前言
LZ77算法是无损压缩算法,由以色列人Abraham Lempel发表于1977年。LZ77是典型的基于字典的压缩算法,现在很多压缩技术都是基于LZ77。鉴于其在数据压缩领域的地位,本文将结合图片和源码详细介绍其原理。
原理介绍:
首先介绍几个专业术语。
1.lookahead buffer(不知道怎么用中文表述,暂时称为待编码区):
等待编码的区域
2. search buffer:
已经编码的区域,搜索缓冲区
3.滑动窗口:
指定大小的窗,包含“搜索缓冲区”(左) + “待编码区”(右)
接下来,介绍具体的编码过程:
为了编码待编码区, 编码器在滑动窗口的搜索缓冲区查找直到找到匹配的字符串。匹配字符串的开始字符串与待编码缓冲区的距离称为“偏移值”,匹配字符串的长度称为“匹配长度”。编码器在编码时,会一直在搜索区中搜索,直到找到最大匹配字符串,并输出(o, l ),其中o是偏移值, l是匹配长度。然后窗口滑动l,继续开始编码。如果没有找到匹配字符串,则输出(0, 0, c),c为待编码区下一个等待编码的字符,窗口滑动“1”。算法实现将类似下面的:
while( lookAheadBuffer not empty )
{
get a pointer (position, match) to the longest match
in the window for the lookAheadBuffer;
output a (position, length, char());
shift the window length+1 characters along;
}
主要步骤为:
1.设置编码位置为输入流的开始
2.在滑窗的待编码区查找搜索区中的最大匹配字符串
3.如果找到字符串,输出(偏移值, 匹配长度), 窗口向前滑动“匹配长度”
4.如果没有找到,输出(0, 0, 待编码区的第一个字符),窗口向前滑动一个单位
5.如果待编码区不为空,回到步骤2
描述实在是太复杂,还是结合实例来讲解吧
实例:
现在有字符串“AABCBBABC”,现在对其进行编码。
一开始,窗口滑入如图位置
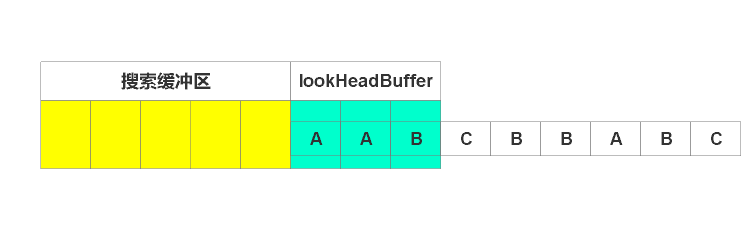
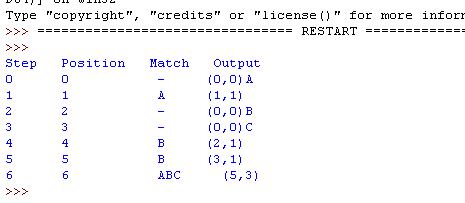
由图可见,待编码缓冲区有“AAB”三个字符,此时搜索缓冲区还是空的。所以编码第一个字符,由于搜索区为空,故找不到匹配串,输出(0,0, A),窗口右移一个单位,如下图
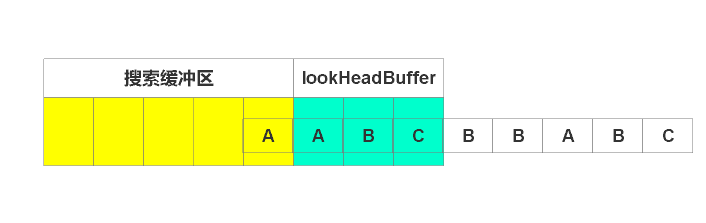
此时待编码区有“ABC”。开始编码。最先编码"A",在搜索区找到"A"。由于没有超过待编码区,故开始编码"AB",但在搜索区没有找到匹配字符串,故无法编码。因此只能编码"A"。
输出(1, 1)。即为相对于待编码区,偏移一个单位,匹配长度为1。窗口右滑动匹配长度,即移动1个单位。如下图
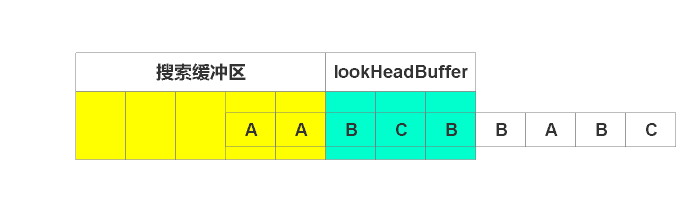
一样,没找到,输出(0, 0, B),右移1个单号,如下图
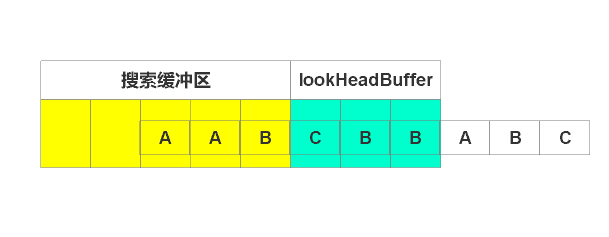
输出(0, 0, C),右移1个单位,如下图
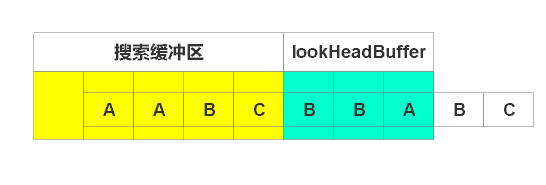
输出(2, 1),右移1个单位,如下图
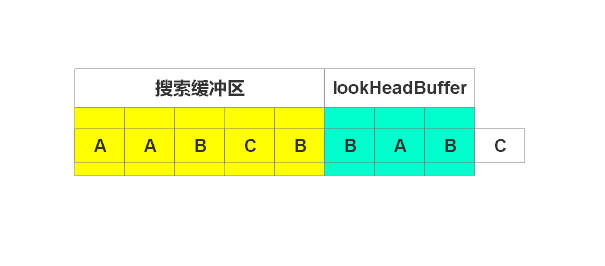
输出(3, 1), 右移1个单位,如下图
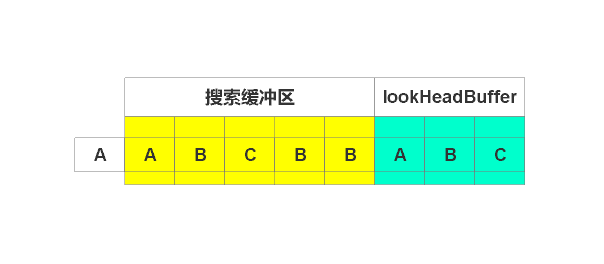
开始编码"A",在搜索缓冲区查找到匹配字符串。由于待编码缓冲区没有超过,继续编码。开始编码"AB",也搜索到。不要停止,继续编码“ABC”,找到匹配字符串。由于继续编码,则超过了窗口,故只编码“ABC”,输出(5, 3),偏移5,长度3。右移3个单位,如下图
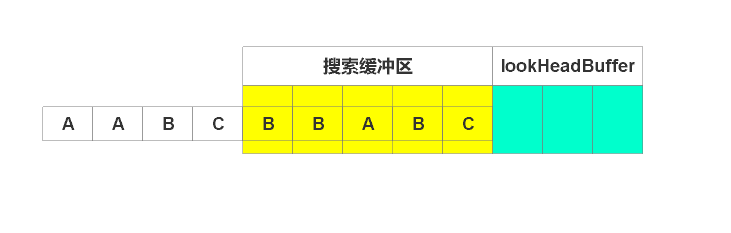
此时待编码缓冲区为空,停止编码。
最终输出结果如下
python代码实现:
1 class Lz77:
2 def __init__(self, inputStr):
3 self.inputStr = inputStr #输入流
4 self.searchSize = 5 #搜索缓冲区(已编码区)大小
5 self.aheadSize = 3 #lookAhead缓冲区(待编码区)大小
6 self.windSpiltIndex = 0 #lookHead缓冲区开始的索引
7 self.move = 0
8 self.notFind = -1 #没有找到匹配字符串
9
10 #得到滑动窗口的末端索引
11 def getWinEndIndex(self):
12 return self.windSpiltIndex + self.aheadSize
13
14 #得到滑动窗口的始端索引
15 def getWinStartIndex(self):
16 return self.windSpiltIndex - self.searchSize
17
18 #判断lookHead缓冲区是否为空
19 def isLookHeadEmpty(self):
20 return True if self.windSpiltIndex + self.move> len(self.inputStr) - 1 else False
21
22 def encoding(self):
23 step = 0
24 print("Step Position Match Output")
25 while not self.isLookHeadEmpty():
26 #1.滑动窗口
27 self.winMove()
28 #2. 得到最大匹配串的偏移值和长度
29 (offset, matchLen) = self.findMaxMatch()
30 #3.设置窗口下一步需要滑动的距离
31 self.setMoveSteps(matchLen)
32 if matchLen == 0:
33 #匹配为0,说明无字符串匹配,输出下一个需要编码的字母
34 nextChar = self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex]
35 result = (step, self.windSpiltIndex, '-', '(0,0)' + nextChar)
36 else:
37 result = (step, self.windSpiltIndex, self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex - offset: self.windSpiltIndex - offset + matchLen], '(' + str(offset) + ',' + str(matchLen) + ')')
38 #4.输出结果
39 self.output(result)
40 step = step + 1 #仅用来设置第几步
41
42
43 #滑动窗口(移动分界点)
44 def winMove(self):
45 self.windSpiltIndex = self.windSpiltIndex + self.move
46
47 #寻找最大匹配字符并返回相对于窗口分界点的偏移值和匹配长度
48 def findMaxMatch(self):
49 matchLen = 0
50 offset = 0
51 minEdge = self.minEdge() + 1 #得到编码区域的右边界
52 #遍历待编码区,寻找最大匹配串
53 for i in range(self.windSpiltIndex + 1, minEdge):
54 #print("i: %d" %i)
55 offsetTemp = self.searchBufferOffest(i)
56 if offsetTemp == self.notFind:
57 return (offset, matchLen)
58 offset = offsetTemp #偏移值
59
60 matchLen = matchLen + 1 #每找到一个匹配串,加1
61
62 return (offset, matchLen)
63
64 #入参字符串是否存在于搜索缓冲区,如果存在,返回匹配字符串的起始索引
65 def searchBufferOffest(self, i):
66 searchStart = self.getWinStartIndex()
67 searchEnd = self.windSpiltIndex
68 #下面几个if是处理开始时的特殊情况
69 if searchEnd < 1:
70 return self.notFind
71 if searchStart < 0:
72 searchStart = 0
73 if searchEnd == 0:
74 searchEnd = 1
75 searchStr = self.inputStr[searchStart : searchEnd] #搜索区字符串
76 findIndex = searchStr.find(self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex : i])
77 if findIndex == -1:
78 return -1
79 return len(searchStr) - findIndex
80
81 #设置下一次窗口需要滑动的步数
82 def setMoveSteps(self, matchLen):
83 if matchLen == 0:
84 self.move = 1
85 else:
86 self.move = matchLen
87
88
89 def minEdge(self):
90 return len(self.inputStr) if len(self.inputStr) - 1 < self.getWinEndIndex() else self.getWinEndIndex() + 1
91
92 def output(self, touple):
93 print("%d %d %s %s" % touple)
94
95
96
97
98 if __name__ == "__main__":
99 lz77 = Lz77("AABCBBABC")
100 lz77.encoding()
只是简单的写了下,没有过多考虑细节,请注意,这不是最终的代码,只是用来阐述原理,仅供参考。输出结果就是上面的输出(格式由于坑爹的博客园固定样式,代码位置有偏移,请注意)
参考文章:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee916854.aspx
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LZ77_and_LZ78
以上几篇文章都是很好的讲解LZ77原理的,大家有兴趣的可以参考下。由于国内介绍该算法的比较少,故这些英文文章帮助还是挺大的。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?