Django-DRF框架
一、RESTfull设计风格
1、什么是RESTfull?
1)REST:即Representational State Transfer的缩写。维基百科称其为“具象状态传输”,国内大部分人理解为“表现层状态转化”。
2)具象的:就是指表现层,要表现的对象也就是“资源”,什么是资源呢?网站就是资源共享的东西,客户端(浏览器)访问web服务器,所获取的就叫资源。比如html,txt,json,图片,视频等等。
3)表现:比如,文本可以用txt格式表现,也可以用HTML格式、XML格式、JSON格式表现,甚至可以采用二进制格式;图片可以用JPG格式表现,也可以用PNG格式表现。
浏览器通过URL确定一个资源,但是如何确定它的具体表现形式呢?应该在HTTP请求的头信息中用Accept和Content-Type字段指定,这两个字段才是对"表现层"的描述。
4)状态转换: 就是客户端和服务器互动的一个过程,在这个过程中, 势必涉及到数据和状态的变化, 这种变化叫做状态转换。
互联网通信协议HTTP协议,客户端访问必然使用HTTP协议,如果客户端想要操作服务器,必须通过某种手段,让服务器端发生"状态转化"(State Transfer)。
总结:
REST与技术无关,代表的是一种软件架构风格
REST从资源的角度审视审视整个网络,它将分布在网络中某个节点的资源通过URL进行标识
所有的数据,无论是通过网络获取的还是操作(增删改查)的数据,都是资源。将一切数据视为资源是REST区别于其他架构风格的最本质的属性。
每一个URL代表一种资源
客户端和服务器之间,传递这种资源的某种表现层;
客户端通过HTTP动词对服务器端资源进行操作,实现“表现层状态转化”(GET,POST,PUT,DELETE)
2、RESTfull设计规范
1.域名
1)子域名方式
https://api.example.com 尽量将API部署在专用域名(会存在跨域问题)
https://www.example.com
2)url方式
https://example.org
https://example.org/api/ API很简单
2.版本
将API的版本号放入URL中。
https://api.example.com/v1/
https://api.example.com/v2/
https://api.example.com/v3/
3.路径
路径又称“终点”,表示API的具体网址,每个网址代表一种资源
1) 资源作为网址,只能有名词,不能有动词,而且所用的名词往往与数据库的表名对应。
2)API中的名词应该使用复数。无论子资源或者所有资源。
/getProducts 不符合REST风格
/Orders 符合REST风格
获取单个产品:http://127.0.0.1:8080/AppName/products/1
获取所有产品:http://127.0.0.1:8080/AppName/products
4.方式
GET :从服务器取出资源(一项或多项)
POST :在服务器新建一个资源
PUT :在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变的完整资源)
PATCH :在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变的属性)
DELETE :从服务器删除资源
5.过滤
通过在url上传参的形式传递搜索条件
https://api.example.com/v1/zoos?limit=10:指定返回记录的数量
https://api.example.com/v1/zoos?offset=10:指定返回记录的开始位置
https://api.example.com/v1/zoos?page=2&per_page=100:指定第几页,以及每页的记录数
https://api.example.com/v1/zoos?sortby=name&order=asc:指定返回结果按照哪个属性排序,以及排序顺序
https://api.example.com/v1/zoos?animal_type_id=1:指定筛选条件
6.状态码

'''1. 2XX请求成功''' # 200 请求成功,一般用于GET与POST请求 # 201 Created - [POST/PUT/PATCH]:用户新建或修改数据成功。 # 202 Accepted - [*]:表示一个请求已经进入后台排队(异步任务) # 204 NO CONTENT - [DELETE]:用户删除数据成功。 '''2. 3XX重定向''' # 301 NO CONTENT - 永久重定向 # 302 NO CONTENT - 临时重定向 '''3. 4XX客户端错误''' # 400 INVALID REQUEST - [POST/PUT/PATCH]:用户发出的请求有错误。 # 401 Unauthorized - [*]:表示用户没有权限(令牌、用户名、密码错误)。 # 403 Forbidden - [*] 表示用户得到授权(与401错误相对),但是访问是被禁止的。 # 404 NOT FOUND - [*]:用户发出的请求针对的是不存在的记录。 # 406 Not Acceptable - [GET]:用户请求的格式不可得(比如用户请求JSON格式,但是只有XML格式)。 # 410 Gone -[GET]:用户请求的资源被永久删除,且不会再得到的。 # 422 Unprocesable entity - [POST/PUT/PATCH] 当创建一个对象时,发生一个验证错误。 '''4. 5XX服务端错误''' # 500 INTERNAL SERVER ERROR - [*]:服务器内部错误,无法完成请求 # 501 Not Implemented 服务器不支持请求的功能,无法完成请求 更多状态码参考:https://www.runoob.com/http/http-status-codes.html 状态码
7.异常处理
如果状态码是4xx,服务器就应该向用户返回出错信息。一般来说,返回的信息中将error作为键名,出错信息作为键值即可。
{ error: "Invalid API key" }
8.返回结果
针对不同操作,服务器向用户返回的结果应该符合以下规范。
GET /collection:返回资源对象的列表(数组)
GET /collection/resource:返回单个资源对象
POST /collection:返回新生成的资源对象
PUT /collection/resource:返回完整的资源对象
PATCH /collection/resource:返回完整的资源对象
DELETE /collection/resource:返回一个空文档
9.超媒体(Hypermedia API)
RESTful API最好做到Hypermedia(即返回结果中提供链接,连向其他API方法),使得用户不查文档,也知道下一步应该做什么。
比如,Github的API就是这种设计,访问api.github.com会得到一个所有可用API的网址列表。
{
"current_user_url": "https://api.github.com/user",
"current_user_authorizations_html_url": "https://github.com/settings/connections/applications{/client_id}",
"authorizations_url": "https://api.github.com/authorizations",
"code_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/code?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}",
"commit_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/commits?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}",
"emails_url": "https://api.github.com/user/emails",
"emojis_url": "https://api.github.com/emojis",
"events_url": "https://api.github.com/events",
"feeds_url": "https://api.github.com/feeds",
"followers_url": "https://api.github.com/user/followers",
"following_url": "https://api.github.com/user/following{/target}",
"gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists{/gist_id}",
"hub_url": "https://api.github.com/hub",
"issue_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/issues?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}",
"issues_url": "https://api.github.com/issues",
"keys_url": "https://api.github.com/user/keys",
"notifications_url": "https://api.github.com/notifications",
"organization_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/{org}/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}",
"organization_url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/{org}",
"public_gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/public",
"rate_limit_url": "https://api.github.com/rate_limit",
"repository_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/{owner}/{repo}",
"repository_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}",
"current_user_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/user/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}",
"starred_url": "https://api.github.com/user/starred{/owner}{/repo}",
"starred_gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/starred",
"team_url": "https://api.github.com/teams",
"user_url": "https://api.github.com/users/{user}",
"user_organizations_url": "https://api.github.com/user/orgs",
"user_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}",
"user_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/users?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}"
}
从上面可以看到,如果想获取当前用户的信息,应该去访问api.github.com/user,然后就得到了下面结果。
{
"message": "Requires authentication",
"documentation_url": "https://developer.github.com/v3/users/#get-the-authenticated-user"
}
二、DRF框架的使用(Django REST Framework)
1、所需依赖
Python(2.7,3.2,3.3,3.5,3.6)
Django(1.10,1.11,2.0)
2、安装DRF
pip install djangorestframework
3、配置DRF

INSTALLED_APPS = [ ... 'rest_framework', ]
4、序列化器的定义
a.可用字段

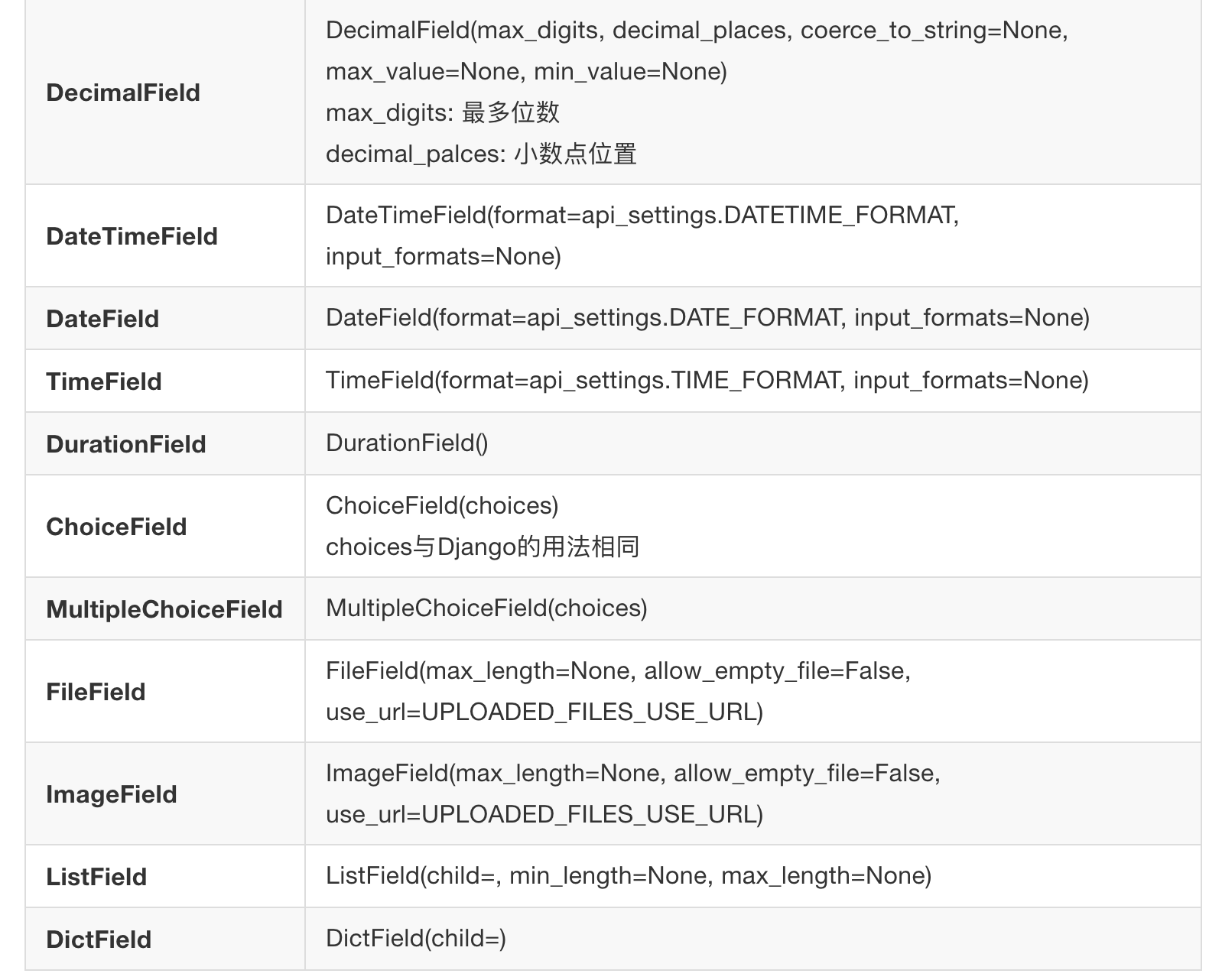
b. 选项参数
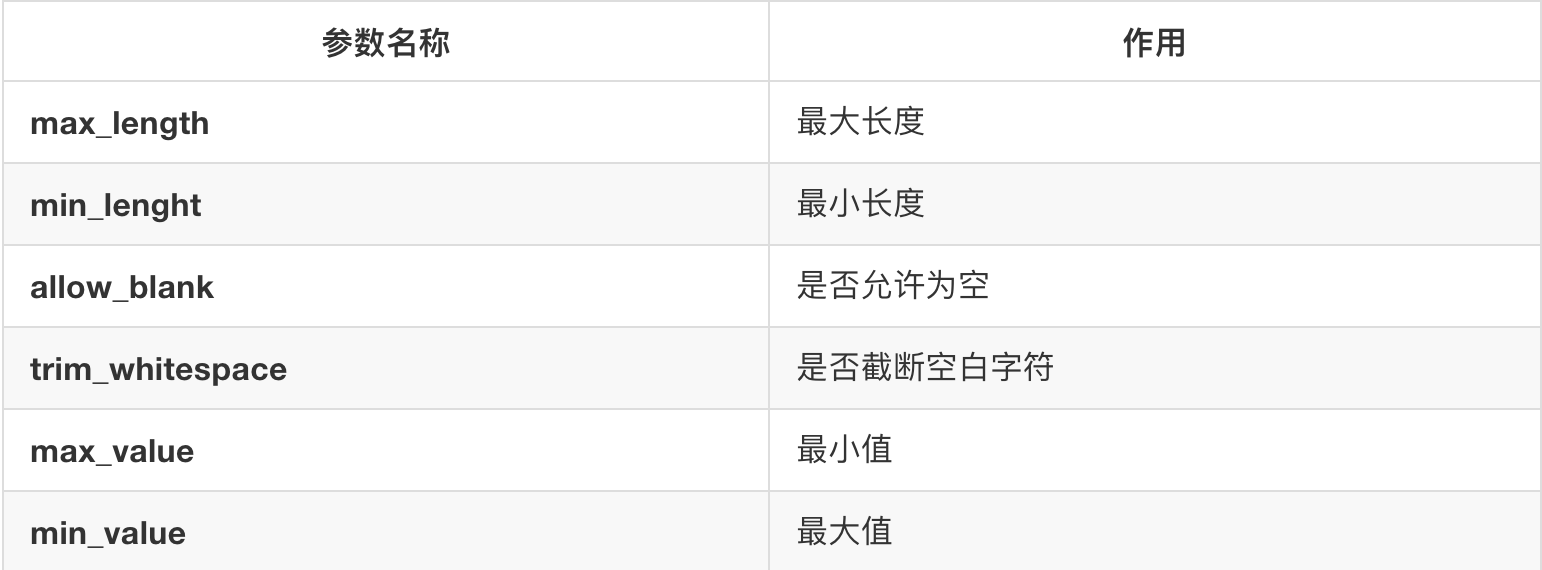
c. 通用参数

d. 定义一个序列化器

class BookInfo(models.Model): btitle = models.CharField(max_length=20, verbose_name='名称') bpub_date = models.DateField(verbose_name='发布日期', null=True) bread = models.IntegerField(default=0, verbose_name='阅读量') bcomment = models.IntegerField(default=0, verbose_name='评论量') image = models.ImageField(upload_to='booktest', verbose_name='图片', null=True)

class BookInfoSerializer(serializers.Serializer): """图书数据序列化器""" id = serializers.IntegerField(label='ID', read_only=True) btitle = serializers.CharField(label='名称', max_length=20) bpub_date = serializers.DateField(label='发布日期', required=False) bread = serializers.IntegerField(label='阅读量', required=False) bcomment = serializers.IntegerField(label='评论量', required=False) image = serializers.ImageField(label='图片', required=False)
e. Serializer的构造方法为:
serializer = BookIndoSerializers(instance=None,data = data, **kwargs)
说明:
1)用于序列化时,将模型类对象传入instance参数
2)用于反序列化时,将要被反序列化的数据传入data参数
5、单表序列化器的序列化使用:

from booktest.serializers import BookInfoSerializer from booktest.models import BookInfo #单个数据序列化 book = BookInfo.objects.get(id=2) serializer = BookInfoSerializer(book) #获取序列化结果 data=serializer.data #多数据的序列化 book_qs = BookInfo.objects.all() serializer = BookInfoSerializer(book_qs, many=True) data = serializer.data
6、单表序列化器的反序列化使用:

class BookInfoSerializer(serializers.Serializer): """图书数据序列化器""" ... def create(self, validated_data): """新建""" return BookInfo(**validated_data) def update(self, instance, validated_data): """更新,instance为要更新的对象实例""" instance.btitle = validated_data.get('btitle', instance.btitle) instance.bpub_date = validated_data.get('bpub_date', instance.bpub_date) instance.bread = validated_data.get('bread', instance.bread) instance.bcomment = validated_data.get('bcomment', instance.bcomment) return instance

from db.serializers import BookInfoSerializer data = {'btitle': '封神演义'} serializer = BookInfoSerializer(data=data) serializer.is_valid() # True serializer.save() # <BookInfo: 封神演义> views.py
注意:
默认序列化器必须传递所有required的字段,否则会抛出验证异常。但是我们可以使用partial参数来允许部分字段更新
serializer = CommentSerializer(comment, data={'content': u'foo bar'}, partial=True)
7、一对多序列化器的使用:

class HeroInfoSerializer(serializers.Serializer): """英雄数据序列化器""" GENDER_CHOICES = ( (0, 'male'), (1, 'female') ) id = serializers.IntegerField(label='ID', read_only=True) hname = serializers.CharField(label='名字', max_length=20) hgender = serializers.ChoiceField(choices=GENDER_CHOICES, label='性别', required=False) hcomment = serializers.CharField(label='描述信息', max_length=200, required=False, allow_null=True) #1) PrimaryKeyRelatedField #此字段将被序列化为关联对象的主键。 hbook = serializers.PrimaryKeyRelatedField(label='图书', read_only=True) from booktest.serializers import HeroInfoSerializer from booktest.models import HeroInfo hero = HeroInfo.objects.get(id=6) serializer = HeroInfoSerializer(hero) serializer.data # {'id': 6, 'hname': '乔峰', 'hgender': 1, 'hcomment': '降龙十八掌', 'hbook': 2} #2) StringRelatedField #此字段将被序列化为关联对象的字符串表示方式(即__str__方法的返回值) hbook = serializers.StringRelatedField(label='图书') #结果 #{'id': 6, 'hname': '乔峰', 'hgender': 1, 'hcomment': '降龙十八掌', 'hbook': '天龙八部'} 3)使用关联对象的序列化器 #hbook = BookInfoSerializer() #结果 #{'id': 6, 'hname': '乔峰', 'hgender': 1, 'hcomment': '降龙十八掌', 'hbook': OrderedDict([('id', 2), ('btitle', '天龙八部')te', '1986-07-24'), ('bread', 36), ('bcomment', 40), ('image', None)])} #4)SlugRelatedField #此字段将被序列化为关联对象的指定字段数据 #hbook = serializers.SlugRelatedField(label='图书', read_only=True, slug_field='bpub_date') #结果 #{'id': 6, 'hname': '乔峰', 'hgender': 1, 'hcomment': '降龙十八掌', 'hbook': datetime.date(1986, 7, 24)}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号