Rsync脚本部署
服务端
[root@junwu_server /]# cat rsync_server.sh #!/bin/bash yum install rsync -y echo \ "uid = rsync gid = rsync fake super = yes use chroot = no max connections = 200 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log ignore errors read only = false list = false hosts allow = 10.0.0.15/24 auth users = rsync_user secrets file = /etc/rsync.password [backup] comment = This is rsync backup! path = /backback/ " \ >> /etc/rsyncd.conf useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M rsync mkdir /backback chown -R rsync.rsync /backback echo "rsync_user:123456" > /etc/rsync.password chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password systemctl restart rsyncd && systemctl enable rsyncd
客户端
[root@junwu_client /]# cat rsync_client.sh #!/bin/bash yum install rsync -y echo "123456" > /etc/rsync.password echo "export RSYNC_PASSWORD=123456" >> /etc/bashrc systemctl start rsyncd touch /tmp/rsync部署成功.txt rsync -acz /tmp/rsync部署成功.txt rsync_user@10.0.0.10::backup

遇到的问题:
1)bind() failed: Address already in use (address-family 2)
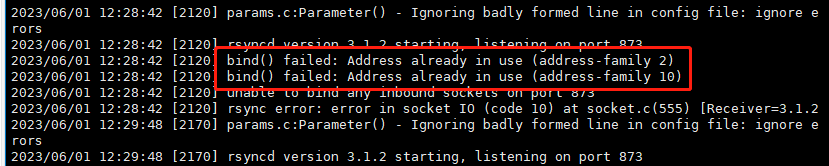
此问题是因为在脚本中启动rsync服务时的命令:systemctl start rsyncd 该服务已经启动了,便不能再启动
脚本中应改成:systemctl restart rsyncd
2)echo "export RSYNC_PASSWORD=123456" >> /etc/bashrc 该变量的作用是什么? 客户端写入该变量RSYNC_PASSWORD后,为什么rsync传输文件时不需要输入密码了?
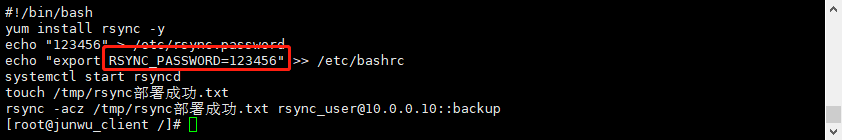
当定义了RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量并设置了正确的密码后,在执行rsync命令时,rsync会自动读取该环境变量并将其用作远程rsync服务器的密码。这样,你就不需要手动输入密码,而是可以在脚本或非交互式环境中自动化地提供密码。
以下是使用RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量执行rsync命令的示例:
export RSYNC_PASSWORD="your_password" rsync -avz /local/path user@remote:/remote/path
在上述示例中,我们首先通过export命令将RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量设置为密码。然后,我们使用rsync命令将本地路径/local/path的文件同步到远程服务器的/remote/path路径。
在执行rsync命令时,rsync会检测RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量的存在,并自动将其作为远程rsync服务器的密码进行身份验证。
请注意,RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量的作用范围仅限于当前会话或当前脚本。如果你希望在不同的会话或脚本中自动提供密码,需要在每个会话或脚本中重新定义和设置RSYNC_PASSWORD环境变量。
只有经历过生活的苦难
才会更加努力去生活
自己梦想的一切
更加需要自己脚踏实地的去践行
结果未必尽如人意
但是路途中的努力
一定比结果更加美丽
----by ljw



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号