实验3:OpenFlow协议分析实践
实验3:OpenFlow协议分析实践
- (一)基本要求
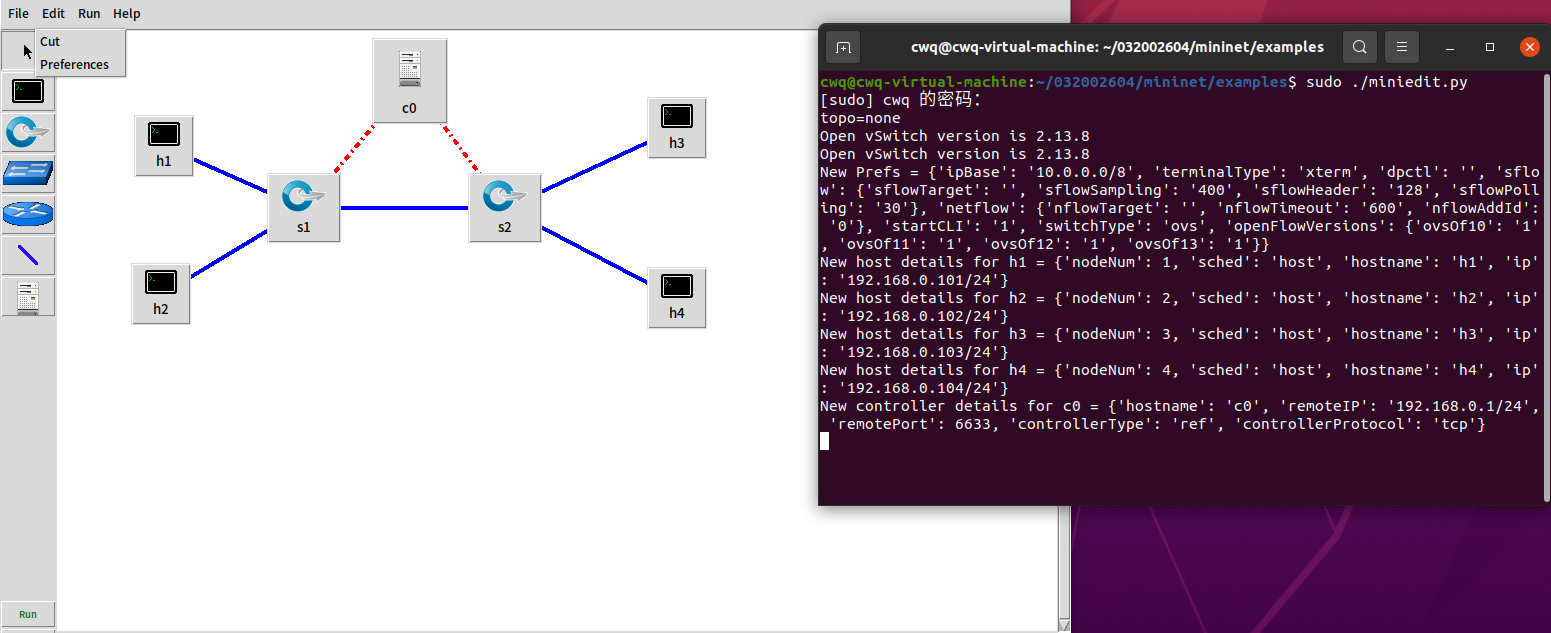
- 1.搭建下图所示拓扑,完成相关 IP 配置,并实现主机与主机之间的 IP 通信。
- 代码部分
- 1.搭建下图所示拓扑,完成相关 IP 配置,并实现主机与主机之间的 IP 通信。
#!/usr/bin/env python
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import Controller, RemoteController, OVSController
from mininet.node import CPULimitedHost, Host, Node
from mininet.node import OVSKernelSwitch, UserSwitch
from mininet.node import IVSSwitch
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel, info
from mininet.link import TCLink, Intf
from subprocess import call
def myNetwork():
net = Mininet( topo=None,
build=False,
ipBase='192.168.0.0/24')
info( '*** Adding controller\n' )
c0=net.addController(name='c0',
controller=Controller,
protocol='tcp',
port=6633)
info( '*** Add switches\n')
s1 = net.addSwitch('s1', cls=OVSKernelSwitch)
s2 = net.addSwitch('s2', cls=OVSKernelSwitch)
info( '*** Add hosts\n')
h1 = net.addHost('h1', cls=Host, ip='192.168.0.101/24', defaultRoute=None)
h2 = net.addHost('h2', cls=Host, ip='192.168.0.102/24', defaultRoute=None)
h3 = net.addHost('h3', cls=Host, ip='192.168.0.103/24', defaultRoute=None)
h4 = net.addHost('h4', cls=Host, ip='192.168.0.104/24', defaultRoute=None)
info( '*** Add links\n')
net.addLink(h1, s1)
net.addLink(s1, h2)
net.addLink(s2, h3)
net.addLink(s2, h4)
net.addLink(s2, s1)
info( '*** Starting network\n')
net.build()
info( '*** Starting controllers\n')
for controller in net.controllers:
controller.start()
info( '*** Starting switches\n')
net.get('s1').start([c0])
net.get('s2').start([c0])
info( '*** Post configure switches and hosts\n')
CLI(net)
net.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
setLogLevel( 'info' )
myNetwork()
-
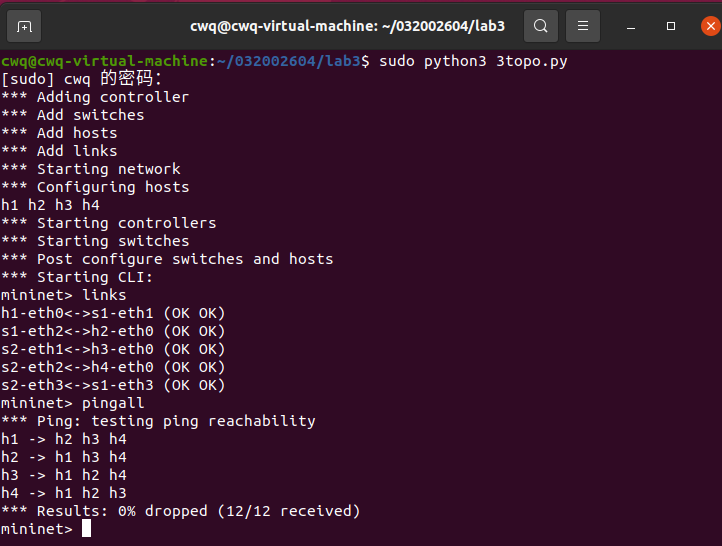
2.wireshark抓包结果
-
(1)HELLO
控制器6633端口(我最高能支持OpenFlow 1.0) ---> 交换机55376端口。
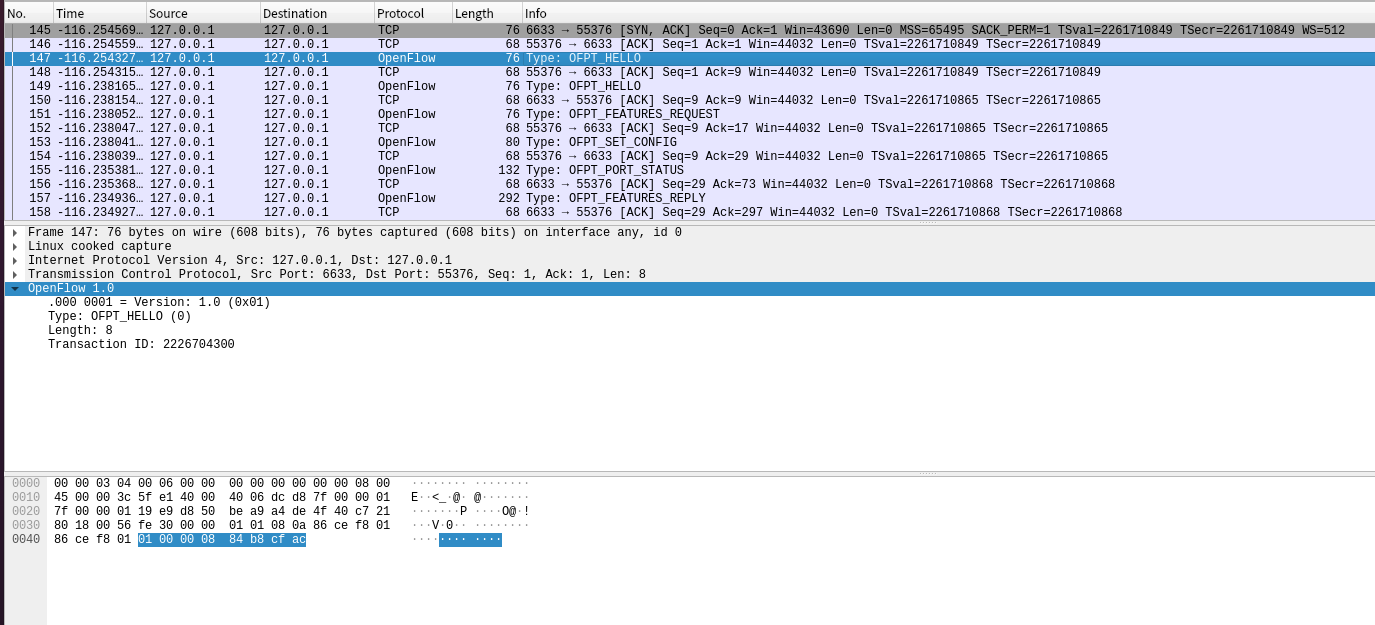
交换机55376端口(我最高能支持OpenFlow 1.5) ---> 控制器6633端口。
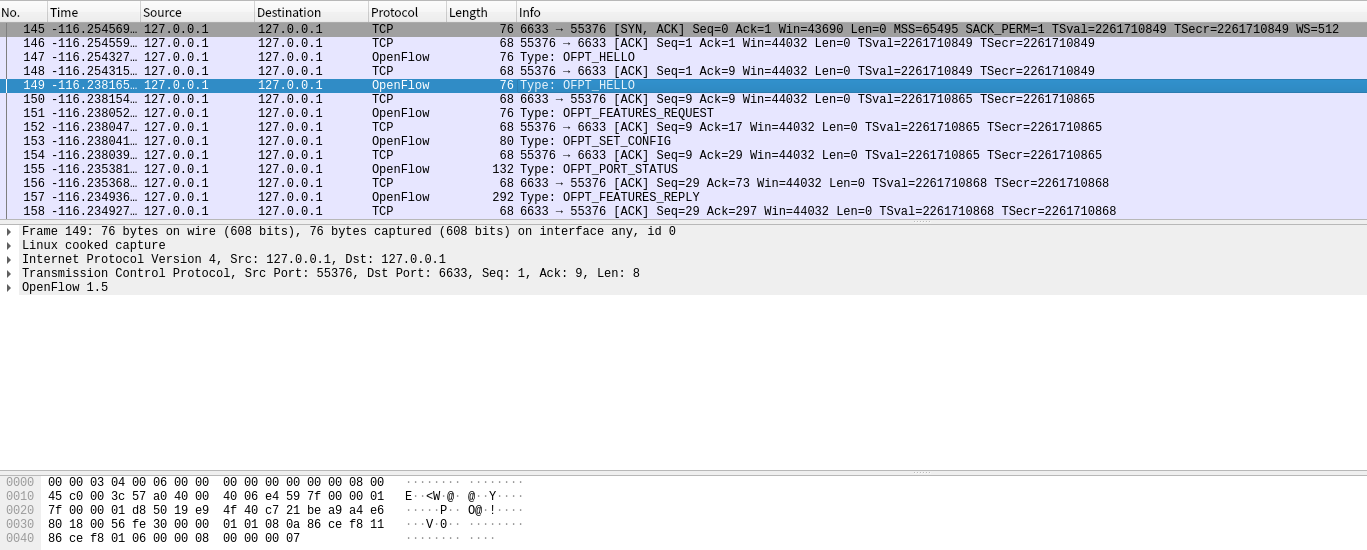
于是双方建立连接,并使用OpenFlow 1.0。 -
(2)Features Request / Set Config
控制器6633端口(我需要你的特征信息) ---> 交换机55376端口。
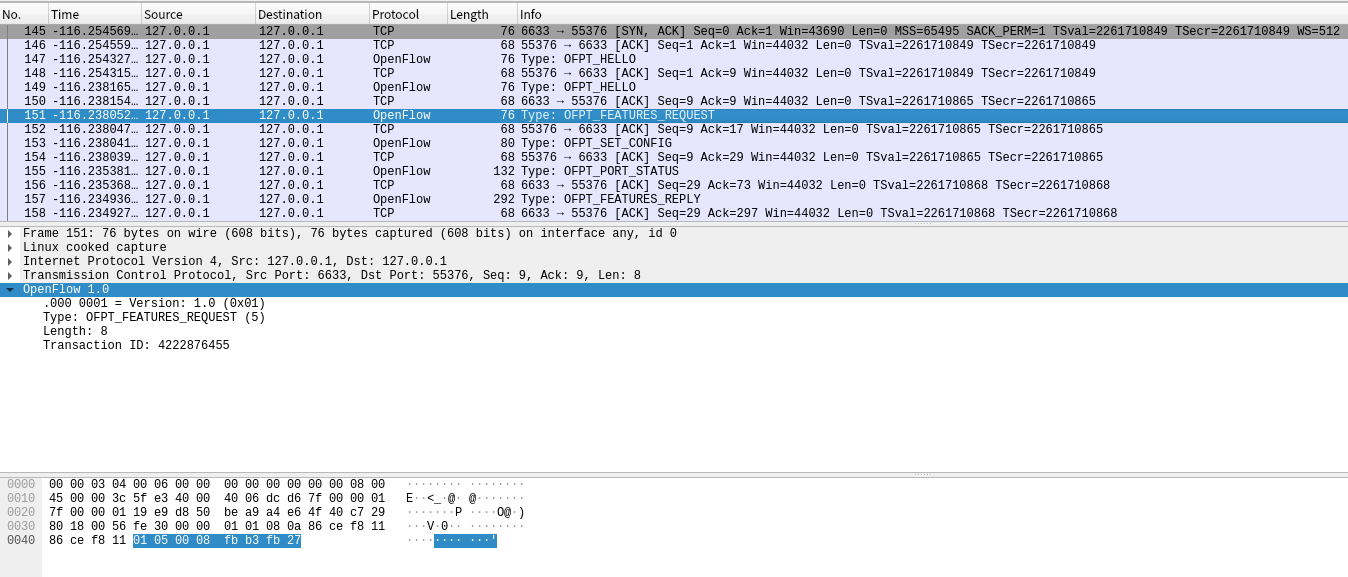
控制器6633端口(请按照我给你的flag和max bytes of packet进行配置) ---> 交换机55376端口。
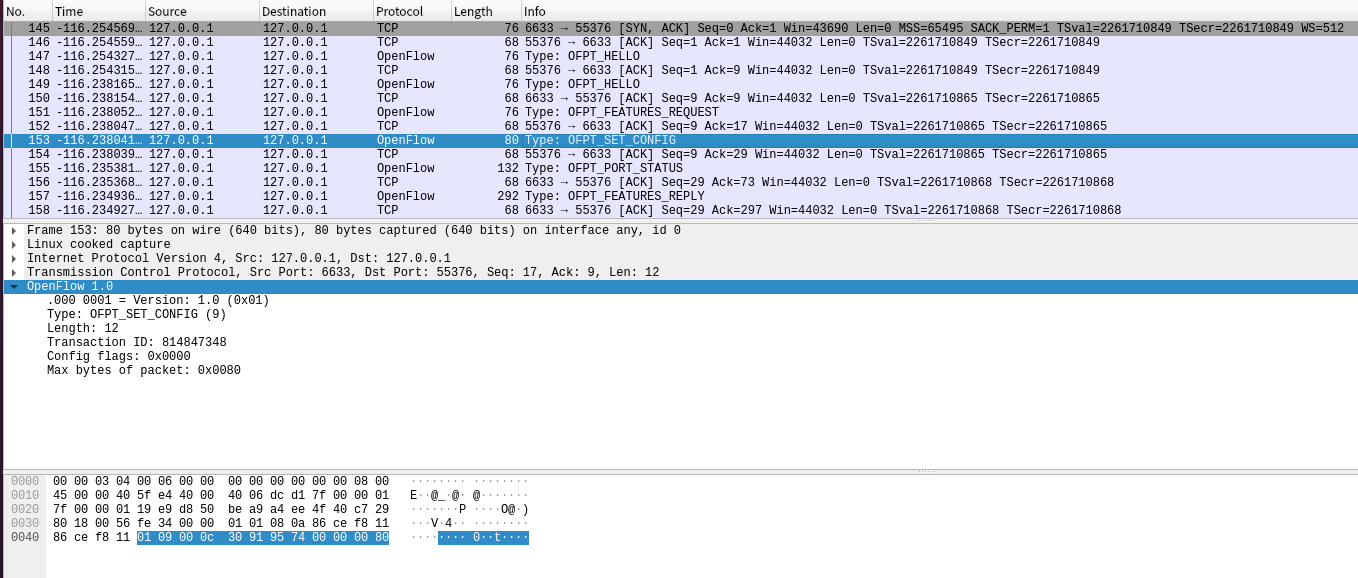
-
(3)Port_Status
当交换机端口发生变化时,告知控制器相应的端口状态。
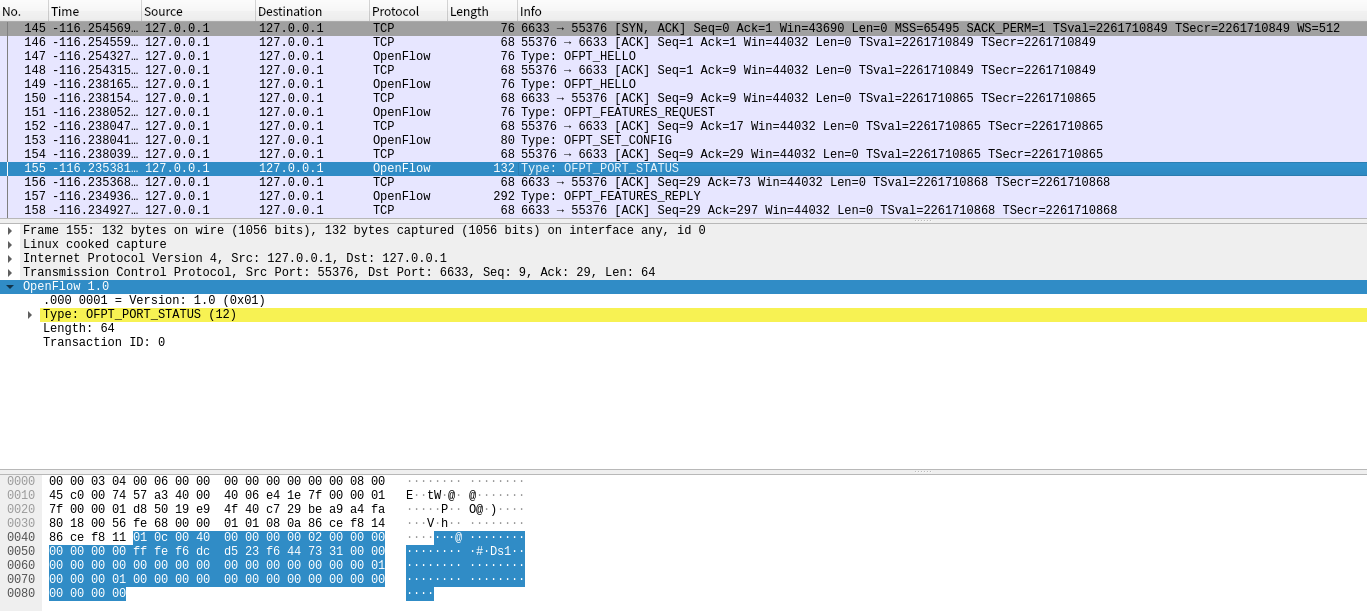
-
(4)Features Reply
交换机55376端口(这是我的特征信息,请查收) ---> 控制器6633端口
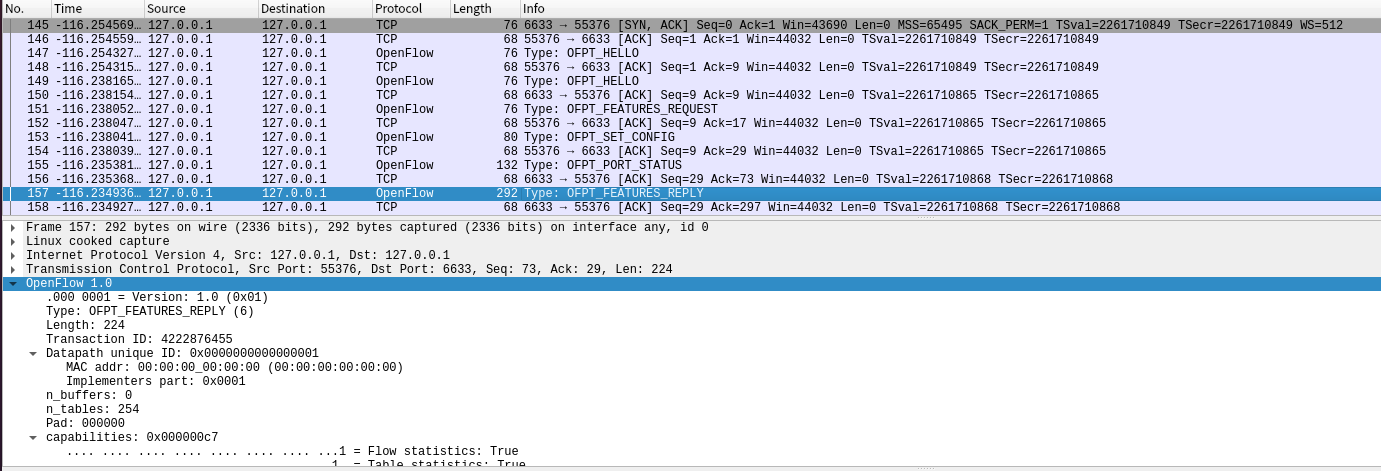
物理描述端口列表
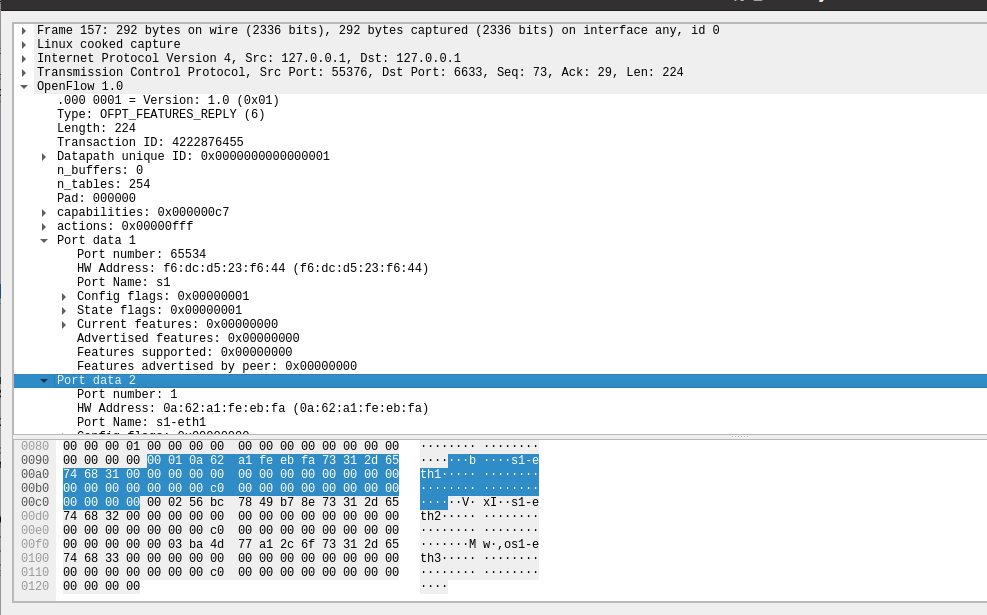
-
(5)Packet_in
交换机55376端口(有数据包进来,请指示)---> 控制器6633端口。
因为交换机发现此时自己并没有匹配的流表(Reason: No matching flow (table-miss flow entry) (0)),所以要问控制器如何处理。
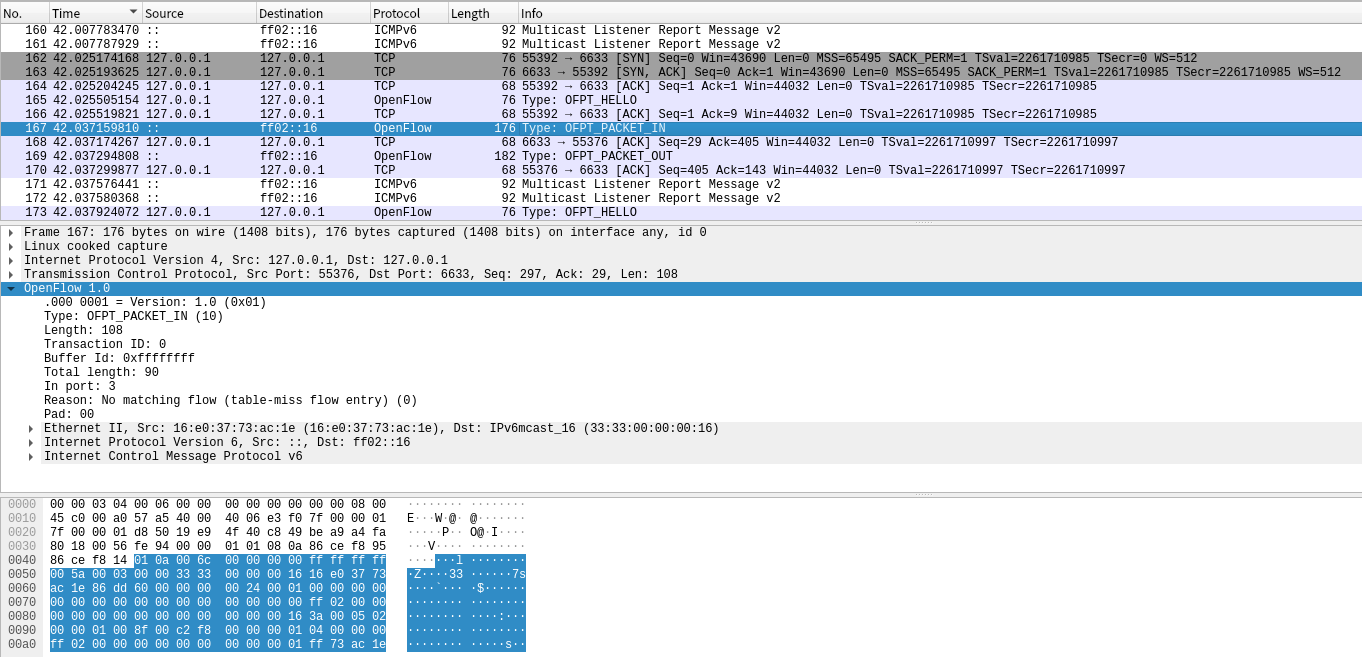
-
(6)Packet_out
控制器6633端口(请按照我给你的action进行处理) ---> 交换机55376端口。
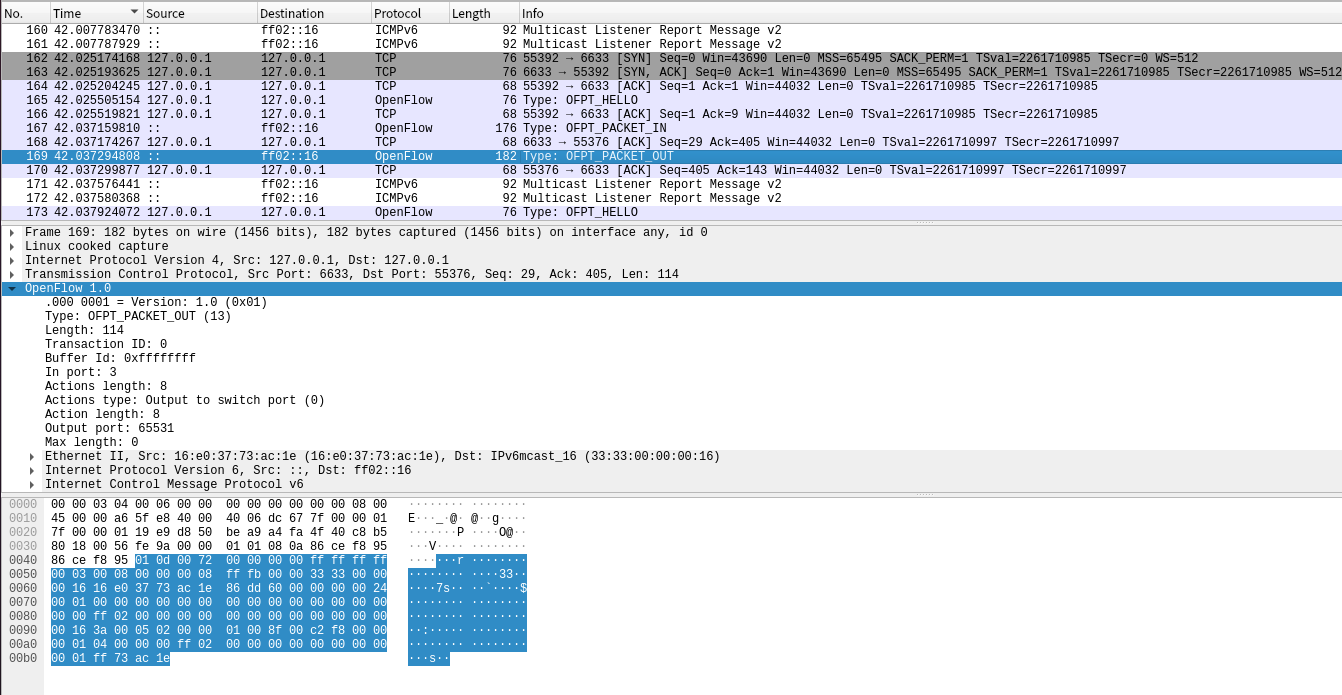
-
(7)Flow_mod
分析抓取的flow_mod数据包,控制器通过6633端口向交换机55284端口下发流表项,指导数据的转发处理
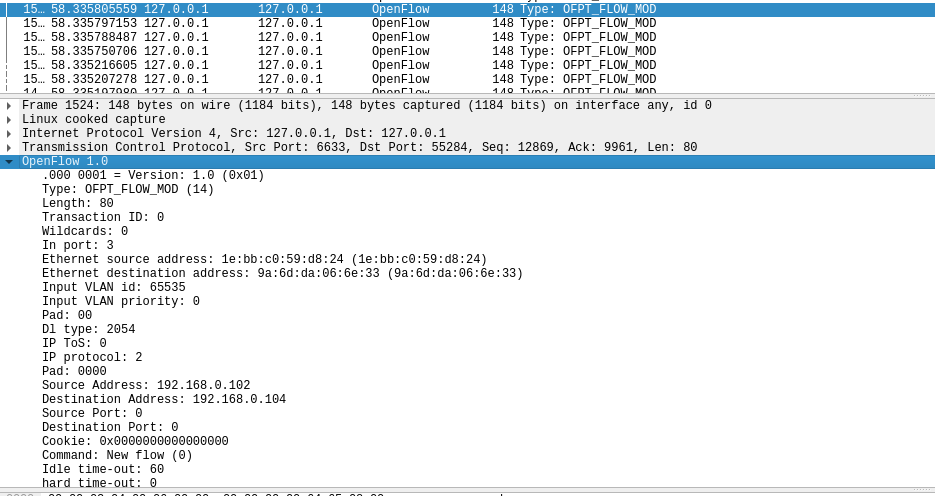
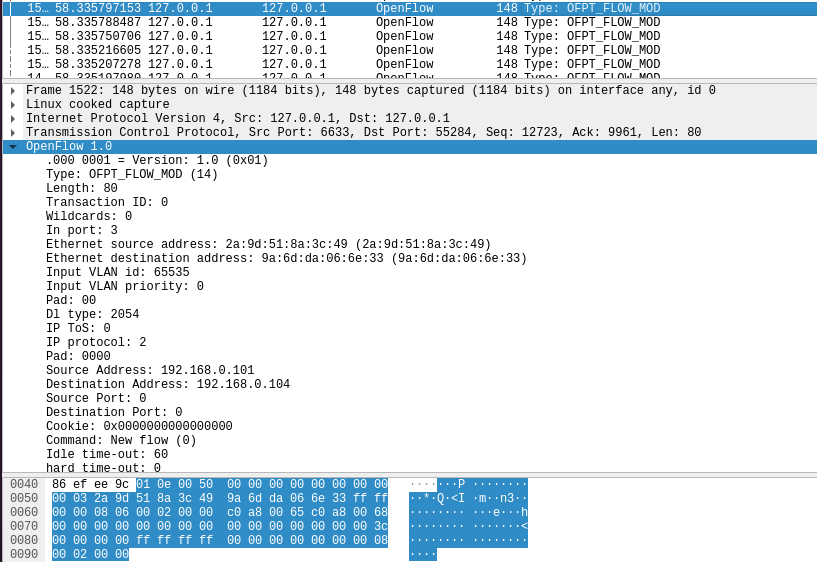
-
-
3.分析OpenFlow协议中交换机与控制器的消息交互过程,画出相关交互图或流程图。
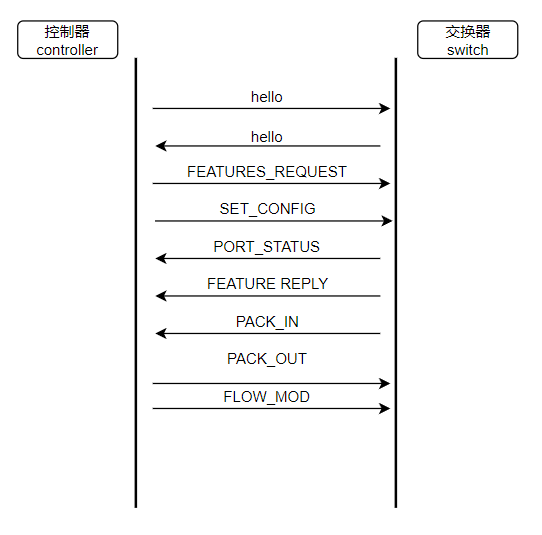
-
4.回答问题:交换机与控制器建立通信时是使用TCP协议还是UDP协议?
答:采用TCP协议。 -
(进阶要求)
-
1.HELLO
struct ofp_header {
uint8_t version; /* OFP_VERSION. */
uint8_t type; /* One of the OFPT_ constants. */
uint16_t length; /* Length including this ofp_header. */
uint32_t xid; /* Transaction id associated with this packet.
Replies use the same id as was in the request
to facilitate pairing. */
};
struct ofp_hello {
struct ofp_header header;
};
//HELLO报文中有四个参数:版本号、消息类型、长度以及事件ID。
- 2.Features Request
//feature_request与hello结构相同
struct ofp_header {
uint8_t version; /* OFP_VERSION. */
uint8_t type; /* One of the OFPT_ constants. */
uint16_t length; /* Length including this ofp_header. */
uint32_t xid; /* Transaction id associated with this packet.
Replies use the same id as was in the request
to facilitate pairing. */
};
struct ofp_hello {
struct ofp_header header;
};
- 3.Set Config
/* Switch configuration. */
struct ofp_switch_config {
struct ofp_header header;
uint16_t flags; /* OFPC_* flags. */
uint16_t miss_send_len; /* Max bytes of new flow that datapath should
send to the controller. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_switch_config) == 12);
//flags 指示交换机如何处理 IP 分片数据包
//miss_send_len 当交换机无法处理到达的数据包时,向控制器发送如何处理的最大字节数
- 4.Port_Status
/* A physical port has changed in the datapath */
struct ofp_port_status {
struct ofp_header header;
uint8_t reason; /* One of OFPPR_*. */
uint8_t pad[7]; /* Align to 64-bits. */
struct ofp_phy_port desc;
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_port_status) == 64);
- 5.Features Reply
/* Switch features. */
struct ofp_switch_features {
struct ofp_header header;
uint64_t datapath_id; /* Datapath unique ID. The lower 48-bits are for
a MAC address, while the upper 16-bits are
implementer-defined. */
uint32_t n_buffers; /* Max packets buffered at once. */
uint8_t n_tables; /* Number of tables supported by datapath. */
uint8_t pad[3]; /* Align to 64-bits. */
/* Features. */
uint32_t capabilities; /* Bitmap of support "ofp_capabilities". */
uint32_t actions; /* Bitmap of supported "ofp_action_type"s. */
/* Port info.*/
struct ofp_phy_port ports[0]; /* Port definitions. The number of ports
is inferred from the length field in
the header. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_switch_features) == 32);
//datapath_id:唯一标识符;
// n_buffers:交换机缓冲区可以缓存的最大数据包个数;
// n_tables:流表数量;
// pad:可以理解为填充值;
// capabilities:支持的特殊功能;
// actions:支持的动作;
// phy_port ports:物理端口描述列表。
/* Description of a physical port */
struct ofp_phy_port {
uint16_t port_no;
uint8_t hw_addr[OFP_ETH_ALEN];
char name[OFP_MAX_PORT_NAME_LEN]; /* Null-terminated */
uint32_t config; /* Bitmap of OFPPC_* flags. */
uint32_t state; /* Bitmap of OFPPS_* flags. */
/* Bitmaps of OFPPF_* that describe features. All bits zeroed if
* unsupported or unavailable. */
uint32_t curr; /* Current features. */
uint32_t advertised; /* Features being advertised by the port. */
uint32_t supported; /* Features supported by the port. */
uint32_t peer; /* Features advertised by peer. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_phy_port) == 48);
- 6.Packet_In
//有两种情况:1.交换机查找流表,发现没有匹配条目时
//2.有匹配条目但是对应的action是OUTPUT=CONTROLLER时
/* Why is this packet being sent to the controller? */
enum ofp_packet_in_reason {
OFPR_NO_MATCH, /* No matching flow. */
OFPR_ACTION /* Action explicitly output to controller. */
};
/* Packet received on port (datapath -> controller). */
struct ofp_packet_in {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /* ID assigned by datapath. */
uint16_t total_len; /* Full length of frame. */
uint16_t in_port; /* Port on which frame was received. */
uint8_t reason; /* Reason packet is being sent (one of OFPR_*) */
uint8_t pad;
uint8_t data[0]; /* Ethernet frame, halfway through 32-bit word,
so the IP header is 32-bit aligned. The
amount of data is inferred from the length
field in the header. Because of padding,
offsetof(struct ofp_packet_in, data) ==
sizeof(struct ofp_packet_in) - 2. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_packet_in) == 20);
- 7.Packet_Out
struct ofp_action_header {
uint16_t type; /* One of OFPAT_*. */
uint16_t len; /* Length of action, including this
header. This is the length of action,
including any padding to make it
64-bit aligned. */
uint8_t pad[4];
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_action_header) == 8);
/* Send packet (controller -> datapath). */
struct ofp_packet_out {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /* ID assigned by datapath (-1 if none). */
uint16_t in_port; /* Packet's input port (OFPP_NONE if none). */
uint16_t actions_len; /* Size of action array in bytes. */
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /* Actions. */
/* uint8_t data[0]; */ /* Packet data. The length is inferred
from the length field in the header.
(Only meaningful if buffer_id == -1.) */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_packet_out) == 16);
//动作列表、输入端口、缓冲区id等
- 8.Flow_Mod
//要匹配字段
/* Fields to match against flows */
struct ofp_match {
uint32_t wildcards; /* Wildcard fields. */
uint16_t in_port; /* Input switch port. */
uint8_t dl_src[OFP_ETH_ALEN]; /* Ethernet source address. */
uint8_t dl_dst[OFP_ETH_ALEN]; /* Ethernet destination address. */
uint16_t dl_vlan; /* Input VLAN id. */
uint8_t dl_vlan_pcp; /* Input VLAN priority. */
uint8_t pad1[1]; /* Align to 64-bits */
uint16_t dl_type; /* Ethernet frame type. */
uint8_t nw_tos; /* IP ToS (actually DSCP field, 6 bits). */
uint8_t nw_proto; /* IP protocol or lower 8 bits of
* ARP opcode. */
uint8_t pad2[2]; /* Align to 64-bits */
uint32_t nw_src; /* IP source address. */
uint32_t nw_dst; /* IP destination address. */
uint16_t tp_src; /* TCP/UDP source port. */
uint16_t tp_dst; /* TCP/UDP destination port. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_match) == 40);
/* Flow setup and teardown (controller -> datapath). */
struct ofp_flow_mod {
struct ofp_header header;
struct ofp_match match; /* Fields to match */
uint64_t cookie; /* Opaque controller-issued identifier. */
//流表动作
/* Flow actions. */
uint16_t command; /* One of OFPFC_*. */
uint16_t idle_timeout; /* Idle time before discarding (seconds). */
uint16_t hard_timeout; /* Max time before discarding (seconds). */
uint16_t priority; /* Priority level of flow entry. */
uint32_t buffer_id; /* Buffered packet to apply to (or -1).
Not meaningful for OFPFC_DELETE*. */
uint16_t out_port; /* For OFPFC_DELETE* commands, require
matching entries to include this as an
output port. A value of OFPP_NONE
indicates no restriction. */
uint16_t flags; /* One of OFPFF_*. */
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /* The action length is inferred
from the length field in the
header. */
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_flow_mod) == 72);
//含cookie、流表动作等
总结
- 首先,是要明白数据抓包的意义,查阅openflow.h 中的相关数据结构及相应语义。
- 其次,是对抓到的数据进行分析,一个是报文消息类型,一个是报文中具体数据代表的含义。
- 最后,是对整个通信过程的理解,如何进行连接、控制、通信等以及会话交互分析。



