Python 多进程代码统计工具(带图形界面)
实现方法
- find_all_file(queue, path, file_type=None):统计文件个数。
- all_file_code_count(queue, path, file_type=None):使用多进程来统计队列中的代码总行数。
- single_file_code_count(queue, total_line_count, total_annotation_count, total_blank_count):作为多进程的任务函数,并传入多进程共享变量,统计单个文件的代码行数。
- gui(queue):实现图形可视化的输入(文件或目录的路径)与输出(统计结果)。
实现效果
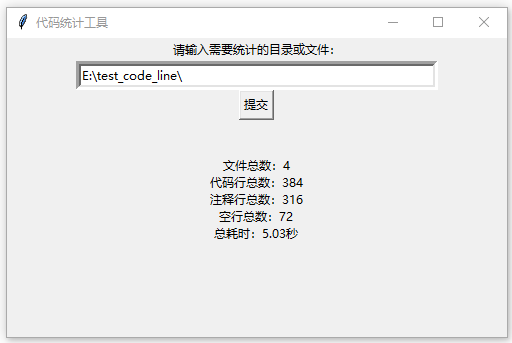
实现代码
GitHub 地址:https://github.com/juno3550/MultiprocessingCodeCounter
1 import os 2 import chardet 3 import tkinter as tk 4 import multiprocessing 5 import time 6 7 8 # 统计指定目录下的代码文件,并添加至队列中 9 def find_all_file(queue, path, file_type=None): 10 # 判断需要统计的文件类型 11 if file_type is None: 12 file_type = [".py",".cpp",".java",".c",".h",".php",".asp"] 13 # 若传入的为单个文件 14 if os.path.isfile(path): 15 if os.path.splitext(path)[1] in file_type: 16 queue.put(path) 17 else: 18 return "文件格式有误" 19 else: 20 for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path): 21 for file in files: 22 if os.path.splitext(file)[1] in file_type: 23 queue.put(os.path.join(root, file)) 24 return queue 25 26 27 # 使用多进程统计队列中的代码总行数 28 def all_file_code_count(queue, path, file_type=None): 29 start = time.time() 30 queue = find_all_file(queue, path, file_type) 31 # 有效文件数 32 total_file_count = queue.qsize() 33 # 有效代码行数 34 total_line_count = multiprocessing.Value("i", 0) 35 # 总注释数 36 total_annotation_count = multiprocessing.Value("i", 0) 37 # 总空行数 38 total_blank_count = multiprocessing.Value("i", 0) 39 # 获取当前计算机的cpu核数 40 cpu_num = multiprocessing.cpu_count() 41 p_list = [multiprocessing.Process(target=single_file_code_count, \ 42 args=(queue, total_line_count, total_annotation_count, total_blank_count)) for i in range(cpu_num)] 43 for p in p_list: 44 p.start() 45 p.join() 46 end = time.time() 47 return total_file_count, total_line_count.value, total_annotation_count.value, total_blank_count.value, end-start 48 49 50 # 统计单个文件的代码行数 51 def single_file_code_count(queue, total_line_count, total_annotation_count, total_blank_count): 52 while not queue.empty(): 53 file_path = queue.get() 54 # 是否多行注释的标识 55 flag = False 56 if not os.path.exists(file_path): 57 return "file doesn't exist" 58 else: 59 # 首先获取文件的编码 60 with open(file_path, "rb") as f: 61 content = f.read() 62 file_chardet = chardet.detect(content)["encoding"] 63 f = open(file_path, encoding=file_chardet) 64 for line in f: 65 # 多行注释的处理 66 if line.strip().startswith("'''") or line.strip().startswith('"""') or \ 67 line.strip().endswith("'''") or line.strip().endswith('"""'): 68 if flag == True: 69 flag = False 70 else: 71 flag = True 72 total_annotation_count.value += 1 73 elif line.strip().startswith("/*"): 74 flag = True 75 elif line.strip().endswith("*/"): 76 flag = False 77 else: 78 # 跳出多行注释才进行判断记录 79 if not flag: 80 # 空行不记录 81 if line.strip() == "": 82 total_blank_count.value += 1 83 continue 84 # 单行注释需要区分是否文件编码声明 85 elif line.strip().startswith("#") or line.strip().startswith("//"): 86 # 编码声明行 87 if line.strip().startswith("#encoding") or line.strip().startswith("#coding") \ 88 or line.strip().startswith("#-*-"): 89 total_line_count.value += 1 90 # 单行注释行 91 else: 92 total_annotation_count.value += 1 93 # 其余情况则为真正代码行 94 else: 95 total_line_count.value += 1 96 # 仍在多行注释内 97 else: 98 total_annotation_count.value += 1 99 f.close() 100 return total_line_count, total_annotation_count, total_blank_count 101 102 103 # GUI:图形化代码统计工具 104 def gui(queue, file_type=None): 105 106 # 创建主窗口 107 window = tk.Tk() 108 109 # 设置主窗口标题 110 window.title("代码统计工具") 111 # 设置主窗口大小(长*宽) 112 window.geometry("500x300") # 小写x 113 114 ## Label部件:界面提示语 115 # 在主窗口上设置标签(显示文本) 116 l = tk.Label(window, text="请输入需要统计的目录或文件:") 117 # 放置标签 118 l.pack() # Label内容content区域放置位置,自动调节尺寸 119 120 121 ## Entry部件:单行文本输入 122 e = tk.Entry(window, bd=5, width=50) 123 e.pack() 124 125 ## 定义Button事件的处理函数 126 def button_click(): 127 # 获取输入框的目录路径 128 path = e.get() 129 # 调用代码统计工具 130 res = all_file_code_count(queue, path, file_type) 131 # 若返回的是异常结果 132 if isinstance(res, str): 133 # 使用configure实现实时刷新数据 134 l2.configure(text=res) 135 # 返回正常结果 136 else: 137 file_count = res[0] 138 line_count = res[1] 139 annotation_count = res[2] 140 blank_count = res[3] 141 time_need = res[4] 142 l2.configure(text="文件总数:%s\n代码行总数:%s\n注释行总数:%s\n空行总数:%s\n总耗时:%s秒\n"\ 143 % (file_count, line_count, annotation_count, blank_count, round(time_need, 2))) 144 145 ## Button部件:按钮 146 b = tk.Button(window, text="提交", command=button_click) 147 b.pack() 148 149 # 用于显示统计结果 150 l2 = tk.Label(window, text="", width=200, height=10) 151 l2.pack() 152 153 # 主窗口循环显示 154 window.mainloop() 155 ''' 156 注意:因为loop是循环的意思,window.mainloop就会让window不断的刷新。 157 如果没有mainloop,就是一个静态的window,传入进去的值就不会有循环。 158 mainloop就相当于一个很大的while循环,有个while,每点击一次就会更新一次,所以我们必须要有循环。 159 所有的窗口文件都必须有类似的mainloop函数,mainloop是窗口文件的关键的关键。 160 ''' 161 162 163 if __name__ == "__main__": 164 queue = multiprocessing.Queue() 165 gui(queue)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号