Linux下生产者与消费者问题
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #define MAX 10 //需要生产的数量 pthread_mutex_t the_mutex; pthread_cond_t condc, condp; int buffer = 0;//生产者、消费者使用的缓冲区 void *producer(void *ptr) { int i; for(i=1; i<=MAX; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&the_mutex); //互斥使用缓冲区 while(buffer !=0) pthread_cond_wait(&condp, &the_mutex); printf("procucer produce item %d\n",i); buffer = i; //将数据插入缓冲区 pthread_cond_signal(&condc);//唤醒消费者 pthread_mutex_unlock(&the_mutex);//释放缓冲区 } pthread_exit(0); } void *consumer(void *ptr) { int i; for(i=1; i<=MAX; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&the_mutex);//互斥使用缓冲区 while(buffer ==0) pthread_cond_wait(&condc, &the_mutex); printf("consumer consume item %d\n",i); buffer = 0;//从缓冲区中取出数据 pthread_cond_signal(&condp);//唤醒生产者 pthread_mutex_unlock(&the_mutex);//释放缓冲区 } pthread_exit(0); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t pro, con; pthread_mutex_init(&the_mutex, 0); pthread_cond_init(&condc,0); pthread_cond_init(&condp,0); pthread_create(&con, 0, consumer, 0); pthread_create(&pro, 0, producer, 0); pthread_join(pro,0); pthread_join(con,0); pthread_cond_destroy(&condc); pthread_cond_destroy(&condp); pthread_mutex_destroy(&the_mutex); return 0; }
gcc -o consumer-producer -lpthread consumer-producer.c
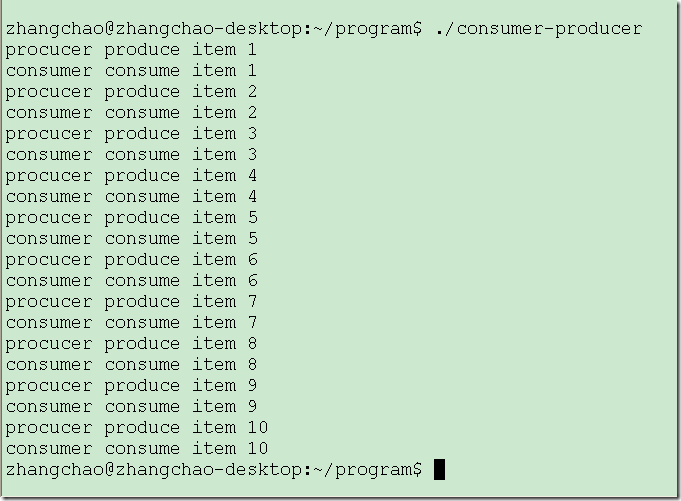
运行结果: