自学Java第二十七课
之前我学过的ArrayList属于集合体系结构的一种,它属于Collection。
Collection包含List和Set集合,List包含ArrayList和LinkList,Set包含HashSet和TreeSet。Collection是单列集合,List可存储重复的元素,set不可以存储重复元素。
Map是双列集合,常用其HashMap。Collection、Map、List、Set均为接口。
Collection使用前需要导包:①单列集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,对象也称Collection元素;②JDk不提供此接口的任何直接实现,提供更具体的子接口实现。
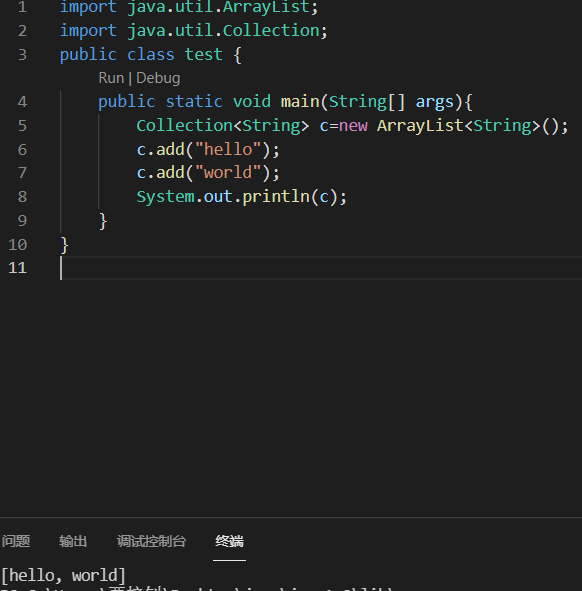
创建Collection对象①多态的形式创建;②具体的实现类ArrayList。
Collection常用方法
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素 |
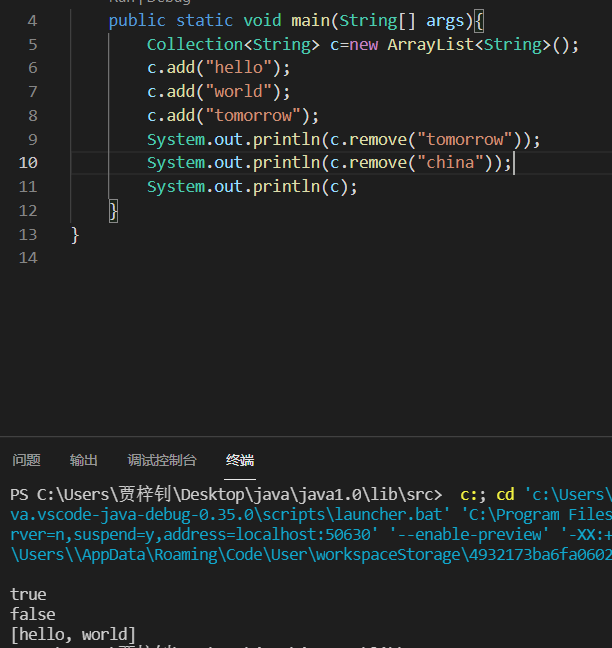
| boolean remove(Object o) | 移除指定元素 |
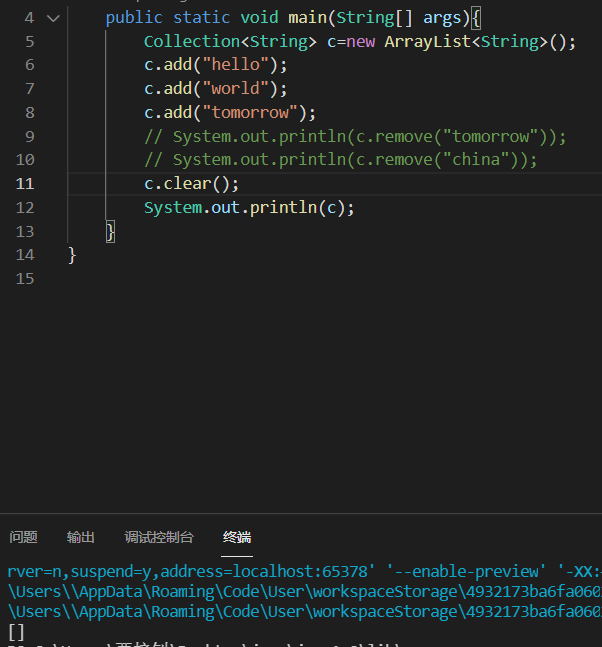
| void clear() | 清空集合中的元素(和linux系统中clear命令相似) |
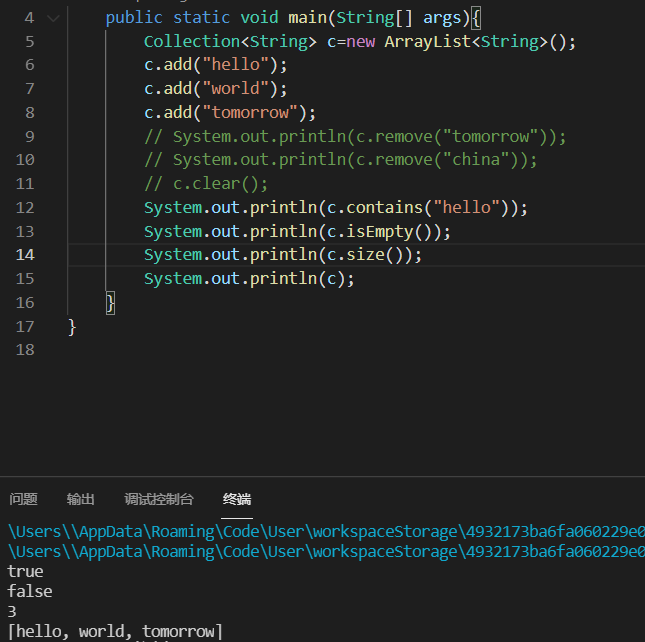
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断集合是否存在指定元素 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 集合长度 |
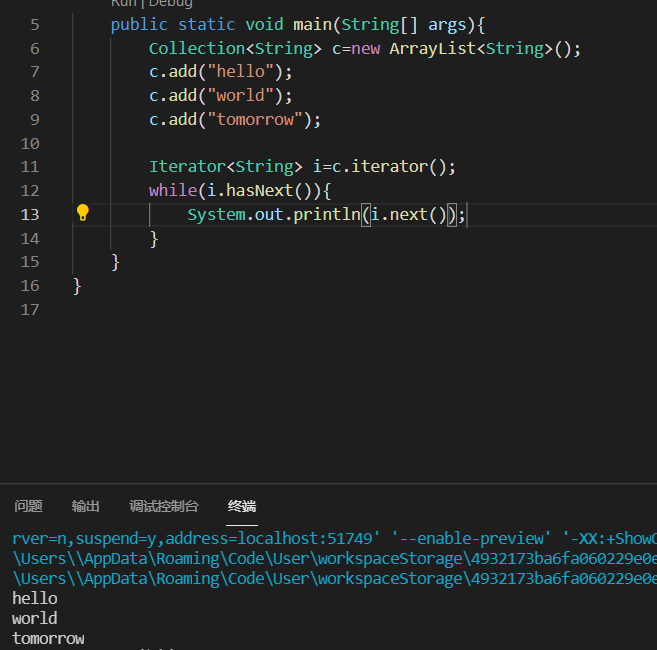
Collection集合遍历
Iterator:迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式。
①Iterator<E>iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator方法得到
②迭代器是通过集合的iterator方法得到的
Iterator常用方法①E next():返回迭代的下一个元素
②boolean hasnext():迭代更多的元素,返回true
集合的使用步骤①创建集合Collection<String> a=new ArrayList<String>();②添加元素 add();③遍历集合迭代器 Iterator i=对象名.iterator;->i.hasNext()->i.next();
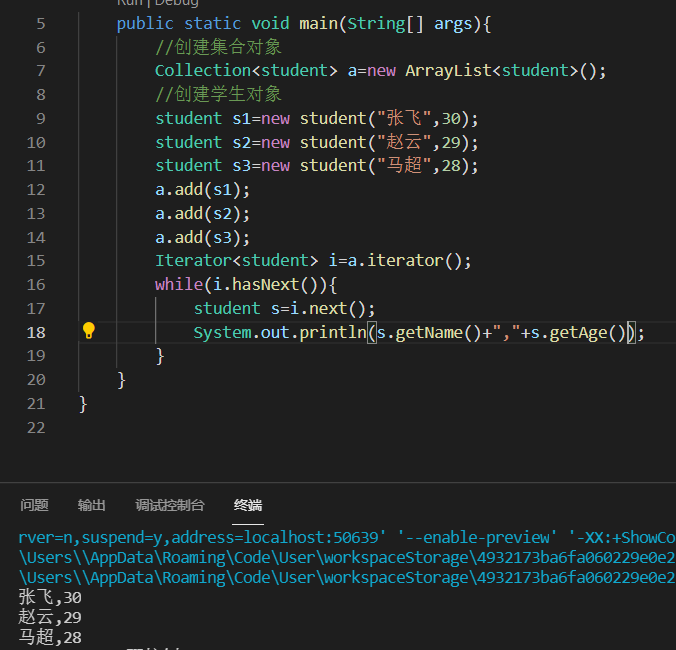
学生案例
明天将会学习集合体系中的List。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署