原型模式
示例
/**
* TODO 序列化实现深拷贝
*
* @author ZhangPeng
* @date 2021年6月2日 下午4:11:29
*/
public class Person implements Cloneable,Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Date birthday;
public Person(Integer id, String name, String email, Date birthday) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//把当前对象写入内存中
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
oos.writeObject(this);
oos.close();
//从内存中取出数据
byte[] bytes = out.toByteArray();
InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
Object clone = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return clone;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", email=" + email
+ ", birthday=" + birthday + "]";
}
}
public class PrototypeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Person person = new Person(1,"卡卡罗特","xxx@163.com",Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
Person person1 = (Person) person.clone();
/**
* person1.getBirthday().setTime(0);
* person1.setBirthday(new Date(0));
*
* 第一行的意思是:get到了共享对象date,然后设置time=0,所以person和person1的birthday都发生了改变;
* 第二行的意思是:set自身的属性,所以并不会对另一个对象产生影响
*/
person1.getBirthday().setTime(0);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(person1);
}
}
克隆对单例的破坏
public class HungarySingleton implements Cloneable {
private static final HungarySingleton hungarySingleton;
static {
hungarySingleton = new HungarySingleton();
}
private HungarySingleton() {
if (hungarySingleton != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("单例构造器防止反射调用");
}
}
public static HungarySingleton getInstance() {
return hungarySingleton;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//return super.clone();//单例实现了克隆接口 可以利用反射破坏单例
return hungarySingleton;//解决办法 即使通过反射调用clone方法 获取到的依然是原来的实例对象
}
}
public class TestSingle {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HungarySingleton instance = HungarySingleton.getInstance();
Method cloneMethod = HungarySingleton.class.getDeclaredMethod("clone");
cloneMethod.setAccessible(true);
HungarySingleton newInstance = (HungarySingleton) cloneMethod.invoke(instance);
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(newInstance);
}
}
结果:
com.demo.tcp.designpattern.HungarySingleton@6d06d69c
com.demo.tcp.designpattern.HungarySingleton@6d06d69c
深克隆和浅克隆的区别
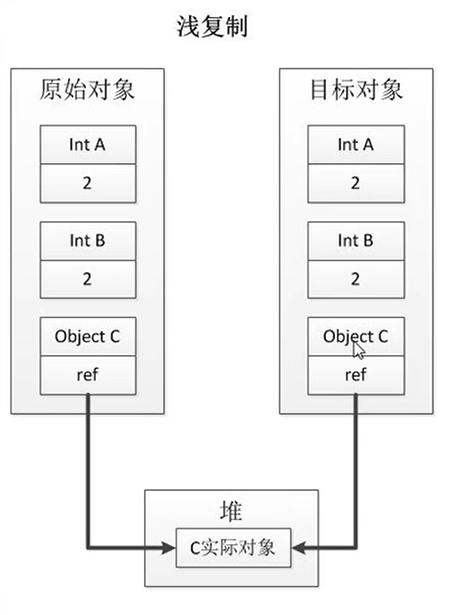
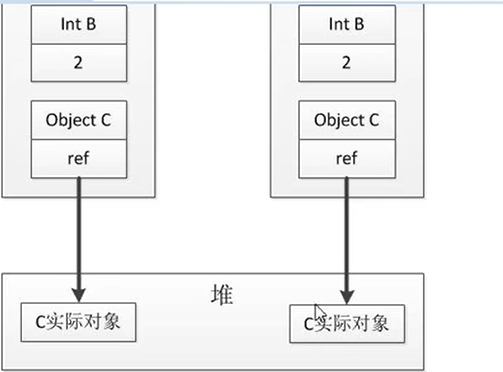
浅拷贝:首先基本属性全部拷贝,然后引用对象属性拷贝的是地址,只要有一方修改会影响另外一方;
深拷贝:可以理解为是完全不同的两个对象,引用对象属性也是相互独立的。
public class User implements Cloneable{
private int id;
private String name;
private LocalDate birth;
private Dog dog;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public LocalDate getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(LocalDate birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public User(int id, String name, LocalDate birth, Dog dog) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", birth=" + birth
+ ", dog=" + dog + "]";
}
//浅克隆
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (User)super.clone();
}
//深克隆
public User deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return (User)ois.readObject();
}
}

