方法传参详解
上代码
public class Exam4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
String str = "hello";
Integer num = 200;
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
MyData my = new MyData();
change(i,str,num,arr,my);
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("str = " + str);
System.out.println("num = " + num);
System.out.println("arr = " + Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("my.a = " + my.a);
}
public static void change(int j, String s, Integer n, int[] a, MyData m) {
j += 1;
s += "world";
n += 1;
a[0] += 1;
m.a += 1;
}
}
class MyData{
int a = 10;
}
结果猜猜看
i = 1str = hello
num = 200
arr = [2, 2, 3, 4, 5]
my.a = 11
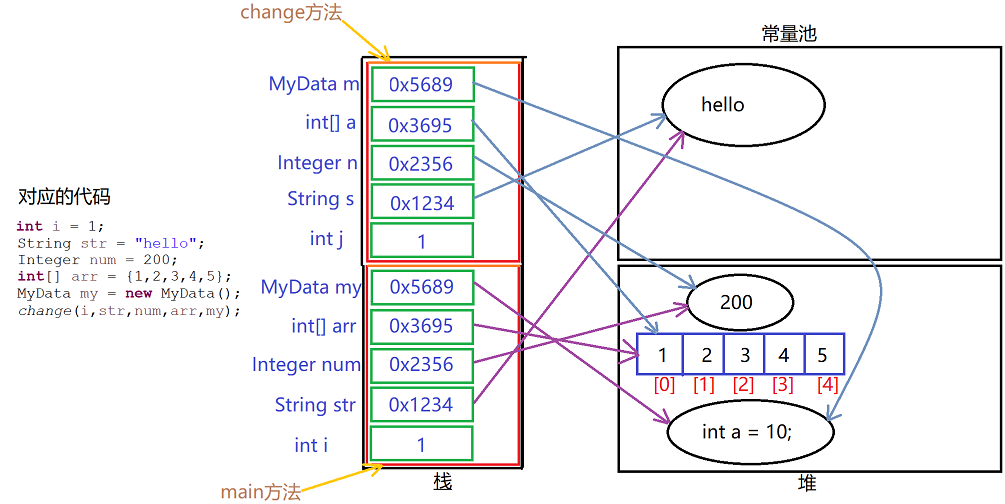
内部原理图示
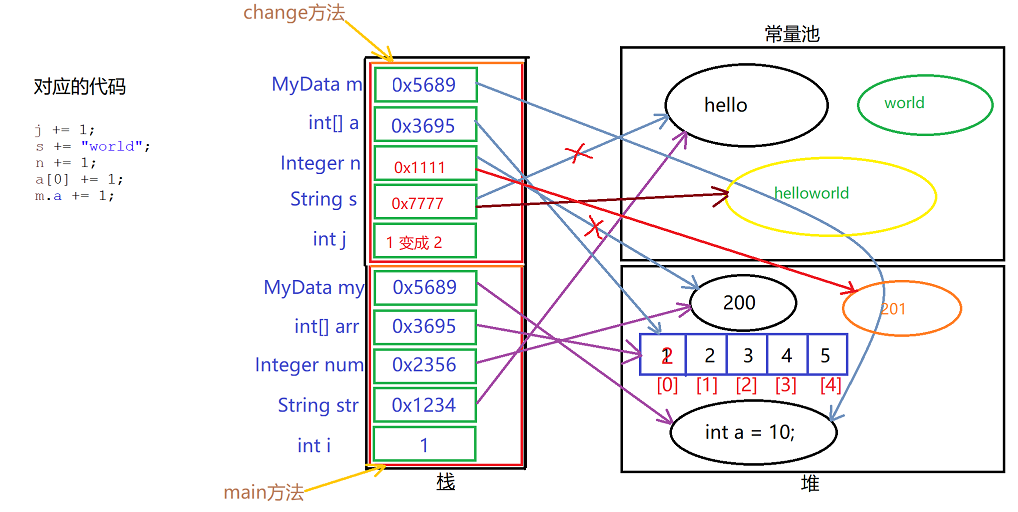
小结
1、String str = "hello";在栈中存的是对应常量池中的地址;
2、处于节省内存的考虑,JVM会缓存-128到127的Integer对象,但是现在num = 200,不在范围内,所以会创建一个新对象;
3、int[] arr在栈中存的也是地址;
4、MyData my在栈中存的也是地址;
方法的参数传递机制:
>1 形参是基本数据类型
a.传递数据值
>2 实参是引用数据类型
a.传递地址值
b.特殊的类型:String、包装类等对象不可变性
1、s += "world";由于string对象的不可变性,因此会在常量池新生成world和helloworld,并且s指向helloworld,因此s的引用地址发生了改变;
2、n += 1;原因同上,生成一个新对象,引用新地址;
3、a[0] += 1;地址并没有发生改变,只是数组中的元素发生了改变;
4、m.a += 1;地址并没有发生改变,内部属性值发生了改变;

