Java反射
1. 介绍
反射是一种能够在程序运行时动态访问、修改某个类中任意属性和方法的机制。
具体:
对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法
对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性
在运行时,当加载完类之后,JVM在堆内存中会自动产生一个Class类型的对象,这个对象包含了完整的类的结构信息
这个Class对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看到类的结构

那么,如何得到这个Class对象呢?以下可否
Class c = new Class();
答案是不行的,因为Class的构造函数定义为私有的,只有JVM可以访问
private Class(ClassLoader loader) { classLoader = loader; }
Class对象获取的三种方式
Class c1 = Code.class; Class c2 = code1.getClass(); Class c3 = Class.forName("com.trigl.reflect.Code");
举例
public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { Student student = new Student(1, "Jack"); Class class1 = student.getClass(); Class class2 = Student.class; Class class3 = Class.forName("com.example.refs.Student"); System.out.println(class1); System.out.println(class2); System.out.println(class3); } }
输出
class com.example.refs.Student class com.example.refs.Student class com.example.refs.Student
2. Java反射相关操作
本文以Student类为例:
接口
package com.example.refs; public interface InterFace { void read(); }
类
package com.example.refs; public class Student implements InterFace{ private int id; public String name; public Student() {} public Student(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } private int getId() { return id; } @Override public void read() {} }
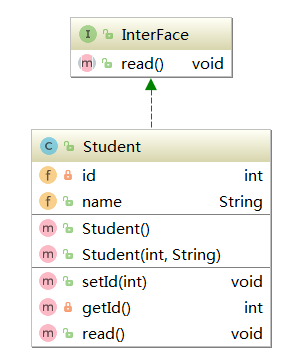

以下具体介绍下具体的用法
2.1 类名称、包名
public class ClassName { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> class2 = Student.class; System.out.println("getSimpleName:" +class2.getSimpleName()); System.out.println("getName:" + class2.getName()); System.out.println("getPackage:" + class2.getPackage()); } }
输出
getSimpleName:Student getName:com.example.refs.Student getPackage:package: com.example.refs
2.2 方法
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>...parameterTypes) // 得到本类所有的方法(public/private/proteceted...) public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>...parameterTypes) //得到该类所有的public方法,包括父类
举例
public class MethodTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> class1 = Student.class; Method[] methods = class1.getMethods(); Method[] declaredMethods = class1.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println("getMethods: " + method); } System.out.println(); for (Method method : declaredMethods) { System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods: " + method); } } }
结果
getMethods: public void com.example.refs.Student.read() getMethods: public void com.example.refs.Student.setId(int) getMethods: public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException getMethods: public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException getMethods: public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException getMethods: public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object) getMethods: public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString() getMethods: public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode() getMethods: public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass() getMethods: public final native void java.lang.Object.notify() getMethods: public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll() getDeclaredMethods: public void com.example.refs.Student.read() getDeclaredMethods: private int com.example.refs.Student.getId() getDeclaredMethods: public void com.example.refs.Student.setId(int)
指定方法
public class MethodChangeVal { public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { Class clazz = Student.class; Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); Method methodGet = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getId"); Method methodSet = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setId", int.class); methodSet.invoke(obj, 123); System.out.println(methodGet.invoke(obj)); } }
异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalAccessException: Class
com.example.refs.MethodChangeVal can not access a member of class
com.example.refs.Student with modifiers "private"
原因:setId为私有方法,利用反射时会进行安全检查,用setAccessible(true)不进行安全检查,可以直接对调用私有方法、修改私有变量
public class MethodChangeVal { public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { Class clazz = Student.class; Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); Method methodGet = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getId"); Method methodSet = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setId", int.class); methodGet.setAccessible(true); methodSet.invoke(obj, 123); System.out.println(methodGet.invoke(obj)); } }
2.3 构造函数
public Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) public Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) Constructor<?>[] allConstructors = class1.getDeclaredConstructors();//获取class对象的所有声明构造函数
Constructor<?>[] publicConstructors = class1.getConstructors();//获取class对象public构造函数
Constructor<?> constructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);//获取指定声明构造函数
Constructor publicConstructor = class1.getConstructor(String.class);//获取指定声明的public构造函数
举例
public class ConstuctorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Class class2 = Student.class; Constructor<?>[] constructors = class2.getConstructors(); for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) { System.out.println(constructor + ", Name:" + constructor.getName()); } } }
结果
public com.example.refs.Student(), Name:com.example.refs.Student public com.example.refs.Student(int,java.lang.String), Name:com.example.refs.Student
2.4 成员变量
getDeclaredFields()获得某个类的所有申明的字段,即包括public、private和proteced,但是不包括父类的申明字段。
getFields()获得某个类的所有的公共(public)的字段,包括父类。
举例
public class FieldTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> aClass = Student.class; Field[] declardFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields(); Field[] fields = aClass.getFields(); for (Field field : declardFields) { System.out.println("declaredField: " + field); } System.out.println(); for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println("field: " + field); } } }
结果
declaredField: private int com.example.refs.Student.id declaredField: public java.lang.String com.example.refs.Student.name field: public java.lang.String com.example.refs.Student.name
2.5 修饰符
举例
public class ModifierTest { public static void main(String args[]) { Class aClass = Student.class; int modifier = aClass.getModifiers(); System.out.println("modifier:" + modifier); System.out.println(String.format("isAbstract: %s", Modifier.isAbstract(modifier))); System.out.println(String.format("isPublic: %s", Modifier.isPublic(modifier))); System.out.println(String.format("isStatic: %s", Modifier.isStatic(modifier))); System.out.println(String.format("isFinal: %s", Modifier.isFinal(modifier))); System.out.println(String.format("isSynchronized: %s", Modifier.isSynchronized(modifier))); } }
结果
modifier:1 isAbstract: false isPublic: true isStatic: false isFinal: false isSynchronized: false
2.6 父类
public class GetParent { public static void main(String[] args) { Class class2 = Student.class; System.out.println(class2.getSuperclass()); } }
结果
class java.lang.Object
2.7 接口
public class InterfaceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> clazz = Student.class; Class<?>[] inters = clazz.getInterfaces(); for(Class<?> classIn : inters) { System.out.println(classIn); } } }
输出
interface com.example.refs.InterFace
2.8 创建对象实例
举例用2种方法创建
public class NewInstanceTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { Class clazz = Student.class; Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(); Object obj2 = constructor.newInstance(); Constructor<?> constructor2 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class); Object obj3 = constructor2.newInstance(1, "HanMeimei"); System.out.println(obj); System.out.println(obj2); System.out.println(obj3); } }
结果
com.example.refs.Student@72ea2f77 com.example.refs.Student@33c7353a com.example.refs.Student@681a9515
2.9 注解
自定义一个注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String value();
注:RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 这个表示运行期注解,这样在反射的时候才能取到
举例
public class AnnotationTest { @MyAnnotation(name="someName", value = "Hello World") public void doSomething() { } @Deprecated public void delFunc() { System.out.println("Hello"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException { Class clazz = AnnotationTest.class; Method method = clazz.getMethod("doSomething"); Annotation[] declaredAnnotations = method.getDeclaredAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : declaredAnnotations) { if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) { MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation)annotation; System.out.println("name:" + myAnnotation.name()); System.out.println("value:" + myAnnotation.value()); } else { System.out.println(annotation); } } } }
结果
name:someName
value:Hello World
2.10 泛型
参数类型、返回值类型举例
public class GenericTest { public void test01(Map<String, Student> map, List<Student> list) { System.out.println("test01"); } public Map<Integer, Student> test02() { System.out.println("test02"); return null; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException { Method method = GenericTest.class.getMethod("test01", Map.class, List.class); Type[] types = method.getGenericParameterTypes(); for (Type type : types) { System.out.println("#:" + type); if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) { Type[] genericType = ((ParameterizedType)type).getActualTypeArguments(); for (Type ontGenericType : genericType) { System.out.println("泛型类型:" + ontGenericType); } } } Method method2 = GenericTest.class.getMethod("test02"); Type returnType = method2.getGenericReturnType(); System.out.println("\nReturntype" + returnType); if (returnType instanceof ParameterizedType) { Type[] genericTypes = ((ParameterizedType)returnType).getActualTypeArguments(); for (Type type : genericTypes) { System.out.println("返回值,泛型类型:" + type); } } } }
结果
#:java.util.Map<java.lang.String, com.example.refs.Student> 泛型类型:class java.lang.String 泛型类型:class com.example.refs.Student #:java.util.List<com.example.refs.Student> 泛型类型:class com.example.refs.Student Returntypejava.util.Map<java.lang.Integer, com.example.refs.Student> 返回值,泛型类型:class java.lang.Integer 返回值,泛型类型:class com.example.refs.Student
2.11 数组
public class ArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] intArray = (int[])Array.newInstance(int.class, 3); Array.set(intArray, 0, 123); Array.set(intArray, 1, 124); Array.set(intArray, 2, 125); for (int i = 0; i < Array.getLength(intArray); ++i) { System.out.println(String.format("array[%s]:%s", i, Array.get(intArray, i))); } Class aClass = intArray.getClass(); System.out.println("intArray是否是数组类型:" + aClass.isArray()); System.out.println("intArray成员类型:" + aClass.getComponentType()); } }
结果
array[0]:123 array[1]:124 array[2]:125 intArray是否是数组类型:true intArray成员类型:int
3. 分析
3.1 使用场景
- 操作因访问权限限制的属性和方法
- 实现自定义注解
- 动态加载第三方jar包
- 按需加载类,节省编译和初始化APK的时间
3.2 优缺点
优点:灵活、自由度高:不受类的访问权限限制
缺点
- 性能问题:通过反射访问、修改类的属性和方法时会远慢于直接操作,但性能问题的严重程度取决于在程序中是如何使用反射的。如果使用得很少,不是很频繁,性能将不是问题
- 安全性问题:反射可以随意访问和修改类的所有状态和行为,破坏了类的封装性,如果不熟悉被反射类的实现原理,随意修改可能导致潜在的逻辑问题
- 兼容性问题:因为反射会涉及到直接访问类的方法名和实例名,不同版本的API如果有变动,反射时找不到对应的属性和方法时会报异常
3.3 说明
- 通过反射访问方法比实例慢很多
- 有用到反射的类不能被混淆
- 反射存在性能问题,但使用不频繁、按需使用时,对程序性能影响并不大
- 反射存在安全性问题,因为可以随意修改类的所有状态和行为(包括private方法和实例)
- 使用反射访问Android的API时需要注意因为不同API版本导致的兼容性问题
3.4 性能对比
不使用反射、启用安全检查、启用安全检查进行对比
public class TestReflect { @Test public void testNoneReflect() { Student oneStudent = new Student(1, "HanMeimei"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (long i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; ++i) { oneStudent.setId(1); } long count = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("没有反射, 共消耗 <" + count + "> 毫秒"); } @Test public void testNotAccess() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { Student oneStudent = new Student(1, "HanMeimei"); Method method = Class.forName("com.example.refs.Student").getMethod("setId", int.class); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (long i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; ++i) { method.invoke(oneStudent, 1); } long count = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("启用安全检查, 共消耗 <" + count + "> 毫秒"); } @Test public void testUseAccess() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { Student oneStudent = new Student(1, "HanMeimei"); Method method = Class.forName("com.example.refs.Student").getMethod("setId", int.class); method.setAccessible(true); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (long i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; ++i) { method.invoke(oneStudent, 1); } long count = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("取消安全检查, 共消耗 <" + count + "> 毫秒"); } }
结果对比
| 差异 | 耗时(ms) |
| 没用反射 | 952 |
| 取消安全检查 | 4283 |
| 启用安全检查 | 14892 |


