After Hasan ruined the Worm puzzle, Rula brought a new game to the office, the Card game.
The game has a group of cards, each card has an integer value Vi written on it.
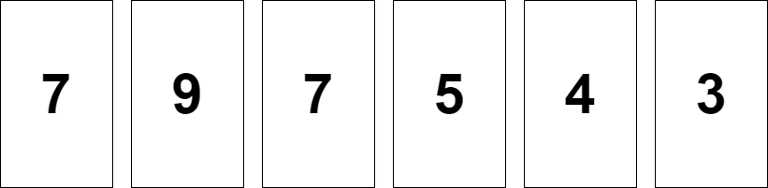
Initially, N cards are placed side by side in a straight line (refer to the picture above). In each turn you will pick two adjacent card sets (a single card is also considered a card set) and merge the cards of the two sets together to form one new set.
After each turn, you will add the maximum card value in each card set to your score. The game is over when no more merges could be performed.
What is the maximum score you can get at the end of the game, given that your initial score is 0?
The first line of input contains a single integer N (2 ≤ N ≤ 105), the number of cards in the game.
The second line contains N space-separated integers, each integer is Vi (1 ≤ Vi ≤ 5000), which represents the number written on the ith card.
On a single line, print the maximum score you can get.
5 1 2 3 2 1
23
6 7 9 7 5 4 3
108
One of the possible solutions for the first sample is as follows:
- Initially, each set will contain a single card: {1} {2} {3} {2} {1}.
- Merge {1} with {2}, the resulting sets are: {1 2} {3} {2} {1}, which will add (2 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 8) to your score.
- Merge {2} with {1}, the resulting sets are: {1 2} {3} {2 1}, which will add (2 + 3 + 2 = 7) to your score.
- Merge {1 2} with {3}, the resulting sets are: {1 2 3} {2 1}, which will add (3 + 2 = 5) to your score.
- Merge {1 2 3} with {2 1}, the resulting sets are: {1 2 3 2 1}, which will add 3 to your score.
Final score is 8 + 7 + 5 + 3 = 23.
# include <iostream>
# include <cstdio>
# include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[100001], n;
long long sum1, sum2;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
sum1 = sum2 = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum1 += a[i];
}
sum1 *= (n-1);
sort(a, a+n);
for(int i=0; i<n-1; ++i)
{
sum2 += a[i];
sum1 -= sum2;
}
printf("%I64d\n",sum1);
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号