器实例的父类。
这个就介绍了双亲委派机制的原理。可参考如下所示的图:
我们还可以通过代码进行验证java虚拟机加载器的层次结构如下所示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
/**
* 打印加载器的层次结构
* sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2 系统类加载器
* sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@610455d6 扩展类加载器
* null 根类加载器
*/
while (systemClassLoader != null) {
//返回父类加载器
// 根类加载器 返回为Null
systemClassLoader = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
}
}
Class loaders that support concurrent loading of classes are known as parallel capable class loaders and are required to register themselves at their class initialization time by invoking the ClassLoader.registerAsParallelCapable method. Note that the ClassLoader class is registered as parallel capable by default. However, its subclasses still need to register themselves if they are parallel capable. In environments in which the delegation model is not strictly hierarchical, class loaders need to be parallel capable, otherwise class loading can lead to deadlocks because the loader lock is held for the duration of the class loading process (see loadClass methods).
翻译:支持类的并发加载的类加载器称为支持并行的类加载器,需要通过调用类加载器在类初始化时注册它们自己。registerAsParallelCapable方法。注意,默认情况下ClassLoader类被注册为支持并行的。但是,它的子类仍然需要注册它们自己,如果它们是并行的。在委托模型没有严格层次结构的环境中,类装入器需要具有并行能力,否则类装入可能会导致死锁,因为装入器锁在类装入过程期间一直持有(请参阅loadClass方法)。
Normally, the Java virtual machine loads classes from the local file system in a platform-dependent manner. For example, on UNIX systems, the virtual machine loads classes from the directory defined by the CLASSPATH environment variable.
翻译:通常,Java虚拟机以平台相关的方式从本地文件系统加载类。例如,在UNIX系统上,虚拟机从CLASSPATH环境变量定义的目录加载类。 换句话说:系统类加载器通过我们系统配置的classpath目录来加载我们项目中的我们程序员编写的class问题
However, some classes may not originate from a file; they may originate from other sources, such as the network, or they could be constructed by an application. The method defineClass converts an array of bytes into an instance of class Class. Instances of this newly defined class can be created using Class.newInstance.
翻译:但是,有些类可能不是起源于文件;它们可能来自其他来源,例如网络,也可能由应用程序构造(动态代理)。方法defineClass将字节数组转换为类的实例。可以使用class . newinstance创建这个新定义的类的实例。
The methods and constructors of objects created by a class loader may reference other classes. To determine the class(es) referred to, the Java virtual machine invokes the loadClass method of the class loader that originally created the class.
翻译: 类装入器创建的对象的方法和构造函数可以引用其他类。为了确定引用的类,Java虚拟机调用最初创建类的类装入器的loadClass方法。
For example, an application could create a network class loader to download class files from a server. Sample code might look like:
ClassLoader loader = new NetworkClassLoader(host, port);
Object main = loader.loadClass("Main", true).newInstance();
. . .
The network class loader subclass must define the methods findClass and loadClassData to load a class from the network. Once it has downloaded the bytes that make up the class, it should use the method defineClass to create a class instance. A sample implementation is:
class NetworkClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
String host;
int port;
public Class findClass(String name) {
byte[] b = loadClassData(name);
return defineClass(name, b, 0, b.length);
}
private byte[] loadClassData(String name) {
// load the class data from the connection
. . .
}
}
上面这两个demo就是展示类加载器加载类的具体案例。
自定义写一个用户类加载器
- 代码如下所示:
public class MyTest11 extends ClassLoader {
// 指定加载器的加载路径
private String path;
private String classsLoaderName;
//文件的扩展名
private final String fileExtension = ".class";
public MyTest11(String classsLoaderName) {
// 指定父加载器 默认系统类加载器 具体可以看源码在这里就不做过多的介绍了
super();
this.classsLoaderName = classsLoaderName;
}
/**
* 显示的指定父类classloader 可以将用户自定义的loader1 作为 用户自定义loader2 的父加载器 提供了很多的扩展性
*/
public MyTest11(ClassLoader parent, String classsLoaderName) {
super(parent);
this.classsLoaderName = classsLoaderName;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 自定义的classloader 自需要重写findCLass 这个类 findClass 类的作用就是通过一个二进制的类名去加载一个class对象
//
System.out.println("findclass invoke" + name);
System.out.println("class loader name" + this.classsLoaderName);
byte[] data = loadClassData(name);
// defineClass 是将一个byte[] 数组转换成一个class 对象
return this.defineClass(name, data, 0, data.length);
}
/**
* 自定义根据二进制类名 加载类的属性以字节数组的形式返回 具体实现就是io操作
* @param name 二进制类名
* @return byte[]
*/
private byte[] loadClassData(String name) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
byte[] data = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = null;
// 匹配路径 mac '/' win '\\'
name = name.replace(".", "/");
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(this.path + name + this.fileExtension));
byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int ch = 0;
while (-1 != (ch = inputStream.read())) {
byteArrayOutputStream.write(ch);
}
data = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return data;
}
/**
* 设置类的加载路径
*/
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
Coding验证类加载器的机制
- 案例01
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//这里我们调用了loadClass 方法内部调用了我们重写的findClass方法
// MyTestBean 是我程序定义的类
// Users/panda/Documents/SourceCode/jvm_lecture/target/classes 项目中的class文件目录
MyTest11 myTest11 = new MyTest11("myLoader");
myTest11.setPath("/Users/panda/Documents/SourceCode/jvm_lecture/target/classes");
Class<?> aClass = myTest11.loadClass("com.study.jvm.day11.MyTestBean");
System.out.println("aClass = " + aClass.hashCode());
Object object = aClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("object = " + object);
System.out.println("aClass 的加载器为:" + aClass.getClassLoader());
}
- 输出结果:
aClass = 1627674070
object = com.study.jvm.day11.MyTestBean@511d50c0
aClass 的加载器为:sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
- 结果分析
从输出结果上来看,并没有打印我们 findclass invoke这句话,说明没有走我们自定义的ClassLoader。因为我们自定义的myLoader准备加载前会先委托给父类加载器系统类加载器进行加载,系统类加载器可以加载(classpath下)就有MyTestBean.class。然后系统类加载器进行加载,而类只会被加载一次。所以没有走我们自定义的classLoader。
- 案例02
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//这里我们调用了loadClass 方法内部调用了我们重写的findClass方法
// MyTestBean 是我程序定义的类
/**
* 需要注意的点:
* 01 首先将本项目中的MyTestBean.class 从本项目转移到自定义的一个路径 本案例中我把它转移到桌面
* 02 删除本项目的MyTestBean.class 不删除我们的系统类加载器根据二进制类名也会加载该class
*/
MyTest11 myTest11 = new MyTest11("myLoader");
myTest11.setPath("/Users/panda/Desktop/");
Class<?> aClass = myTest11.loadClass("com.study.jvm.day11.MyTestBean");
System.out.println("aClass = " + aClass.hashCode());
Object object = aClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("object = " + object);
System.out.println("aClass 的加载器为:" + aClass.getClassLoader());
}
- 输出结果:
findclass invoke: com.study.jvm.day11.MyTestBean
class loader name: myLoader
aClass = 1625635731
object = com.study.jvm.day11.MyTestBean@5e2de80c
aClass 的加载器为:com.study.jvm.day11.MyTest11@610455d6
- 结果分析
从输出的结果可以看到MyTestBean是由我们自定义的MyTest11加载的,因为在加载的时候MyTest11会将委托任务交给父加载器们,他们都加载不了,然后就会自己去加载。
结束语
- ClassLoader里面还有很多有用的方法,小伙伴们可以借助文中的案例慢慢手动体会。