activiti监听器
疑问:当我们流程流转到某一节点、某一连线或者流程开始和结束的时候我们怎么添加一些业务处理呢?
这就是我们今天讨论的主题了。
activiti的监听应用场景:在某一流程开始或者结束的时候,我们可以加入部分的业务处理,例如:在流程结束后,我们发邮件或者推送短信给我们的申请人,告诉他审批完成。又或者,当有审批人不同意该次请求的时候,我们也需要通知申请人,让其修改该申请。又或者该流程流转到某一节点,也就是需要他审批的时候,需要通知负责人,这时候也可以使用该监听。也可以用在指定下一个节点的处理人等等。
activiti的监听器分为:全局监听、连线监听、节点监听。
本次演示使用的流程图如下:
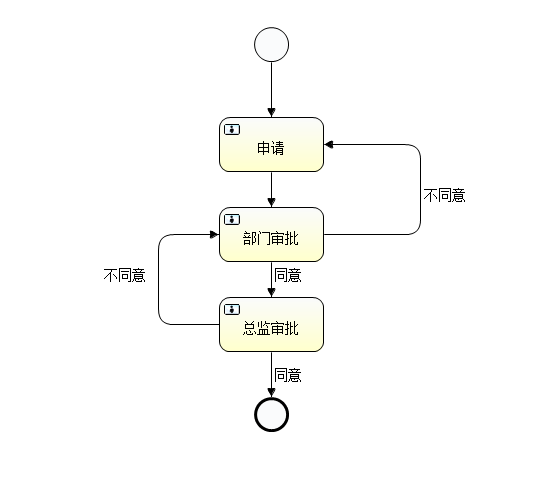
全局监听:
主要用于监听流程的开始和结束。
bpmn xml文件如下:
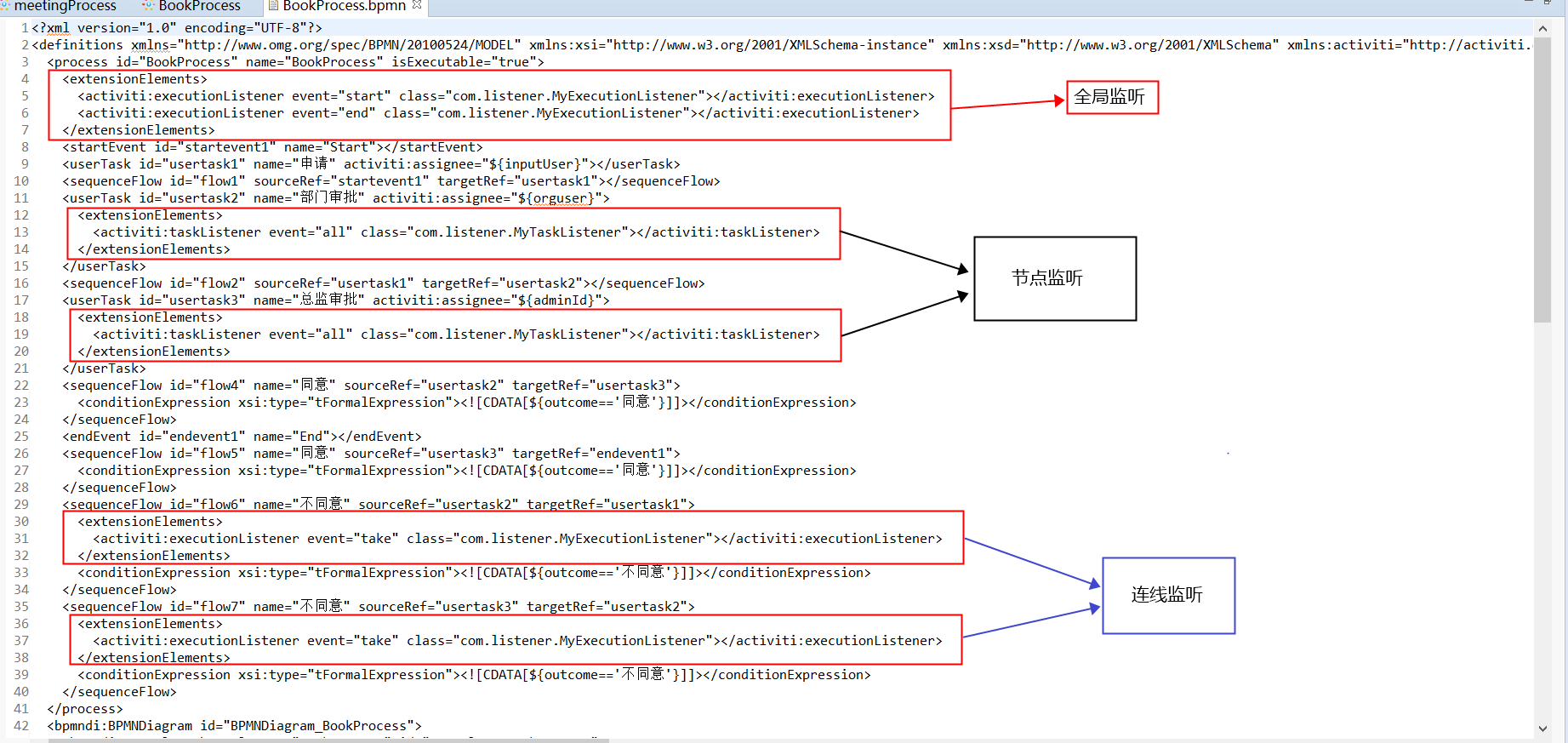
如何去实现呢?我们可以在bpmn的xml文件的 <process id="BookProcess" name="BookProcess" isExecutable="true">的下面添加上我们的监听配置:
<extensionElements>
<activiti:executionListener event="start" class="com.listener.MyExecutionListener"></activiti:executionListener>
<activiti:executionListener event="end" class="com.listener.MyExecutionListener"></activiti:executionListener>
</extensionElements>
其中MyExecutionListener是我们自己定义的监听器类,该类需要实现ExecutionListener接口:
public class MyExecutionListener implements ExecutionListener { public void notify(DelegateExecution delegateExecution) throws Exception { String eventName = delegateExecution.getEventName(); if ("start".equals(eventName)) { System.out.println("start========="); }else if ("end".equals(eventName)) { System.out.println("end========="); } else if ("take".equals(eventName)) {//连线监听 System.out.println("take========="); } } }
这样我们就可以在start或者end的下面添加一些业务处理。
在DelegateExecution对象中,可获取到的参数有如下:
public interface DelegateExecution extends VariableScope { String getId(); String getProcessInstanceId(); String getEventName(); /** @deprecated */ String getBusinessKey(); String getProcessBusinessKey(); String getProcessDefinitionId(); String getParentId(); String getCurrentActivityId(); String getCurrentActivityName(); String getTenantId(); EngineServices getEngineServices(); }
通过上述的参数可获取到我们需要的参数,例如getProcessBusinessKey()获取到业务id,通过业务id可以修改我们业务单的状态等等。
连线接听:
当我们的流程经过某一连线的时候,需要实现一些业务,这就需要连线监听。
连线监听的实现和全局监听类似,都需要去实现实现ExecutionListener接口,该接口可获取到所需的参数。
我们只需要在bpmn 的xml的连线下添加监听配置;
<sequenceFlow id="flow6" name="不同意" sourceRef="usertask2" targetRef="usertask1">
<extensionElements>
<activiti:executionListener event="take" class="com.listener.MyExecutionListener"></activiti:executionListener>
</extensionElements>
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression"><![CDATA[${outcome=='不同意'}]]></conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
extensionElements中就是添加我们的监听类,每当流程经过该连线的时候,就会进入MyExecutionListener类,执行else if ("take".equals(eventName))下的代码。这样我们就可以在该方法下面添加我们需要的业务处理。
节点监听:
当流程转到某一节点的时候,需要触发我们自定义的业务,这一节点监听在流程中是经常使用的。
首先,我们需要自定义我们的监听类,自定义监听类需要实现TaskListener接口;
自定义类如下:
public class MyTaskListener implements TaskListener { public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { String eventName = delegateTask.getEventName(); if ("create".endsWith(eventName)) { System.out.println("create========="); }else if ("assignment".endsWith(eventName)) { System.out.println("assignment========"+delegateTask.getAssignee()); }else if ("complete".endsWith(eventName)) { System.out.println("complete==========="); }else if ("delete".endsWith(eventName)) { System.out.println("delete============="); } } }
DelegateTask对象中,我们可以获取到参数有如下:
public interface DelegateTask extends VariableScope { String getId(); String getName(); void setName(String var1); String getDescription(); void setDescription(String var1); int getPriority(); void setPriority(int var1); String getProcessInstanceId(); String getExecutionId(); String getProcessDefinitionId(); Date getCreateTime(); String getTaskDefinitionKey(); boolean isSuspended(); String getTenantId(); String getFormKey(); void setFormKey(String var1); DelegateExecution getExecution(); String getEventName(); DelegationState getDelegationState(); void addCandidateUser(String var1); void addCandidateUsers(Collection<String> var1); void addCandidateGroup(String var1); void addCandidateGroups(Collection<String> var1); String getOwner(); void setOwner(String var1); String getAssignee(); void setAssignee(String var1); Date getDueDate(); void setDueDate(Date var1); String getCategory(); void setCategory(String var1); void addUserIdentityLink(String var1, String var2); void addGroupIdentityLink(String var1, String var2); void deleteCandidateUser(String var1); void deleteCandidateGroup(String var1); void deleteUserIdentityLink(String var1, String var2); void deleteGroupIdentityLink(String var1, String var2); Set<IdentityLink> getCandidates(); }
通过该对象可以获取处理人,或者指定下一个处理人等等。
接着,我们需要在bpmn的xml文件中配置监听类,在我们的任务节点中加入extensionElements配置,其中class是我们自定义的监听类:
<userTask id="usertask2" name="部门审批" activiti:assignee="${orguser}">
<extensionElements>
<activiti:taskListener event="all" class="com.listener.MyTaskListener"></activiti:taskListener>
</extensionElements>
</userTask>
当流程转到该节点的时候,就会触发该类执行,这样我们就可以加入我们的业务处理了。
除了我们直接在bpmn的xml文件中配置外,我们也可以通过如下方法添加全局、连线、节点的自定义监听类:
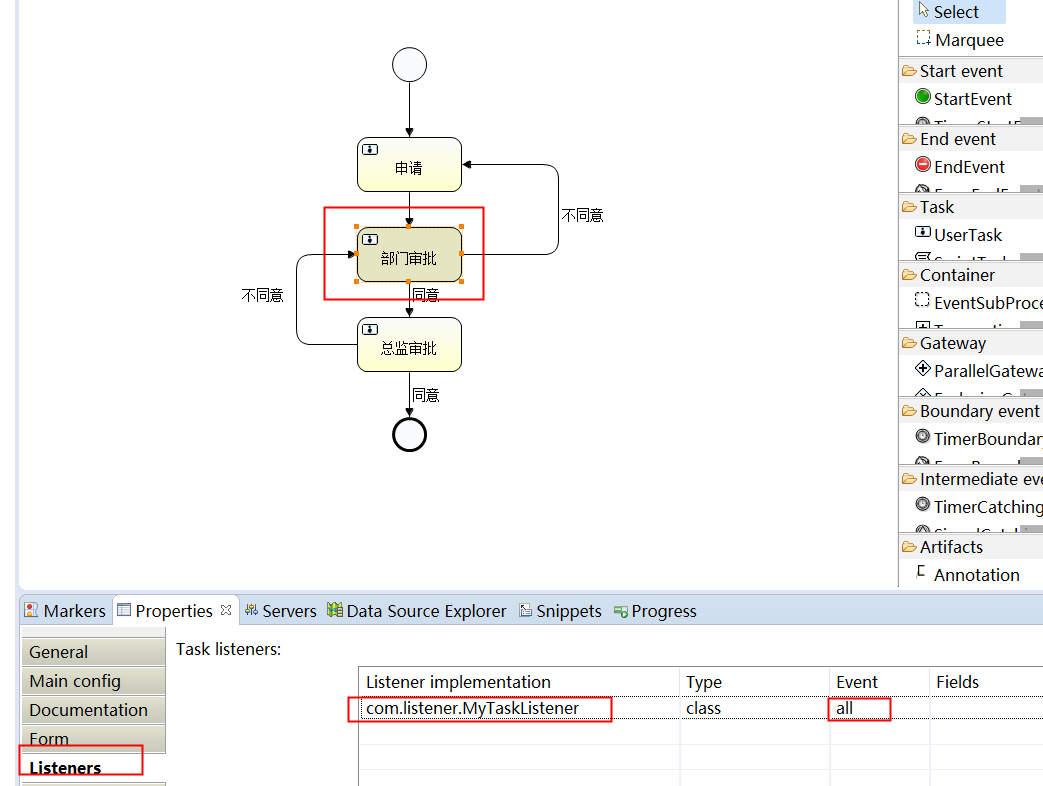
以上就是全局、连线、以及节点监听的描述与介绍,当然也需要执行验证,执行验证类如下:
我们验证类是结合spring的方式:
验证类:
public class activitiTest extends SpringBase { @Autowired private RepositoryService repositoryService; @Autowired private RuntimeService runtimeService; @Autowired private TaskService taskService; @Test public void deploymentProcessDefinition() { Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment() .name("Book") .addClasspathResource("BookProcess.bpmn") .deploy(); System.out.println("deploymentId=" + deployment.getId()); System.out.println("deploymentName=" + deployment.getName()); } /** * 执行流程实例 */ @Test public void startProcessInstance() { String processInstanceKey = "BookProcess"; Map<String,Object> values = new HashMap<String,Object>(); values.put("inputUser","张三"); values.put("orguser","李四"); values.put("adminId","王五"); String objId="Book"+"."+"123"; values.put("objId",objId); ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService .startProcessInstanceByKey(processInstanceKey,objId,values); System.out.println("流程实例id:" + pi.getId()); //流程实例id 101 System.out.println("流程定义id:" + pi.getProcessDefinitionId()); //流程定义ID helloworld:1:4 } /** * 查找个人当前的要执行的任务 */ @Test public void findMyTaskInfo(){ String assignee = "李四";//流程流转的处理的人物 List<Task> listTask = taskService .createTaskQuery() .taskAssignee(assignee) .list(); if (listTask!= null && listTask.size() >0) { for (Task task : listTask) { System.out.println("任务ID:" + task.getId()); System.out.println("任务名称:" + task.getName()); System.out.println("任务时间:" + task.getCreateTime()); System.out.println("任务的班里人:" + task.getAssignee()); System.out.println("任务的实例ID:" + task.getProcessDefinitionId()); System.out.println("执行对象的ID:" + task.getExecutionId()); System.out.println("任务的班里人:" + task.getAssignee()); System.out.println("流程定义ID:" + task.getProcessInstanceId()); } } } /**完成任务*/ @Test public void completeMyPersoinTask() { String taskId = "60003"; Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String,Object>(); variables.put("outcome","同意"); taskService.complete(taskId,variables); /* taskService.complete(taskId);*/ System.out.println("完成任务,任务ID:" + taskId); } }
SpringBase类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath*:/applicationContext.xml" }) public class SpringBase { }
applicationContext.xml配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd "> <!-- 引入properties文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> <!-- 扫描注解 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com"/> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="maxActive" value="300" /> <property name="maxIdle" value="30" /> <property name="minIdle" value="10" /> <property name="initialSize" value="15" /> <property name="maxWait" value="20000" /> </bean> <!-- 事务管理 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 配置事务通知属性 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!-- 定义事务传播属性 --> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="get*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 引擎 --> <bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.spring.SpringProcessEngineConfiguration"> <!-- 数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <!-- 配置事务,统一事务 --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" /> <!--设置建表策略 --> <property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true" /> </bean> <!-- 创建引擎对象 --> <bean id="processEngine" class="org.activiti.spring.ProcessEngineFactoryBean"> <property name="processEngineConfiguration" ref="processEngineConfiguration" /> </bean> <bean id="repositoryService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getRepositoryService" /> <bean id="runtimeService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getRuntimeService" /> <bean id="taskService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getTaskService" /> <bean id="historyService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getHistoryService" /> <bean id="formService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getFormService" /> </beans>
本人在这就不把执行结果展示出来了,大家可以自己运行测试一下。如有错误的地方请大家指正。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号