MyBatis事务管理机制
目录
一、概述
二、事务的配置创建和使用
- 事务的配置
- 事务工厂的创建
- 事务工厂TransactionFactory
- 事务Transaction的创建
- JdbcTransaction
- ManagedTransaction
一、概述
对数据库的事务而言,应该具有以下几点:创建(create)、提交(commit)、回滚(rollback)、关闭(close)。对应地,MyBatis将事务抽象成了Transaction接口:其接口定义如下:
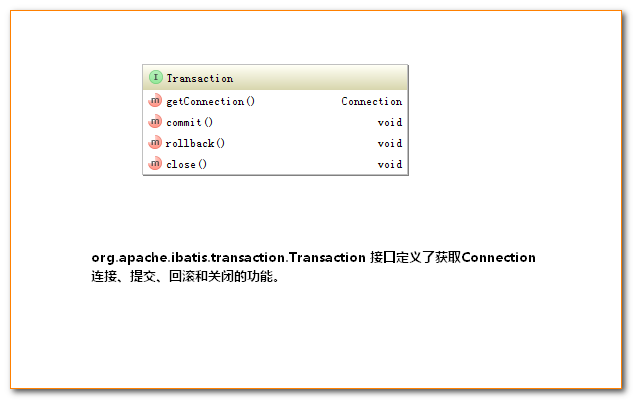
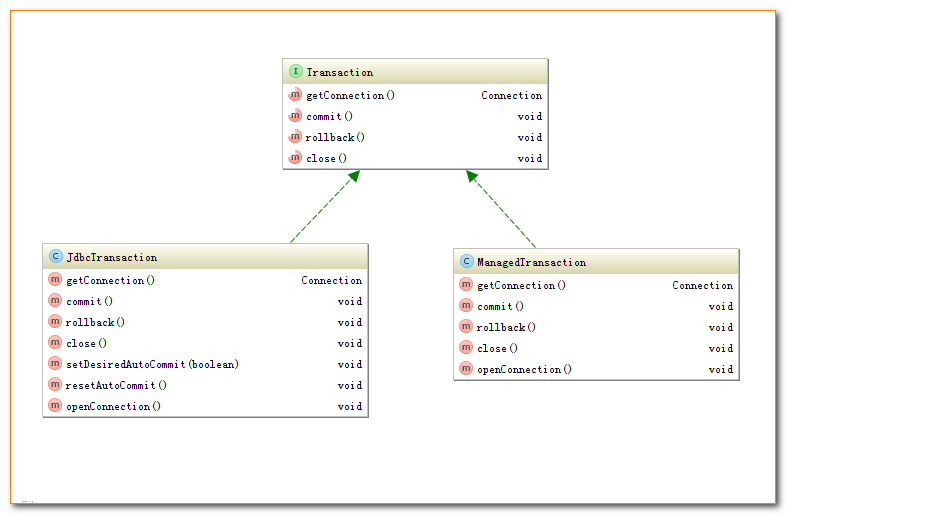
MyBatis的事务管理分为两种形式:
- 使用JDBC的事务管理机制:即利用java.sql.Connection对象完成对事务的提交(commit())、回滚(rollback())、关闭(close())等。
- 使用MANAGED的事务管理机制:这种机制MyBatis自身不会去实现事务管理,而是让程序的容器如(JBOSS,Weblogic)来实现对事务的管理。
这两者的类图如下所示:
二、事务的配置、创建和使用
1. 事务的配置
我们在使用MyBatis时,一般会在MyBatisXML配置文件中定义类似如下的信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--映入外部文件定义的属性,供此配置文件使用-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties>
<environments default="development">
<!-- 连接环境信息,取一个任意唯一的名字 -->
<environment id="development">
<!-- mybatis使用jdbc事务管理方式 -->
<transactionManager type="jdbc"/>
<!-- mybatis使用连接池方式来获取连接 -->
<dataSource type="pooled">
<!-- 配置与数据库交互的4个必要属性 -->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载映射文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/mybatis/EmployeeMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
<environment>节点定义了连接某个数据库的信息,其子节点<transactionManager> 的type 会决定我们用什么类型的事务管理机制。
2.事务工厂的创建
MyBatis事务的创建是交给TransactionFactory 事务工厂来创建的,如果我们将<transactionManager>的type 配置为"JDBC",那么,在MyBatis初始化解析<environment>节点时,会根据type="JDBC"创建一个JdbcTransactionFactory工厂,其源码如下:
/**
* 解析<transactionManager>节点,创建对应的TransactionFactory
* @param context
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
/*
在Configuration初始化的时候,会通过以下语句,给JDBC和MANAGED对应的工厂类
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
下述的resolveClass(type).newInstance()会创建对应的工厂实例
*/
TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");
}
如上述代码所示,如果type = "JDBC",则MyBatis会创建一个JdbcTransactionFactory.class 实例;如果type="MANAGED",则MyBatis会创建一个MangedTransactionFactory.class实例。
作为<environment>节点,会根据TransactionFactory和DataSource实例创建一个Environment对象,代码如下所示:
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
//是和默认的环境相同时,解析之
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
//1.解析<transactionManager>节点,决定创建什么类型的TransactionFactory
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
//2. 创建dataSource
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
//3. 使用了Environment内置的构造器Builder,传递id 事务工厂TransactionFactory和数据源DataSource
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}

上述一直在讲事务工厂TransactionFactory来创建的Transaction,现在让我们看一下MyBatis中的TransactionFactory的定义吧。
3. 事务工厂TransactionFactory
事务工厂Transaction定义了创建Transaction的两个方法:
- 通过指定的Connection对象创建Transaction
- 通过数据源DataSource来创建Transaction
与JDBC 和MANAGED两种Transaction相对应,TransactionFactory有两个对应的实现的子类:如下所示:
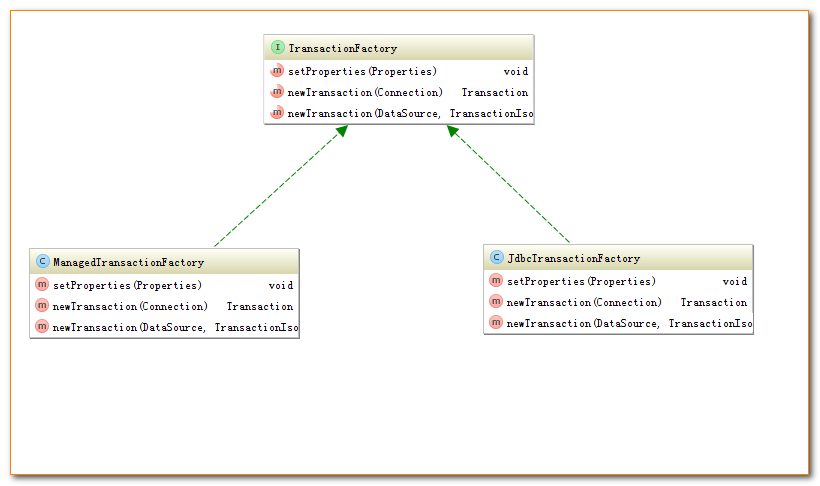
4. 事务Transaction的创建
通过事务工厂TransactionFactory很容易获取到Transaction对象实例。我们以JdbcTransaction为例,看一下JdbcTransactionFactory是怎样生成JdbcTransaction的,代码如下:
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
}
/**
* 根据给定的数据库连接Connection创建Transaction
* @param conn Existing database connection
* @return
*/
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
/**
* 根据DataSource、隔离级别和是否自动提交创建Transacion
*
* @param ds
* @param level Desired isolation level
* @param autoCommit Desired autocommit
* @return
*/
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
}
如上说是,JdbcTransactionFactory会创建JDBC类型的Transaction,即JdbcTransaction。类似地,ManagedTransactionFactory也会创建ManagedTransaction。下面我们会分别深入JdbcTranaction 和ManagedTransaction,看它们到底是怎样实现事务管理的。
5. JdbcTransaction
JdbcTransaction直接使用JDBC的提交和回滚事务管理机制 。它依赖与从dataSource中取得的连接connection 来管理transaction 的作用域,connection对象的获取被延迟到调用getConnection()方法。如果autocommit设置为on,开启状态的话,它会忽略commit和rollback。
直观地讲,就是JdbcTransaction是使用的java.sql.Connection 上的commit和rollback功能,JdbcTransaction只是相当于对java.sql.Connection事务处理进行了一次包装(wrapper),Transaction的事务管理都是通过java.sql.Connection实现的。JdbcTransaction的代码实现如下:
/**
* @see JdbcTransactionFactory
*/
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
//数据库连接
protected Connection connection;
//数据源
protected DataSource dataSource;
//隔离级别
protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
//是否为自动提交
protected boolean autoCommmit;
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
/**
* commit()功能 使用connection的commit()
* @throws SQLException
*/
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
/**
* rollback()功能 使用connection的rollback()
* @throws SQLException
*/
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
/**
* close()功能 使用connection的close()
* @throws SQLException
*/
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
try {
if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Only a very poorly implemented driver would fail here,
// and there's not much we can do about that.
throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
+ "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
+ "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected void resetAutoCommit() {
try {
if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
// MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed.
// Some databases start transactions with select statements
// and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection.
// A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection.
// Sybase throws an exception here.
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
}
6. ManagedTransaction
ManagedTransaction让容器来管理事务Transaction的整个生命周期,意思就是说,使用ManagedTransaction的commit和rollback功能不会对事务有任何的影响,它什么都不会做,它将事务管理的权利移交给了容器来实现。看如下Managed的实现代码大家就会一目了然:
/**
*
* 让容器管理事务transaction的整个生命周期
* connection的获取延迟到getConnection()方法的调用
* 忽略所有的commit和rollback操作
* 默认情况下,可以关闭一个连接connection,也可以配置它不可以关闭一个连接
* 让容器来管理transaction的整个生命周期
* @see ManagedTransactionFactory
*/
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class);
private DataSource dataSource;
private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
private Connection connection;
private boolean closeConnection;
public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
this.connection = connection;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
this.dataSource = ds;
this.level = level;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.close();
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if (this.level != null) {
this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号