SSM 框架整合案例、Maven 高级
整合流程简介
SSM(Spring + SpringMVC + MyBatis)整合步骤分析:
-
Spring
- 框架基础
-
MyBatis
- mysql + druid + pagehelper
-
Spring 整合 MyBatis
-
junit 测试业务层接口
-
SpringMVC
- rest 风格(postman 测试请求结果)
- 数据封装 json(jackson)
-
Spring 整合 SpringMVC
- Controller 调用 Service
-
其他
-
表现层数据封装
-
自定义异常
-
5 个关键步骤:
- Spring 环境
- MyBatis 环境
- Spring 整合 MyBatis
- SpringMVC 环境
- Spring 整合 SpringMVC
环境准备
数据表
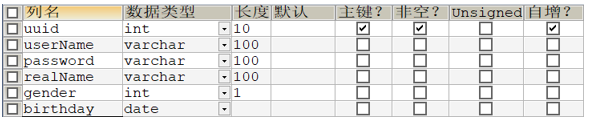
create table user (
uuid int(10) not null auto_increment,
userName varchar(100) default null,
password varchar(100) default null,
realName varchar(100) default null,
gender int(1) default null,
birthday date default null,
primary key (uuid)
);
Maven 依赖
<!-- spring环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.11</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 分页插件坐标 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springmvc环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- servlet环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- jackson相关坐标3个 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 其他组件 -->
<!-- junit5单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
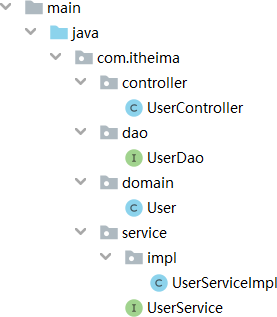
项目结构
-
创建项目,组织项目结构,创建包
-
创建表与实体类
-
创建三层架构对应的模块、接口与实体类,并建立关联关系
-
数据层接口(代理自动创建实现类)
- 业务层接口 + 业务层实现类
- 表现层类
配置文件+注解 开发
Spring 整合 Mybatis
Mybatis 配置
- Mapper 映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.dao.UserDao">
<!--添加-->
<insert id="save" parameterType="user">
insert into user(userName,password,realName,gender,birthday)values(#{userName},#{password},#{realName},#{gender},#{birthday})
</insert>
<!-- 删除 -->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from user where uuid = #{uuid}
</delete>
<!-- 修改 -->
<update id="update" parameterType="user">
update user set userName=#{userName},password=#{password},realName=#{realName},gender=#{gender},birthday=#{birthday} where uuid=#{uuid}
</update>
<!-- 查询单个 -->
<select id="get" resultType="user" parameterType="int">
select * from user where uuid= #{uuid}
</select>
<!-- 分页查询 -->
<select id="getAll" resultType="user">
select * from user
</select>
<!-- 登录 -->
<select id="getByUserNameAndPassword" resultType="user" >
select * from user where userName=#{userName} and password=#{password}
</select>
</mapper>
- Dao 接口:
package com.dao;
import com.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 添加用户
* @param user
* @return
*/
public boolean save(User user);
/**
* 修改用户
* @param user
* @return
*/
public boolean update(User user);
/**
* 删除用户
* @param uuid
* @return
*/
public boolean delete(Integer uuid);
/**
* 查询所有用户
* 由于会在服务层使用分页插件,因此此处不用传页数和条数
* @return
*/
public List<User> getAll();
/**
* 查询单个用户
* @param uuid
* @return
*/
public User get(Integer uuid);
/**
* 根据用户名密码查询用户信息
* 注意:数据层操作不要和业务层操作的名称混淆。通常数据层仅反映与数据库间的信息交换,不体现业务逻辑
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
public User getByUserNameAndPassword(@Param("userName") String username, @Param("password") String password);
}
Service 实现类
package com.service.impl;
import com.dao.UserDao;
import com.domain.User;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import com.service.UserService;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public boolean save(User user) {
return userDao.save(user);
}
@Override
public boolean update(User user) {
return userDao.update(user);
}
@Override
public boolean delete(Integer uuid) {
return userDao.delete(uuid);
}
@Override
public PageInfo<User> getAll(int page, int size) {
PageHelper.startPage(page, size);
List<User> all = userDao.getAll();
return new PageInfo<User>(all);
}
@Override
public User get(Integer uuid) {
return userDao.get(uuid);
}
@Override
public User login(String username, String password) {
return userDao.getByUserNameAndPassword(username, password);
}
}
Spring 核心配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 开启bean注解扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
<!-- 整合Mybatis到spring中 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.domain"/>
<!--分页插件-->
<property name="plugins">
<array>
<bean class="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="helperDialect">mysql</prop>
<prop key="reasonable">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 加载properties文件,获取数据库连接信息 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 映射扫描:加载Mapper配置文件 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.dao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
</beans>
整合 junit5
package com.service;
import com.domain.User;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.Date;
// 设定 spring 专用的类加载器
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
class UserServiceTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testSave(){
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("Jock");
user.setPassword("root");
user.setRealName("Jockme");
user.setGender(1);
user.setBirthday(new Date(333333000000L));
boolean result = userService.save(user);
assert result;
}
@Test
public void testDelete(){
User user = new User();
boolean result = userService.delete(3);
assert result;
}
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
user.setUuid(1);
user.setUserName("Jockme");
user.setPassword("root");
user.setRealName("JockIsMe");
user.setGender(1);
user.setBirthday(new Date(333333000000L));
boolean result = userService.update(user);
assert result;
}
@Test
public void testGet(){
User user = userService.get(1);
System.out.println(user);
assert user != null;
}
@Test
public void testGetAll(){
PageInfo<User> all = userService.getAll(2, 2);
System.out.println(all);
assert all.getList().size() == 2;
System.out.println(all.getList().get(0));
System.out.println(all.getList().get(1));
}
@Test
public void testLogin(){
User user = userService.login("Jockme", "root");
System.out.println(user);
assert user != null;
}
}
Spring 整合 SpringMVC
SpringMVC
- web.xml:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
- spring-mvc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.controller"/>
</beans>
- controller 层:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public boolean save(User user) {
System.out.println("save ..." + user); return true;
}
@PostMapping("/login")
public User login(String userName,String password){
System.out.println("login ..." + userName + " ," +password);
return null;
}
}
Spring 整合 SpringMVC
- web.xml 加载 Spring 环境:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--启动服务器时,通过监听器加载spring运行环境-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
- Controller 调用 Service:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping
public boolean save(User user){
return userService.save(user);
}
}
表现层数据封装
前端接收表现层返回的数据种类各式各样:
| 数据类型 | 示例 | 格式 |
|---|---|---|
| 操作是否成功 | true / false | 格式 A |
| 基本数据 | 数值、字符串 | 格式 B |
| 对象数据 | json 对象 | 格式 C |
| 集合数据 | json 数组 | 格式 D |
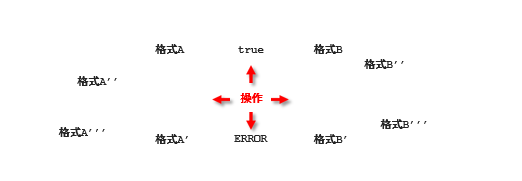
返回的数据格式应统一设计:

示例代码:
- 返回数据对象封装:
public class Result {
// 操作结果编码
private Integer code;
// 操作数据结果
private Object data;
// 消息
private String message;
public Result(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public Result(Integer code, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.data = data;
}
// 省略展示 getter、setter
}
- 状态码常量可以根据自己的业务需求设定:
public class Code {
public static final Integer SAVE_OK = 20011;
public static final Integer SAVE_ERROR = 20010;
// 其他编码
}
- controller 调用:
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping
public Result save(User user){
boolean flag = userService.save(user);
return new Result(flag ? Code.SAVE_OK:Code.SAVE_ERROR);
}
@GetMapping("/{uuid}")
public Result get(@PathVariable Integer uuid){
User user = userService.get(uuid);
return new Result(null != user ?Code.GET_OK: Code.GET_ERROR,user);
}
}
自定义异常
设定自定义异常,封装程序执行过程中出现的问题,便于表现层进行统一的异常拦截并进行处理。
- BusinessException
- SystemException
自定义异常消息返回时需要与业务正常执行的消息按照统一的格式进行处理。
代码示例:
- 定义 BusinessException:
public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {
//自定义异常中封装对应的错误编码,用于异常处理时获取对应的操作编码
private Integer code;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message, Integer code) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause,Integer code) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(Throwable cause,Integer code) {
super(cause);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace,Integer code) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
this.code = code;
}
}
- 控制层:
@GetMapping("/{uuid}")
public Result get(@PathVariable Integer uuid){
User user = userService.get(uuid);
// 模拟出现异常,使用条件控制,便于测试结果
if (uuid == 10 ) throw new BusinessException("查询出错啦,请重试!",Code.GET_ERROR);
return new Result(null != user ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERROR, user);
}
- 返回消息兼容异常信息:
@Component
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionAdivce {
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
// 对出现异常的情况进行拦截,并将其处理成统一的页面数据结果格式
public Result doBusinessException(BusinessException e){
return new Result(e.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}
}
纯注解 开发
注解替代 applicationContext.xml
package com.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(
// 等同于<context:component-scan base-package="com">
value = "com",
// 等同于<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes={Controller.class})
)
// 等同于<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:jdbc.properties"/>
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
// 等同于<tx:annotation-driven/>,bean的名称默认取transactionManager
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Import({MybatisConfig.class, JdbcConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
// 等同于<bean id="txManager"/>
@Bean("transactionManager")
// 等同于<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
public DataSourceTransactionManager getTxManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager tm = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
// 等同于<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
tm.setDataSource(dataSource);
return tm;
}
}
注解替代 spring-mvc.xml
package com.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
@Configuration
// 等同于<context:component-scan base-package="com.controller"/>
@ComponentScan("com.controller")
// 功能强大于<mvc:annotation-driven/>
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
@EnableWebMvc 功能:
- 支持 ConversionService 的配置,可以方便配置自定义类型转换器。
- 支持 @NumberFormat 注解格式化数字类型。
- 支持 @DateTimeFormat 注解格式化日期数据,包括 Date、Calendar、JodaTime(JodaTime 要导包)。
- 支持@Valid的参数校验(需要导入 JSR-303 规范)。
- 配合第三方 jar 包和 SpringMVC 提供的注解读写 XML 和 JSON 格式数据。
Maven 高级
分模块开发
- 模块中仅包含当前模块对应的功能类与配置文件。
- Spring 核心配置文件根据模块功能不同进行独立制作。
- 当前模块所依赖的模块通过导入坐标的形式加入当前模块后才可以使用。
- web.xml 需要加载所有的 Spring 核心配置文件。
聚合与继承
作用:
- 聚合用于快速构建项目继承用于快速配置。
相同点:
- 聚合与继承的 pom.xml 文件打包方式均为 pom,可以将两种关系制作到同一个 pom 文件中。
- 聚合与继承均属于设计型模块,并无实际的模块内容。
不同点:
- 聚合是在当前模块中配置关系,聚合可以感知到参与聚合的模块有哪些。
- 继承是在子模块中配置关系,父模块无法感知哪些子模块继承了自己。
聚合
作用:聚合用于快速构建 maven 工程,可以一次性构建多个项目/模块。
制作方式:
- 创建一个空模块,打包类型定义为“pom”:
<packaging>pom</packaging>
- 定义当前模块进行构建操作时关联的其他模块名称:
<modules>
<module>../ssm controller</module>
<module>../ssm service</module>
<module>../ssm dao</module>
<module>../ssm pojo</module>
</modules>
注意事项:参与聚合操作的模块最终执行顺序与模块间的依赖关系有关,与配置顺序无关。
继承
作用:通过继承可以实现在子工程中沿用父工程中的配置。
* Maven 中的继承与 java 中的继承相似,在子工程中配置继承关系。
制作方式:
- 在子工程中声明其父工程坐标与对应的位置:
<!--定义该工程的父工程-->
<parent>
<groupId>com</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
继承依赖定义:
- 在父工程中定义依赖管理:
<!--声明此处进行依赖管理-->
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- 具体的依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RETFASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
Maven 提供的 dependentcyManagement 元素既能让子模块继承到父模块的依赖配置,又能保证子模块依赖使用的灵活度。在 dependentcyManagement 元素下的依赖声明不会引入实际的依赖,而是定义了依赖的版本,对版本进行同一管理,避免出现版本不一致的情况。
继承依赖使用:
- 在子工程中定义依赖关系,无需声明依赖版本,版本参照父工程中依赖的版本:
<dependencies>
<!-- spring环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
可继承的资源:
- groupld:项目组 ID,项目坐标的核心元素
- version:项目版本,项目坐标的核心因素
- description:项目的描述信息
- organization:项目的组织信息
- inceptionYear:项目的创始年份
- url:项目的 URL 地址
- developers:项目的开发者信息
- contributors:项目的贡献者信息
- distributionManagement:项目的部署配置
- issueManagement:项目的缺陷跟踪系统信息
- dependencyManagement:项目的依赖管理配置
- properties:自定义的 Maven 属性
- dependencies项目的依赖配置
- build:包括项目的源码目录配置、输出目录配置、插件配置、插件管理配置等
- repositories:项目的仓库配置
- ciManagement项目的持续集成系统信息
- scm:项目的版本控制系统信息
- malilingLists:项目的邮件列表信息
- reporting:包括项目的报告输出目录配置、报告插件配置等
属性
1)自定义属性
-
作用:等同于定义变量,方便统一维护。
-
定义格式:
<!-- 定义自定义属性 -->
<properties>
<spring.version>5.1.9.RELEASE</spring.version>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
</properties>
- 调用格式:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
2)内置属性
-
作用:使用 Maven 内置属性,快速配置。
-
调用格式:
${basedir}
${version}
3)Setting 属性
-
作用:使用 Maven 配置文件 setting.xml 中的标签属性,用于动态配置。
-
调用格式:
${settings.localRepository)
4)Java 系统属性
-
作用:读取 Java 系统属性。
-
调用格式:
${user.home}
- 系统属性查询方式:
mvn help:system
版本管理
工程版本:
-
SNAPSHOT(快照版本)
- 项目开发过程中,为方便团队成员合作,解决模块间相互依赖和时时更新的问题,开发者对每个模块进行构建的时候,输出的临时性版本叫快照版本(测试阶段版本)。
- 快照版本会随着开发的进展不断更新。
-
RELEASE(发布版本)
- 项目开发到进入阶段里程碑后,向团队外部发布较为稳定的版本,这种版本所对应的构件文件是稳定的,即便进行功能的后续开发,也不会改变当前发布版本内容,这种版本称为发布版本。
工程版本号约定规范:
<主版本>.<次版本>.<增量版本>.<里程碑版本>- 主版本:表示项目重大构的变更,如 spring5 相较于 spring4 的迭代。
- 次版本:表示有较大的功能增加和变化,或者全面系统地修复漏洞。
- 增量版本:表示有重大漏洞的修复。
- 里程碑版本:表明一个版本的里程碑(版本内部)。这样的版本同下一个正式版本相比,相对来说不是很稳定,有待更多的测试。
- 范例:5.1.9.RELEASE
资源配置
多文件维护:
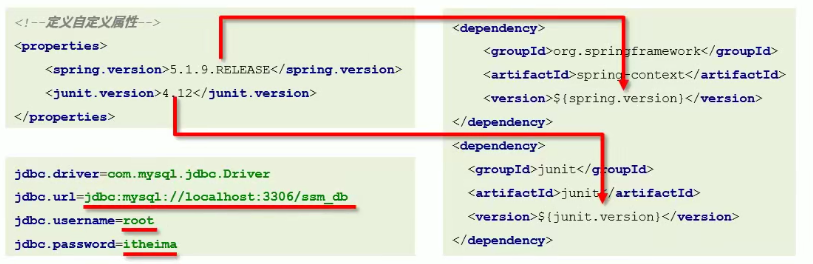
配置文件引用 pom 属性:
-
作用:在任意配置文件中加载 pom 文件中定义的属性。
-
调用格式:
# 在配置文件中调用自定义属性
${jdbc.url}
- 开启配置文件加载 pom 属性:
<!-- 配置资源文件对应的信息 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<!-- 设定配居文件对应的位造目录,支持使用属性动态没定路径 -->
<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
<!-- 开启对配置文件的资源加载过滤 -->
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
多环境开发配置
多环境配置:
<!-- 创建多环境 -->
<profiles>
<!-- 定义生产环境 -->
<profile>
<!-- 定义环境对应的唯一名称 -->
<id>pro env</id>
<!-- 定义环境中专用的属性值 -->
<properties>
<jdbc.url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world?serverTimezone=UTC</jdbc.url>
</properties>
<!-- 设置默认启动 -->
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<!-- 定义开发环境 -->
<profile>
<id>dev env</id>
</profile>
</profiles>
加载指定环境:
# 格式
mvn 指令 -P 定义的环境id
# 范例
mvn install -P pro_env
测试配置
方法一:通过命令跳过测试:
mvn 指令 -D skipTests
- 注意事项:执行的指令的生命周期必须包含测试环节。
方法二:通过 IDEA 界面操作跳过测试:
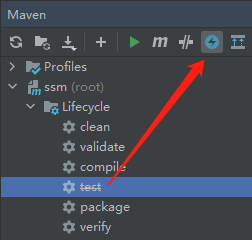
方法三:通过 pom 进行测试配置:
<!-- 测试配置 -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M5</version>
<!-- <configuration>-->
<!-- 跳过测试 -->
<!-- <skipTests>true</skipTests> -->
<!-- </configuration> -->
<configuration>
<!-- 包含指定的测试用例 -->
<includes>
<!-- 默认测试文件的命名规则:
"**/Test*.java"
"**/*Test.java"
"**/*Tests.java"
"**/*TestCase.java"
如果现有测试文件不符合以上命名,可以在 pom.xml 添加自定义规则
-->
<include>**/**.java</include>
</includes>
<!-- 忽略指定的测试用例
<excludes>
<exclude>
</exclude>
</excludes>
-->
</configuration>
</plugin>




