thinkphp5源码解析(1)数据库
前言
tp5的数据库操作全部通过Db类完成,比较符合国人的习惯,比如简单的Db::query()、Db::execute(),还有复杂的链式操作Db::table('user')->where('id=1')->select(),下面就通过源码来了解其工作流程
看代码之前,先看看涉及到的类都有哪些,tp5的数据库相关的类有以下几个:
- Db(用户接口)
- Connection(连接器)
- Query(查询器)
- Builder(SQL生成器)
Db::query()发生了什么?
假定配置文件设置驱动为Mysql,当执行以下代码时,tp5的数据库类是怎么工作的?
Db::query("select * from user where id=?", [1]);为了节省篇章以及更好地理解流程,下面只展示核心代码,部分代码被简化或改造,我们来看看Db类:
class Db
{
private static $instance = [];
private static function parseConfig($config)
{
if (empty($config)) {
$config = Config::get('database');
} else {
$config = Config::get($config);
}
return $config;
}
public static function connect($config = [])
{
$name = md5(serialize($config));
if (!isset(self::$instance[$name])) {
$options = self::parseConfig($config);
self::$instance[$name] = new \think\db\connector\Mysql($options);
}
return self::$instance[$name];
}
public static function __callStatic($method, $params)
{
return call_user_func_array([self::connect(), $method], $params);
}
}
因为Db类没有定义query(),所以触发了__callStatic(),__callStatic()又调用自身的connect(),connect()实例化Mysql连接器(传入数据库配置$options),然后保存到$instance(数据库连接实例数组),再来看看Mysql连接器:
namespace think\db\connector;
class Mysql extends Connection
{
protected $builder = '\\think\\db\\builder\\Mysql';
}
Mysql连接器也没有定义query()呀,它继承了Connection,看看Connection有没有:
abstract class Connection
{
protected $PDOStatement;
protected $linkID;
protected $config = [];
public function __construct(array $config = [])
{
if (!empty($config)) {
$this->config = array_merge($this->config, $config);
}
}
protected function getResult()
{
return $this->PDOStatement->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
}
protected function bindValue(array $bind = [])
{
foreach ($bind as $key => $val) {
$param = is_numeric($key) ? $key + 1 : ':' . $key;
if (is_array($val)) {
if (PDO::PARAM_INT == $val[1] && '' === $val[0]) {
$val[0] = 0;
}
$result = $this->PDOStatement->bindValue($param, $val[0], $val[1]);
} else {
$result = $this->PDOStatement->bindValue($param, $val);
}
}
}
public function connect()
{
if (!$this->linkID) {
$config = $this->config;
$this->linkID = new PDO($config['dsn'], $config['username'], $config['password']);
}
return $this->linkID;
}
public function query($sql, $bind = [])
{
$this->connect();
if (empty($this->PDOStatement)) {
$this->PDOStatement = $this->linkID->prepare($sql);
}
$this->bindValue($bind);
$this->PDOStatement->execute();
return $this->getResult();
}
}
结论
Db::query()触发Db::__callStatic(),实例化Mysql连接器并调用Mysql->query(),而Mysql连接器继承了Connection,所以实际上是调用了Connection->query()
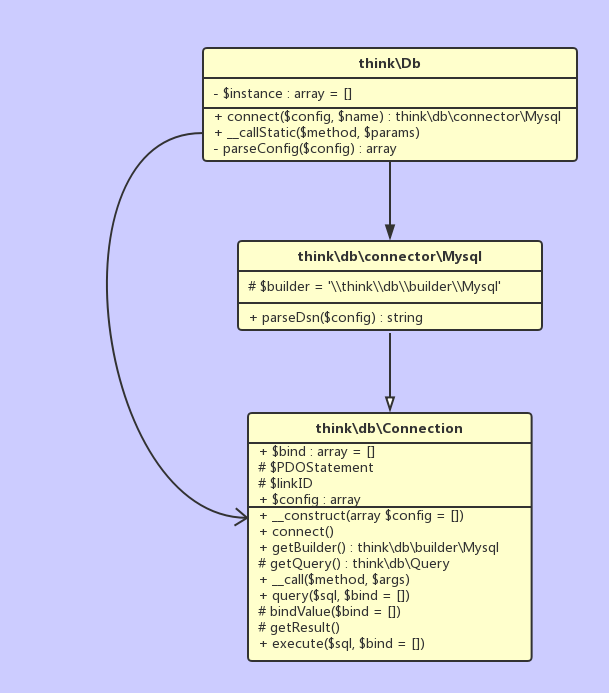
Db::table('user')->where('id=1')->select()发生了什么?
Db和Mysql连接器都没有定义table()方法,发现Connection也有个__call():
protected function getQuery()
{
return new \think\db\Query($this);
}
public function __call($method, $args)
{
return call_user_func_array([$this->getQuery(), $method], $args);
}
所以Db::table('user')实际上是触发了__call()魔术方法,然后实例化了一个Query对象(构造函数传入当前Mysql连接器对象),看看Query里面做了什么:
namespace think\db;
class Query
{
protected $connection;
protected $builder;
public function __construct(Connection $connection)
{
$this->connection = $connection;
$this->setBuilder();
}
protected function setBuilder()
{
$this->builder = new \think\db\builder\Mysql($this->connection, $this);
}
public function table($table)
{
$this->options['table'] = $table;
return $this;
}
public function where($where)
{
$this->options['where'] = $where;
return $this;
}
public function query($sql)
{
return $this->connection->query($sql);
}
public function select()
{
$options = $this->options;
$this->options = [];
$sql = $this->builder->select($options);
return $this->query($sql);
}
}
首先构造函数保存了当前的Mysql连接器对象,并实例化think\db\builder\Mysql
Query->table()把表名保存到$options数组,然后返回$this(当前实例)从而实现链式操作,where()同样,重点看看select(),它拿到$options之后把它清空以便下次使用,然后调用了Builder->select()拿到拼装好的sql,交由Connection->query()查询数据库获得结果集,整个流程到此结束,那么Builder是怎么拼装sql的呢?
namespace think\db\builder;
class Mysql extends Builder
{
protected function parseRand()
{
return 'rand()';
}
}
think\db\builder\Mysql并没有定义select(),不过它继承了Builder,看看Builder代码:
namespace think\db;
abstract class Builder
{
protected $connection;
protected $query;
protected $selectSql = 'SELECT %FIELD% FROM %TABLE% %WHERE%';
public function select($options = [])
{
$sql = str_replace(
['%TABLE%', '%FIELD%', '%WHERE%'],
[
$options['table'],
$options['field'] ?: '*',
$options['where'] ? 'WHERE'.$options['where'] : '',
], $this->selectSql);
return $sql;
}
}
Builder通过$options替换sql模板拿到sql
结论
Db::table()触发了__callStatic()实例化Connection并调用table(),由于Connection也没有定义table(),又触发了自身的__call()实例化Query并调用table(),table()返回$this实现链式操作DB::table()->where()->select(),而select又调用Builder->select()拿到sql,最终调用Connection->query()获取查询结果,固完整的类图表示如下:


