Mybatis的动态sql和StatementHandler
一年前为了在公司刷积分还写过关于mybatis的动态sql的原理,一年后就发现自己有点忘了,再写一次加深印象
一 初始化
还是先从MapperStatement说起
XMLMapperBuilder.buildStatementFromContext
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) { for (XNode context : list) { final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId); try { statementParser.parseStatementNode(); } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser); } } }
每个XNode都是一个 select|update|delete|insert 的完整标签
<select resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.String" id="selectByPrimaryKey">
<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
</select>
精简了代码,第8行表示把mapper文件中的一个 select|update|delete|insert 一种构造成一个MapperStatement并加入到configuration里
1 public void parseStatementNode() { 2 3 ... 4 // Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed) 5 SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass); 6 ... 7 8 builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, 9 fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, 10 resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, 11 keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets); 12 }
而本篇重点分析第5行,获取SqlSource的过程
现在有一个带有动态标签的sql语句
<insert parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" id="insertSelective">
<trim suffixOverrides="," prefix="(" suffix=")">
<if test="userId != null">
user_id,
</if>
<if test="userName != null">
user_name,
</if>
<if test="userBirthday != null">
user_birthday,
</if>
<if test="userSalary != null">
user_salary,
</if>
</trim>
<trim suffixOverrides="," prefix="values (" suffix=")">
<if test="userId != null">
#{userId,jdbcType=CHAR},
</if>
<if test="userName != null">
#{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="userBirthday != null">
#{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE},
</if>
<if test="userSalary != null">
#{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
XMLScriptBuilder
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() { List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(context); MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents); SqlSource sqlSource = null; if (isDynamic) { sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode); } else { sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType); } return sqlSource; }
跟代码的结果就是 经过 parseDynamicTags 的处理后, List<SqlNode> contents 的样子
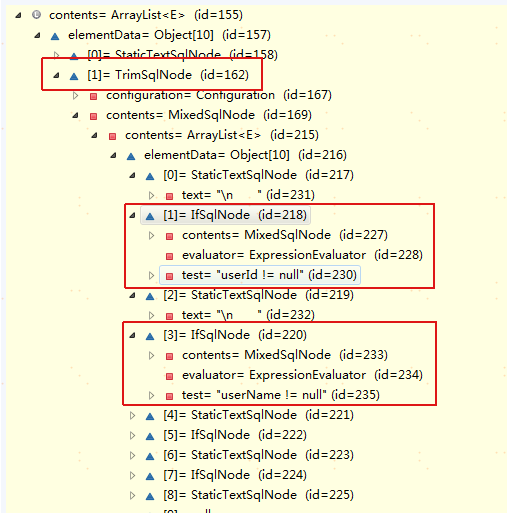
再把这些SqlNode都汇聚成一个 MixedSqlNode ,再通过 MixedSqlNode 构造成SqlSource
总结,现在有了MappedStatement,在MappedStatement中有SqlSource,注意此时的SqlSource还是静态的,为什么呢?因为mybatis提供的动态sql功能,每次执行的sql是根据输入的入参
决定的,每次的sql是不同的。
二 执行阶段
先说一下mybatis的执行过程吧,sqlSession -> executor -> statementHandler
一个SqlSession有一个成员Executor,而每次调用executor的方法时,都是会新建一个StatementHandler。为啥会new出来一个StatementHandler呢?
因为mybatis的动态sql是根据入参的不同,每次执行的sql也不一定相同,所以每当调用executor的方法就只能new一个StatementHandler
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
那就来看看new一个statementHandler的逻辑,在new一个statementHandler的过程中就要获取BoundSql
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); this.executor = executor; this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; this.rowBounds = rowBounds; this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement generateKeys(parameterObject); boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject); } this.boundSql = boundSql;
最终还是调用到 DynamicSqlSource.public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject)
1 public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { 2 DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);//parameterObject就是入参,也就是PO对象 3 rootSqlNode.apply(context);//经过这一步之后,动态sql就会被确定下来了 4 SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration); 5 Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass(); 6 SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());//sqlSource就长下面图片的样子 7 BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);//BoundSql就是在SqlSource的基础上再加上实际的入参 8 for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) { 9 boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); 10 } 11 return boundSql; 12 }
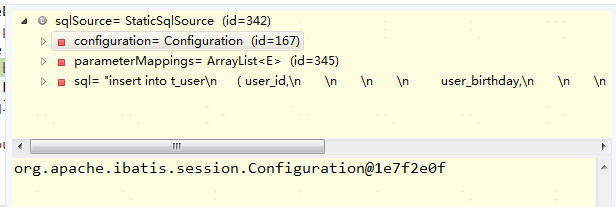
SqlSource
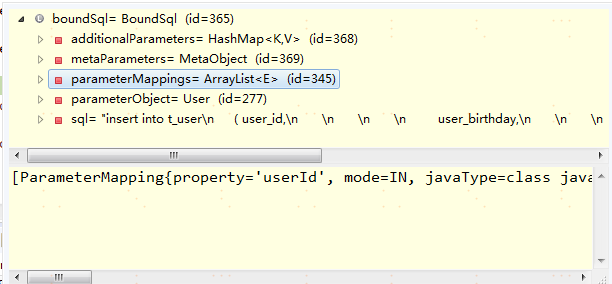
三 #{}解析以及parameterMappings
BoundSql里有一个成员变量很重要,那就是parameterMappings
public BoundSql(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings, Object parameterObject) { this.sql = sql; this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings; this.parameterObject = parameterObject; this.additionalParameters = new HashMap<String, Object>(); this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters); }
parameterMappings表示的意思是本次要执行的sql需要用到入参对象的哪些参数,比如上一次用到了id,name,salary,可能这次只是用到了name,salary。该参数也是很BoundSql一样是动态的
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
SqlSourceBuilder.parse
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) { ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters); GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);//这里ParameterMappingTokenHandler作为参数 执行构造方法 String sql = parser.parse(originalSql); return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings()); }
通过跟代码此时的 originalSql 是这样的
insert into t_user ( user_id, user_name ) values ( #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR}, #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR} )
注意哦,这个时候还是带着#{}的
接着分析 GenericTokenParser.parse
public String parse(String text) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); if (text != null && text.length() > 0) { char[] src = text.toCharArray(); int offset = 0; int start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);//openToken就是 #{ while (start > -1) { if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') { // the variable is escaped. remove the backslash. builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken); offset = start + openToken.length(); } else { int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, start); if (end == -1) { builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset); offset = src.length; } else { builder.append(src, offset, start - offset); // insert into t_user ( user_id, user_name ) values ( offset = start + openToken.length(); String content = new String(src, offset, end - offset);// userId,jdbcType=CHAR builder.append(handler.handleToken(content));// insert into t_user ( user_id, user_name ) values ( ? offset = end + closeToken.length(); } } start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset); } if (offset < src.length) { builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset); } } return builder.toString(); }
接着就要分析 ParameterMappingTokenHandler.handleToken
现在知道问号是哪里来得了吧
public String handleToken(String content) { parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content)); return "?"; }
还是要看看 buildParameterMapping
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) { Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content); String property = propertiesMap.get("property"); // userId Class<?> propertyType; if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) { // issue #448 get type from additional params propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property); } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) { propertyType = parameterType; } else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) { propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class; } else if (property != null) { MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory()); if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) { propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property); // java.lang.String } else { propertyType = Object.class; } } else { propertyType = Object.class; } ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);//这里得到了对象入参的属性名字和属性的类型 Class<?> javaType = propertyType; String typeHandlerAlias = null; for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) { String name = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); if ("javaType".equals(name)) { javaType = resolveClass(value); builder.javaType(javaType); } else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) { builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value)); } else if ("mode".equals(name)) { builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value)); } else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) { builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value)); } else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) { builder.resultMapId(value); } else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) { typeHandlerAlias = value; } else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) { builder.jdbcTypeName(value); } else if ("property".equals(name)) { // Do Nothing } else if ("expression".equals(name)) { throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet"); } else { throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Valid properties are " + parameterProperties); } } if (typeHandlerAlias != null) { builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias)); } return builder.build(); //最终我们拿到了第一个属性userId }
最终,构成一个BoundSql的要素就齐全了
public BoundSql(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings, Object parameterObject) { this.sql = sql;//已经把#{}替换成了? this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;//本次执行要用到的对象中的属性列表 this.parameterObject = parameterObject;//本次入参的对象 this.additionalParameters = new HashMap<String, Object>(); this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters); }
总结
configuration中会缓存所有的MappedStatement,MappedStatement在解析mapper文件的过程中就会保留一个SqlSource,而这个SqlSource里有SqlNode的集合,对于一个Update标签来说,它
的每一个子节点比如if,都会形成一个SqlNode。这些信息相当于是静态的信息,缓存在MappedStatement中
当要执行某一个方法的时候,每次Executor都会new一个StatementHandler,在new的过程中就会通过真实的入参将这些SqlNode依次解析,最终构成本次要执行的SqlSource,把SqlSource和入参合并变成BoundSql交给StatementHandler,准备执行


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号