用户登录注册案例
用户注册登录案例
接下来我们通过两个比较常见的案例,一个是注册,一个是登录来对今天学习的内容进行一个实战演练,首先来实现用户登录。
1 、用户登录
1.1、 需求分析

- 用户在登录页面输入用户名和密码,提交请求给LoginServlet
- 在LoginServlet中接收请求和数据[用户名和密码]
- 在LoginServlt中通过Mybatis实现调用UserMapper来根据用户名和密码查询数据库表
- 将查询的结果封装到User对象中进行返回
- 在LoginServlet中判断返回的User对象是否为null
- 如果为nul,说明根据用户名和密码没有查询到用户,则登录失败,返回"登录失败"数据给前端
- 如果不为null,则说明用户存在并且密码正确,则登录成功,返回"登录成功"数据给前端
1.2、 环境准备
- 自己准备静态页面到项目的webapp目录下(可随意,能实现功能即可)
- 创建db1数据库,创建tb_user表,创建User实体类
2.1

2.2 将资料\1. 登陆注册案例\2. MyBatis环境\User.java拷贝到com.itheima.pojo

- 在项目的pom.xml导入Mybatis和Mysql驱动坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.34</version>
</dependency>
- 创建mybatis-config.xml核心配置文件,UserMapper.xml映射文件,UserMapper接口
4.1 将资料\1. 登陆注册案例\2. MyBatis环境\mybatis-config.xml拷贝到resources目录下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--起别名-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!--
useSSL:关闭SSL安全连接 性能更高
useServerPrepStmts:开启预编译功能
& 等同于 & ,xml配置文件中不能直接写 &符号
-->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///db1?useSSL=false&useServerPrepStmts=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--扫描mapper-->
<package name="com.itheima.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
4.2 在com.itheima.mapper包下创建UserMapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
}
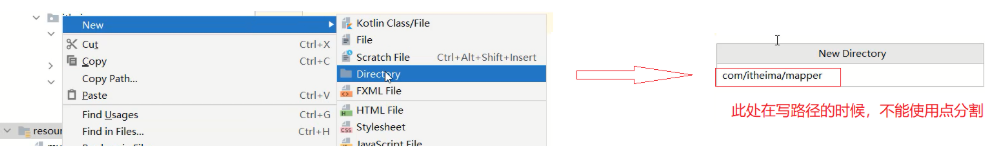
4.3 将资料\1. 登陆注册案例\2. MyBatis环境\UserMapper.xml拷贝到resources目录下
注意:在resources下创建UserMapper.xml的目录时,要使用/分割
至此我们所需要的环境就都已经准备好了,具体该如何实现?
1.3、 代码实现
- 在UserMapper接口中提供一个根据用户名和密码查询用户对象的方法
/**
* 根据用户名和密码查询用户对象
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from tb_user where username = #{username} and password = #{password}")
User select(@Param("username") String username,@Param("password") String password);
说明
@Param注解的作用:用于传递参数,是方法的参数可以与SQL中的字段名相对应。
- 修改loign.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login</title>
<link href="css/login.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="loginDiv">
<form action="/request-demo/loginServlet" method="post" id="form">
<h1 id="loginMsg">LOGIN IN</h1>
<p>Username:<input id="username" name="username" type="text"></p>
<p>Password:<input id="password" name="password" type="password"></p>
<div id="subDiv">
<input type="submit" class="button" value="login up">
<input type="reset" class="button" value="reset">
<a href="register.html">没有账号?点击注册</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 编写LoginServlet
@WebServlet("/loginServlet")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. 接收用户名和密码
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//2. 调用MyBatis完成查询
//2.1 获取SqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.2 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//2.3 获取Mapper
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//2.4 调用方法
User user = userMapper.select(username, password);
//2.5 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
//获取字符输出流,并设置content type
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
//3. 判断user释放为null
if(user != null){
// 登陆成功
writer.write("登陆成功");
}else {
// 登陆失败
writer.write("登陆失败");
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 启动服务器测试
4.1 如果用户名和密码输入错误,则

4.2 如果用户名和密码输入正确,则
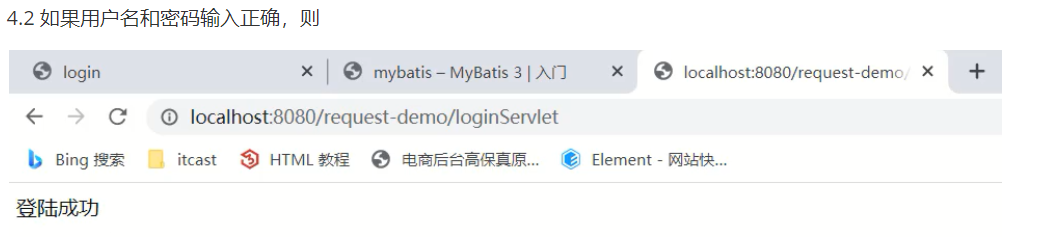
至此用户的登录功能就已经完成了~
2 、用户注册
2.1、 需求分析

- 用户在注册页面输入用户名和密码,提交请求给RegisterServlet
- 在RegisterServlet中接收请求和数据[用户名和密码]
- 在RegisterServlet中通过Mybatis实现调用UserMapper来根据用户名查询数据库表
- 将查询的结果封装到User对象中进行返回
- 在RegisterServlet中判断返回的User对象是否为null
- 如果为nul,说明根据用户名可用,则调用UserMapper来实现添加用户
- 如果不为null,则说明用户不可以,返回"用户名已存在"数据给前端
2.2、 代码编写
- 编写UserMapper提供根据用户名查询用户数据方法和添加用户方法
/**
* 根据用户名查询用户对象
* @param username
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from tb_user where username = #{username}")
User selectByUsername(String username);
/**
* 添加用户
* @param user
*/
@Insert("insert into tb_user values(null,#{username},#{password})")
void add(User user);
- 修改register.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>欢迎注册</title>
<link href="css/register.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="form-div">
<div class="reg-content">
<h1>欢迎注册</h1>
<span>已有帐号?</span> <a href="login.html">登录</a>
</div>
<form id="reg-form" action="/request-demo/registerServlet" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名</td>
<td class="inputs">
<input name="username" type="text" id="username">
<br>
<span id="username_err" class="err_msg" style="display: none">用户名不太受欢迎</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码</td>
<td class="inputs">
<input name="password" type="password" id="password">
<br>
<span id="password_err" class="err_msg" style="display: none">密码格式有误</span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<div class="buttons">
<input value="注 册" type="submit" id="reg_btn">
</div>
<br class="clear">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 创建RegisterServlet类
@WebServlet("/registerServlet")
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. 接收用户数据
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//封装用户对象
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
//2. 调用mapper 根据用户名查询用户对象
//2.1 获取SqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.2 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//2.3 获取Mapper
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//2.4 调用方法
User u = userMapper.selectByUsername(username);
//3. 判断用户对象释放为null
if( u == null){
// 用户名不存在,添加用户
userMapper.add(user);
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}else {
// 用户名存在,给出提示信息
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write("用户名已存在");
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 启动服务器进行测试
4.1 如果测试成功,则在数据库中就能查看到新注册的数据
4.2 如果用户已经存在,则在页面上展示 用户名已存在 的提示信息
3、 SqlSessionFactory工具类抽取
上面两个功能已经实现,但是在写Servlet的时候,因为需要使用Mybatis来完成数据库的操作,所以对于Mybatis的基础操作就出现了些重复代码,如下
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
有了这些重复代码就会造成一些问题:
- 重复代码不利于后期的维护
- SqlSessionFactory工厂类进行重复创建
- 就相当于每次买手机都需要重新创建一个手机生产工厂来给你制造一个手机一样,资源消耗非常大但性能却非常低。所以这么做是不允许的。
那如何来优化呢?
- 代码重复可以抽取工具类
- 对指定代码只需要执行一次可以使用静态代码块
有了这两个方向后,代码具体该如何编写?
public class SqlSessionFactoryUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
//静态代码块会随着类的加载而自动执行,且只执行一次
try {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory(){
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}
工具类抽取以后,以后在对Mybatis的SqlSession进行操作的时候,就可以直接使用
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSessionFactory();
这样就可以很好的解决上面所说的代码重复和重复创建工厂导致性能低的问题了。


