代码随想录-链表基础
链表
链表基础
单链表
package com.lee;
/**
* @author Jun
* @date 2023/2/17 21:53
* @description ListNode
*/
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(){}
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
class MyLinkedList {
// 存除链表元素的个数
int size;
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode head;
// 初始化链表
public MyLinkedList(){
size = 0;
head = new ListNode();
}
// 获取第index个节点的数值,从0开始,第0个节点就是头结点
public int get(int index) {
// index非法,返回-1
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return -1;
}
ListNode currentNode = head;
// 包含一个虚拟头节点,所以查找第index+1个节点
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode.val;
}
// 在链表最前面插入一个元素,等价于第0个元素前添加
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
// 在链表最后一个节点插入一个元素
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
/**
* 在第index个节点之前插入一个新节点,如果为0则该节点为头结点
* 如果index等于链表的长度,则新插入节点为链表尾节点
* 如果index大于链表长度,则返回空
*/
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {
return ;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
// 添加元素所以长度加一
size++;
// 找到要插入节点的前驱
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.next = pred.next;
pred.next = toAdd;
}
// 删除第index个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return;
}
// 减少元素长度减一
size--;
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
pred.next = pred.next.next;
}
}
//打印输出方法
static void print(ListNode listNoed){
//创建链表节点
while(listNoed!=null){
System.out.println("节点:"+listNoed.val);
listNoed=listNoed.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建链表
ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur;
cur = node;
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
ListNode one = new ListNode(i);
cur.next = one;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
移除链表元素
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
设置虚拟头结点:return头结点的时候,需要return dummyNode.next,这才是新的头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 如果头结点为空,直接返回空链表
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 设置虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
// 设置前、后两个结点
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
// 如果当前结点不为空的话就一直循环
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
// 与目标值相同,则切换pre的next
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
// 不同的话,顺理成章前往后移
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
反转链表
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
// 双指针
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 设置头结点为空
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
// 设置临时结点
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 类似替换前后数
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// 因为反转,最后返回prev
return prev;
}
两两交换列表中的结点(虚拟头结点)

public static ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// 设置虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
// 虚拟头结点指向head
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
// 设置临时结点,保存两个结点后面的结点
ListNode temp;
// 临时结点,保存两个结点中的第一个
ListNode firNode;
// 保存第二个
ListNode secNode;
// 当前结点的后一和后二都是空,就停止循环,因为没有足够数进行交换
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
// 临时结点用来保存第三个数,交换后的第二个数需要指向它
temp = cur.next.next.next;
// 当前结点的一二
firNode = cur.next;
secNode = cur.next.next;
// 一二交换成二一
cur.next = secNode;
secNode.next = firNode;
// 交换后的二指向下一个结点,也就是临时结点
firNode.next = temp;
// 当前结点移至交换后的第二个结点
cur = firNode;
}
return dummy.next;
}
删除链表的第n个结点 (双指针)
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5] 示例 2:
- 设置虚拟头结点
- 定义fast和slow双指针
- fast先走n步,当fast的next为空时,删除掉slow的next即可
public static ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int index) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 这里画图理解
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
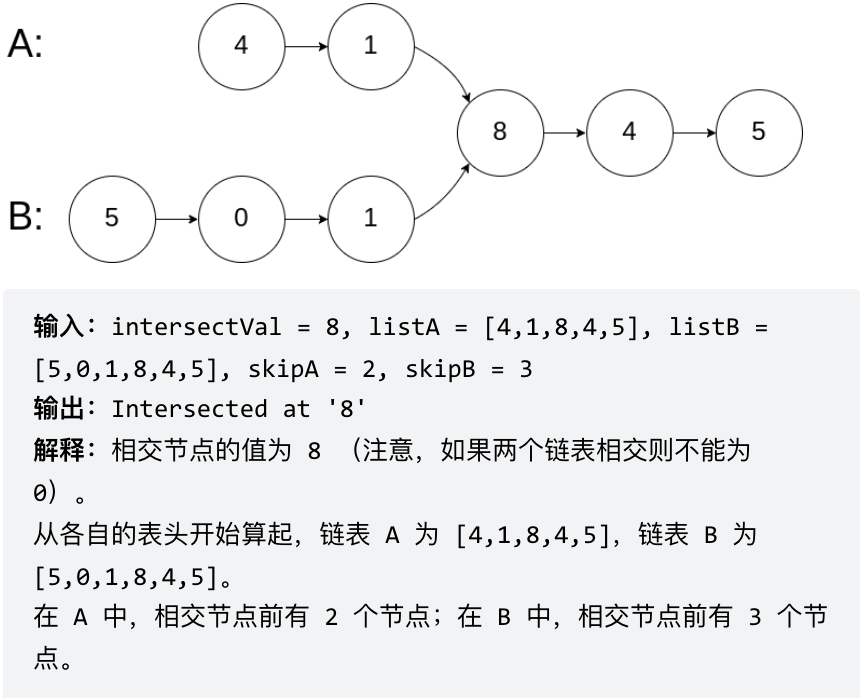
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 定义头结点
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
// 求链表A的长度
while (curA != null) {
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
// 链表B的长度
while (curB != null) {
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// 如果B的长度大,则调整链表及其长度
if (lenB > lenA) {
int tmpLen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmpLen;
ListNode tmpNode = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
// 定义两者之间的长度差
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// 循环调增,直到两链表差值为0
while (gap-- > 0) {
curA = curA.next;
}
// 如果两者值相同则返回交点值,否则返回空
while (curA != null) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号